选择排序法
第1趟,在待排序记录r[1]~r[n]中选出最小的记录,将它与r[1]交换;第2趟,在待排序记录r[2]~r[n]中选出最小的记录,将它与r[2]交换;以此类推,第i趟在待排序记录r[i]~r[n]中选出最小的记录,将它与r[i]交换,使有序序列不断增长直到全部排序完毕。
初始序列:{ 49 27 65 97 76 12 38 }
第1趟:12与49交换:12 { 27 65 97 76 49 38 }
第2趟:27不动:12 27 { 65 97 76 49 38 }
第3趟:65与38交换:12 27 38 { 97 76 49 65 }
第4趟:97与49交换:12 27 38 49 { 76 97 65 }
第5趟:65与76交换:12 27 38 49 65 { 97 76 }
第6趟:97与76交换:12 27 38 49 65 76 97 完成
代码
public class Sort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] i = { 1, 5, 6, 12, 4, 9, 3, 23, 39, 403, 596, 87 }; System.out.println("结果:"); xuanZe(i); System.out.println(); } // 选择排序算法 public static void xuanZe(int[] x) { for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) { int lowerIndex = i; // 找出最小的一个索引 for (int j = i + 1; j < x.length; j++) { if (x[j] < x[lowerIndex]) { lowerIndex = j; } } // 交换 int temp = x[i]; x[i] = x[lowerIndex]; x[lowerIndex] = temp; } for (int i : x) { System.out.print(i + " "); } } }
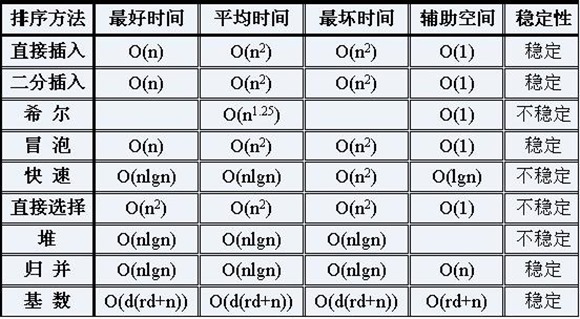
时间复杂度为O(N2) 。
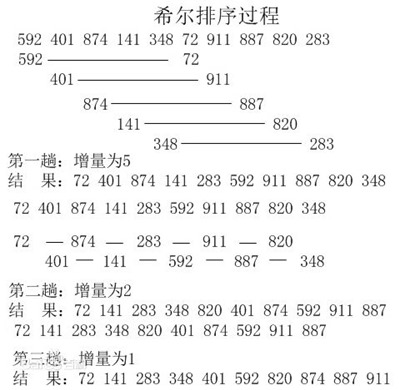
希尔排序
对于n个元素的数组,假设增量为 h:
第一趟 : 从第1个元素开始,每隔h取一个元素,那么最后可以得到n/h个元素,一边取,一边通过直接插入将这h个元素排序
第二趟 : 从第2个元素开始,每隔h取一个元素,跟第一趟一样。
...
第h趟 : 从第h个元素开始,每隔h取一个元素,跟第一趟一样。
(此时,整个数组还不是有序的)
然后,减少h的值,重复上面的操作,直到h减小为1,排序完成。
代码
public static void sort(int[] nums) { int len = nums.length / 2; while (len >=1) { for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { // 直接插入排序对分组进行排序 for (int k = i; k < nums.length-len; k +=len) { int j = k + len; int temp = nums[j]; while (k >= 0 && nums[k] > temp) { nums[j] = nums[k]; k -= len; j -= len; } nums[j] = temp; } } len = len/2; } }
时间复杂度是O(N*lgN)。
二分插入排序
二分查找插入排序的原理:是直接插入排序的一个变种,区别是:在有序区中查找新元素插入位置时,为了减少元素比较次数提高效率,采用二分查找算法进行插入位置的确定。
代码
public class BinarySearch1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int array[]={49,38,65,97,76,13,27}; binarySort(array,array.length); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } //二分查找 public static int binarySearch(int array[],int low,int high,int temp) { int mid=0; while(low<=high) { mid=(low+high)/2; if(array[mid]<temp&&temp<=array[mid+1]) return (mid+1); else if(array[mid]<temp) low = mid + 1; else high = mid -1; } return high; } //二分排序 public static void binarySort(int array[],int size) { int i,j,k,temp; for(i=1;i<size;i++) { temp=array[i]; if(array[i]<array[0]) k=0; else k = binarySearch(array,0,i,temp); for(j=i;j>k;j--) { array[j]=array[j-1]; } array[k]=temp; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } } }
时间复杂度为O(N2) ;空间复杂度为O(1)。
我是天王盖地虎的分割线