第4章 并发编程
摘要
论述了并发编程,介绍了并行计算的概念,指出了并行计算的重要性;
比较了顺序算法与并行算法,以及并行性与并发性;
解释了线程的原理及其相对于进程的优势;
介绍了Pthread中的线程操作,包括线程管理函数,互斥量、连接、条件变量和屏障等线程同步工具;
了如何使用线程进行并发编程,包括矩阵计算、快速排序和用并发线程求解线性方程组等方法;
解释了死锁问题,并说明了如何防止并发程序中的死锁问题;
信号量,并论证了它们相对于条件变量的优点;
解释了支持Linux中线程的独特方式。编程项目是为了实现用户级线程。它提供了一个基础系统来帮助读者开始工作这个基础系统支持并发任务的动态创建、执行和终止,相当于在某个进程的同一地址空间中执行线程。读者可通过该项目实现线程同步的线程连接、互斥量和信号量,并演示它们在并发程序中的用法。
并行计算导论
大多数计算机只有一个处理组件,称为处理器或中央处理器(CPU),只有一个CPU,每次只能按顺序执行某算法的一个指令和步骤。
并行计算时一种计算方案,使用多个执行并行算法的处理器来更快速地解决问题。
顺序算法与并行算法
- 顺序算法:所有步骤都是通过单个任务依次执行的,每次执行一个步骤;
- 并行算法:搜友任务都是并行执行的;
并行性与并发性
- 真正的并行执行只能在多个处理组件的系统中实现,比如多处理器或多核系统。
- 在单CPU系统中,并发性是通过多任务处理实现的。
线程
线程的原理
在进程模型中,进程时独立的执行单元。所有进程均在内核模式或用户模式下执行。
- 在内核模式下,各进程在唯一地址空间上执行,与其他进程是分开的,只有一个执行路径;
- 线程是某进程同一地址空间上的独立执行单元,如果只有一个主线程,那么进程和线程并没有什么本质区别。
线程的优点
线程创建和切换速度更快。
线程的响应速度更快。
线程更适合并行计算
线程的缺点
由于地址空间共享,线程需要来自用户的明确同步。
许多库函数可能对线程不安全。
在单CPU系统上,使用线程解决间题实际上要比使用顺序程序慢,这是由在运行时创建线程和切换上下文的系统开销造成的。
线程操作
线程可在内核模式或用户模式下执行。
- 用户模式下,线程在进程的相同地址空间中执行,但每个线程都有自己的执行堆栈。
- 线程是独立的执行单元,可根据操作系统内核的调度策略,对内核进行系统调用,变为桂起激活以继续执行等。
- 为利用线程的共享地址空间,操作系统内核的调度策略可能会优先选择同一进程中的线程,而不是不同进程中的线程。
线程管理函数
Pthread库提供了用于线程管理的以下API
pthread_create(thread, attr, function, arg): create thread
pthread_exit(status):terminate thread
pthread_cancel(thread) : cancel thread
pthread_attr_init(attr) : initialize thread attributes
pthread_attr_destroy(attr): destroy thread attribute
创建线程
使用pthread_create()函数创建线程
int pthread_create (pthread_t *pthread_id,pthread_attr_t *attr,void * (*func) (void *), void *arg);
- pthreadid是指向pthreadt类型变量的指针。它会被操作系统内核分配的唯一线程 ID填充。在POSIX中,pthreadt是一种不透明的类型。程序员应该不知道不透明对象的内容,因为它可能取决于实现情况。线程可通过pthreadselfo函数获得自己的ID。在Linux中,pthreadt类型被定义为无符号长整型,因此线程ID可以打印为%lu。
- attr是指向另一种不透明数据类型的指针,它指定线程属性,下面将对此进行更详细的说明。
- func是要执行的新线程函数的人口地址。 earg是指向线程函数参数的指针,可写为:
voia*func(void*arg)
线程ID
线程ID是一种不透明的数据类型,取决于实现情况。因此,不应该直接比较线程ID。如果需要,可以使用pthread_equal()函数对它们进行比较
线程终止
线程函数结束后,线程即终止,或者,线程可以调用函数
int pthraad_exit {void *status)
进行显式终止,其中状态是线程的退出状态。
线程连接
一个线程可以等待另一个线程的终止, 通过:
int pthread_join (pthread_t thread, void **status__ptr);
终止线程的退出状态以status_ptr返回。
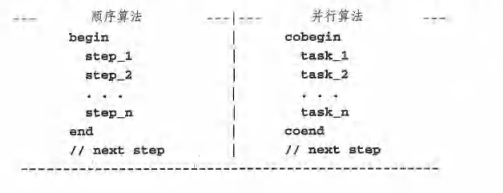
线程示例程序
用线程计算矩阵的和
线程链接操作演示
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define N 4
int A[N][N], sum[N];
void *func(void *arg)
{
int j, row;
pthread_t tid = pthread_self();
row = *(int *)arg;
printf("Thread %d [%lu] computes sum of row %d \n", row, tid, row);
for(j=0; j<N; j++)
sum[row] += A[row][j];
printf("Thread %d [%lu] done: sum[%d] = %d\n",row ,tid, row, sum[row]);
pthread_exit((void*)0);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread[N];
int j, r, total = 0;
long i;
void *status;
printf("Main: initialize A matrix\n");
for(i=0; i<N;i++){
sum[i] = 0;
for(j=0;j<N;j++){
A[i][j] = i*N +j +1;
printf("%4d ",A[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("Main: create %d threads\n", N);
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
pthread_create(&thread[i],NULL,func,(void *)i);
}
printf("Main: try to join with threads\n");
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
pthread_join(thread[i], &status);
printf("Main: joined with %ld [%lu]: status=%d\n",i, thread[i],*(int *)status);
}
printf("Main: compute and print total sum: ");
for(i=0; i<N;i++)
total += sum[i];
printf("tatal = %d\n",total);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
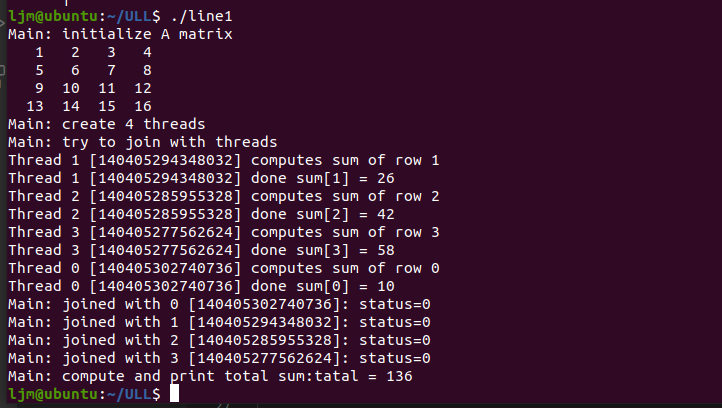
用并发线程快速排序
/****** C4.2.c: quicksort by threads *****/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define N 10
typedef struct{
int upperbound;
int lowerbound;
}PARM;
int A[N]={5,1,6,4,7,2,9,8,0,3};
int print()
{
int i;
printf("[ ");
for (i=0; i<N; i++)
{
printf("%d ", A[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
}
void *qsort_1(void *aptr)
{
PARM *ap, aleft, aright;
int pivot, pivotIndex, left, right, temp;
int upperbound, lowerbound;
pthread_t me, leftThread, rightThread;
me = pthread_self();
ap = (PARM *)aptr;
upperbound = ap->upperbound;
lowerbound = ap->lowerbound;
pivot = A[upperbound];
left = lowerbound - 1;
right = upperbound;
if (lowerbound >= upperbound)
pthread_exit(NULL);
while (left < right)
{
do { left++;} while (A[left] < pivot);
do { right--;}while (A[right] > pivot);
if (left < right )
{
temp = A[left];
A[left] = A[right];
A[right] = temp;
}
}
print();
pivotIndex = left;
temp = A[pivotIndex];
A[pivotIndex] = pivot;
A[upperbound] = temp;
aleft.upperbound = pivotIndex - 1;
aleft.lowerbound = lowerbound;
aright.upperbound = upperbound;
aright.lowerbound = pivotIndex + 1;
printf("%lu: create left and right threads\n", me);
pthread_create(&leftThread, NULL, qsort_1, (void *)&aleft);
pthread_create(&rightThread, NULL, qsort_1, (void *)&aright);// wait for left and right threads
pthread_join(leftThread, NULL);
pthread_join(rightThread, NULL);
printf("%lu: joined with left & right threads\n", me);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
PARM arg;
int i, *array;
pthread_t me, thread;
me = pthread_self();
printf("main %lu: unsorted array =" ,me);
print();
arg.upperbound = N-1;
arg.lowerbound = 0;
printf("main %lu create a thread to do QS\n", me);
pthread_create(&thread, NULL, qsort_1, (void *)&arg);
pthread_join(thread, NULL);
printf("main %lu sorted array = ", me);
print();
}
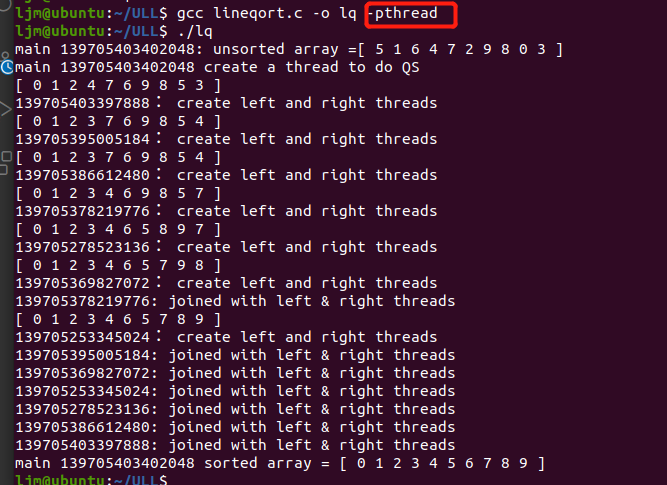
演示Pthread中的互斥量
/** C4.3.c: matrix sum by threads with mutex lock **/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define N 4
int A[N][N];
int total = 0;
pthread_mutex_t *m;
void *func(void *arg)
{
int i, row, sum = 0;
pthread_t tid = pthread_self(); // get thread ID number
row = (int)arg; // get row number from arg
printf("Thread %d [%lu] computes sum of row %d\n", row, tid, row);
for (i=0; i<N; i++)
sum += A[row][i];
printf("Thread %d [%lu] update total with %d : Thread %d : ", row, tid, sum,row);
//pthread_mutx_lock(m);
pthread_mutex_lock(m);
total += sum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(m);
printf ("total = %d\n", total);
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thread[N];
int i, j, r;
void *status;
printf("Main: initialize A matrix\n");
for (i=0; i<N; i++)
{
//sum[i] = 0;
for (j=0; j<N; j++)
{
A[i][j] = i*N + j + 1;
printf("%4d ", A[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// create a mutex m
m = (pthread_mutex_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
pthread_mutex_init(m, NULL); // initialize mutex m
printf("Main: create %d threads\n", N);
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
{
pthread_create(&thread[i], NULL, func, (void *)i);
}
printf("Main: try to join with threads\n");
for(i=0; i<N; i++)
{
pthread_join(thread[1], &status);
printf("Main: joined with %d [%lu]: status=%d\n",i, thread[i]/ (int)status);
}
printf("Main: tatal = %d\n", total);
pthread_mutex_destroy (m); // destroy mutex m
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
生产者-消费者示例程序
/* C4.4 .c: producer-consximer by threads with condition variables */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NBUF 5
#define N 10
// shared global variables
int buf[NBUF]; // circular buffers
int head, tail; // indices
int data; // number of full buffers
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t empty, full;
int init()
{
head = tail = data = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&full, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&empty, NULL);
}
void *producer()
{
int i;
pthread_t me = pthread_self();
for (i=0; i<N; i++) // try to put N items into buf[]
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // lock mutex
if (data == NBUF)
{
printf ("producer %lu: all bufs FULL: wait\n", me);
pthread_cond_wait(&empty, &mutex); // wait
}
buf[head++] = i+1;
head %= NBUF;
data++;
printf("producer %lu: data=%d value=%d\n", me, data, i+1);
pthread_mutex_unlock (&mutex);
pthread_cond_signal(&full);
}
printf("producer %lu: exit\n", me);
}
void *consumer()
{
int i, c;
pthread_t me = pthread_self();
for (i=0; i<N; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // lock mutex
if (data == 0)
{
printf ("consumer %lu: all bufs EMPTY: wait\n", me);
pthread_cond_wait(&full, &mutex); // wait
}
c = buf[tail++]; // get an item
tail %= NBUF;
data--; // dec data by 1
printf("consumer %lu: value=%d\n", me, c);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // unlock mutex
pthread_cond_signal(&empty); // unblock a producer, if any
}
printf("consumer %lu: exit\n", me);
}
int main ()
{
pthread_t pro, con;
init();
printf("main: create producer and consumer threads\n");
pthread_create(&pro, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create(&con, NULL, consumer, NULL);
printf("main: join with threads\n");
pthread_join(pro, NULL);
pthread_join(con, NULL);
printf("main: exit\n");
}
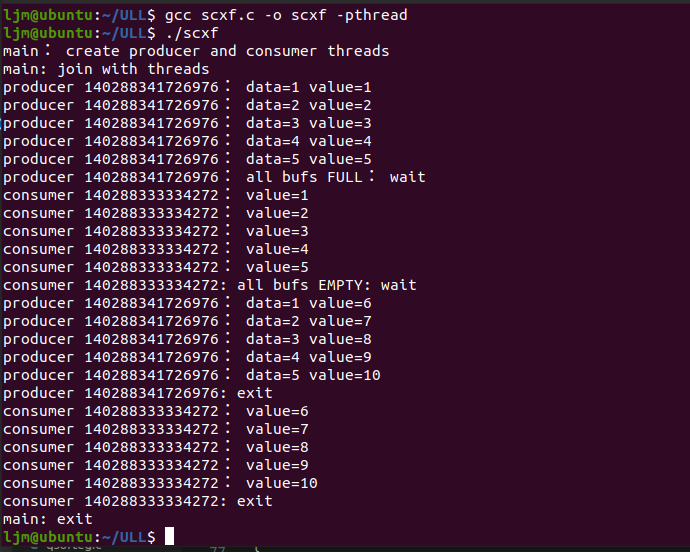
线程同步
由于线程在进程的同一地址空间中执行,它们共享同一地址空间中的所有全局变量和数据结构。当多个线程试图修改同一共享变量或数据结构时,如果修改结果取决于线程的执行顺序,则称之为竞态条件
互斥量
在 Pthread中,锁被称为互斥量,意思是相互排斥。
互斥变呈是用 ptbread_mutex_t类型声明的在使,用之前必须对它们进行初始化。
有两种方法可以初始化互斥址:
1.静态方法:
pthreaa—mutex_t m = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER
定义互斥量 m, 并使用默认属性对其进行初始化。
2.动态方法,使用
pthread_ mutex _init()
函数线程通过互斥量来保护共享数据对象
死锁预防
互斥量使用封锁协议。吐过某线程不能获取互斥量,就会被阻塞,等待互斥量解锁后再继续。
死锁是一种状态,在这种状态下,许多执行实体相互等待,因此都无法继续下去。
死锁预防,试图在设计并行算法时防止死锁的发生。
一种简单的死锁预防方法是对互斥量进行排序,并确保每个线程只在一个方向请求互斥量,这样请求序列中就不会有循环。
条件变量
条件变量提供了一种线程协作的方法。
在Pthread中,使用类型pthread_cond_t来声明条件变量,而且必须在使用前进行初始化。
与互斥变量一样,条件变量也可以通过两种方法进行初始化。
1.静态方法:pthread_cond_t con= PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;定义一个条件变屾con,并使用默认属性对其进行初始化。
2.动态方法:使用pthread_cond_init()函数,可通过attr参数设置条件变量。为简便起见,我们总是使用NULLattr参数作为默认属性。
信号量
信号量是进程同步的一般机制。
信号量是一种数据结构
struct sem{
int value;
struct process *queue
}s;
LInux中的线程
Linux不区分进程和线程。对于Linux内核,线程只是一个与其他进程共享某些资源的进程。在Linux中,线程和进程都是由clone()系统调用创建
int clone(int (*fn)(void *), void *child_stack, int flags, void *arg)
可以看出,clone()更像一个线程创建函数。
问题:出现warning: cast to pointer from integer of different size [-Wint-to-pointer-cast]
解决:是将int强制转换成void*,而sizeof(void *) 和 sizeof(int)的输出它们的大小分别为8和4(不同的操作系统不一样)所以编译后才出现int 到 (void *)转换大小不匹配,所以将int改为long后再进行转换
问题:再进行线程编程的时候,出现错误
undefined reference to 'pthread_create'
undefined reference to 'pthread_join
解决:
pthread 库不是 Linux 系统默认的库,连接时需要使用静态库 libpthread.a,所以在使用pthread_create()创建线程,以及调用 pthread_atfork()函数建立fork处理程序时,需要链接该库。
在编译中要加 -lpthread参数
gcc line.c -o line -lpthread