P教授要去看奥运,但是他舍不下他的玩具,于是他决定把所有的玩具运到北京。他使用自己的压缩器进行压
缩,其可以将任意物品变成一堆,再放到一种特殊的一维容器中。P教授有编号为1...N的N件玩具,第i件玩具经过
压缩后变成一维长度为Ci.为了方便整理,P教授要求在一个一维容器中的玩具编号是连续的。同时如果一个一维容
器中有多个玩具,那么两件玩具之间要加入一个单位长度的填充物,形式地说如果将第i件玩具到第j个玩具放到一
个容器中,那么容器的长度将为 x=j-i+Sigma(Ck) i<=K<=j 制作容器的费用与容器的长度有关,根据教授研究,
如果容器长度为x,其制作费用为(X-L)^2.其中L是一个常量。P教授不关心容器的数目,他可以制作出任意长度的容
器,甚至超过L。但他希望费用最小.
Input
第一行输入两个整数N,L.接下来N行输入Ci.1<=N<=50000,1<=L,Ci<=10^7
Output
输出最小费用
Sample Input
5 4 3 4 2 1 4
Sample Output
1
先推出普通dp的方程 f[i] = min{f[j] + (sum[i] - sum[j] + i - j - 1 - L)2}
这方程明显是O(n2)级别的,再看看这卖萌的数据范围,不用质疑,铁定超时。还是来考虑一下优化(例如斜率优化)吧。由于这方程长得太丑了,于是决定简化一下
设S(i) = sum[i] + i,C = L + 1
于是方程变成了这样 f[i] = min{f[j] + (S(i) - S(j) - C)2}
现在假设在状态i之前有两个可以转移到i的两个状态j, k(j < k),现在使j比k更优,那么它要满足
f[j] + (S(i) - S(j) - C)2 < f[k] + (S(i) - S(k) - C)2
看平方不爽,而且无法化简,果断完全平方公式拆掉
f[j] + [S(i) - (S(j) + C)]2 < f[k] + [S(i) - (S(k) + C)]2
f[j] + (S(j) + C)2 - 2S(i)[S(j) + C] < f[j] + (S(k) + C)2 - 2S(i)[S(k) + C]
(其实可以一起拆掉,只不过中途有些地方可以直接"抵消")继续"拆"括号,移项
f[j] + S(j)2 + 2S(j)C - 2S(i)[S(j) - S(k)] < f[k] + S(k)2 + 2S(k)C
继续,右边只留一个和i有关的单项式
(f[j] + S(j)2 + 2S(j)C) - (f[k] + S(k)2 + 2S(k)C) < 2S(i)[S(j) - S(k)]
继续移项,右边只留和i有关的式子
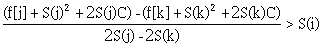
注意,S(i)是单调递增,所以S(j) - S(k) < 0,移项的时候不等号方向相反,于是我们愉快地得到了斜率方程(干什么?斜率优化去掉一个n)。
对于状态i,用(f[i] + S(i)2 + 2S(i)C)作纵坐标,2S(i)作横坐标,删掉上凸点,维护一条斜率递增的折线即可。
Code
1 /** 2 * bzoj 3 * Problem#1010 4 * Accepted 5 * Time:172ms 6 * Memory:2468k 7 */ 8 #include<iostream> 9 #include<sstream> 10 #include<cstdio> 11 #include<cmath> 12 #include<cstdlib> 13 #include<cstring> 14 #include<cctype> 15 #include<queue> 16 #include<set> 17 #include<map> 18 #include<stack> 19 #include<vector> 20 #include<algorithm> 21 #ifdef WIN32 22 #define AUTO "%I64d" 23 #else 24 #define AUTO "%lld" 25 #endif 26 using namespace std; 27 typedef bool boolean; 28 #define smin(a, b) (a) = min((a), (b)) 29 #define smax(a, b) (a) = max((a), (b)) 30 template<typename T> 31 inline void readInteger(T& u){ 32 char x; 33 int aFlag = 1; 34 while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-'); 35 if(x == '-'){ 36 aFlag = -1; 37 x = getchar(); 38 } 39 for(u = x - '0'; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = u * 10 + x - '0'); 40 ungetc(x, stdin); 41 u *= aFlag; 42 } 43 44 template<typename T> 45 class IndexedDeque{ 46 public: 47 T* list; 48 int pfront; 49 int prear; 50 IndexedDeque():list(NULL), pfront(0), prear(0){ } 51 IndexedDeque(int size):pfront(0), prear(0){ 52 list = new T[size]; 53 } 54 void push_front(T x){ list[--pfront] = x; } 55 void push_back(T x) { list[prear++] = x; } 56 void pop_front() { ++pfront; } 57 void pop_back() { --prear; } 58 T front() { return list[pfront]; } 59 T rear() { return list[prear - 1]; } 60 T& operator [](int pos){ return list[pfront + pos]; } 61 int size() { return prear - pfront; } 62 }; 63 64 int n, L; 65 long long* f; 66 long long* sum; 67 int C; 68 69 #define s(i) (sum[(i)] + (i)) 70 #define y_pos(i) (f[(i)] + pow2(s(i)) + 2 * C * s(i)) 71 #define x_pos(i) (2 * s(i)) 72 73 template<typename T> 74 inline long long pow2(T x){ return x * x; } 75 inline long long segsum(int from, int end){ return sum[end] - sum[from - 1]; } 76 inline double slope(long long x1, long long y1, long long x2, long long y2){ return (y2 - y1) * 1.0 / (x2 - x1); } 77 inline double slope(int j, int k){ return slope(x_pos(j), y_pos(j), x_pos(k), y_pos(k)); } 78 inline double cmpSlope(int j, int k, int i){ return slope(x_pos(j), y_pos(j), x_pos(k), y_pos(k)) - s(i); } 79 80 inline void init(){ 81 readInteger(n); 82 readInteger(L); 83 sum = new long long[(const int)(n + 1)]; 84 f = new long long[(const int)(n + 1)]; 85 sum[0] = 0; 86 for(int i = 1, a; i <= n; i++){ 87 readInteger(a); 88 sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a; 89 } 90 } 91 92 IndexedDeque<int> que; 93 inline void solve(){ 94 C = L + 1; 95 que = IndexedDeque<int>(2 * n); 96 que.push_back(0); 97 f[0] = 0; 98 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ 99 while(que.size() > 1 && cmpSlope(que[0], que[1], i) <= 0) que.pop_front(); 100 int p = que.front(); 101 f[i] = f[p] + pow2(segsum(p + 1, i) + i - p - C); 102 while(que.size() > 1 && slope(que[que.size() - 2], que[que.size() - 1]) >= slope(que[que.size() - 1], i)) que.pop_back(); 103 que.push_back(i); 104 } 105 printf("%lld ", f[n]); 106 } 107 108 int main(){ 109 init(); 110 solve(); 111 return 0; 112 }
(2017-2-2,更正之前贴错的代码
2017-5-6,更正打错的内容)