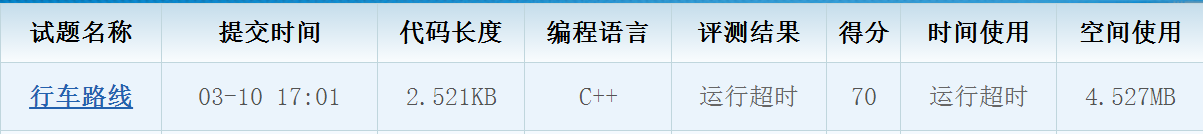
ccf 201712-4 行车路线
解题思路:
首先Dijkstra是基于贪心算法的,即每一次作出的选择都具有贪心选择性。此题由于有“如果连续走小道,小明的疲劳值会快速增加,连续走s公里小明会增加s2的疲劳度。”这种情况,所以不能使用Dijkstra算法。
这里使用Bellman-Ford算法
70分备份待修改:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 int n,m;//n为路口的数量,m为道路的数量 5 const int maxn = 500 + 5; 6 const int maxm = 100000 + 5; 7 const int INF = 1000000;//无穷大 8 struct node{ 9 int ci,cj; 10 int type; 11 int cij; 12 }path[2*maxm]; 13 14 int Edge[maxn][maxn];//记录两个点之间路径的编号 15 int dist[maxn];//记录源点1到每一个节点的最短路 16 int pro[maxn];//记录每一个节点的前驱结点 17 18 void bellman() 19 { 20 memset(dist,INF,sizeof(dist)); 21 dist[1] = 0; 22 memset(pro,-1,sizeof(pro)); 23 pro[1] = 0;//1没有前驱 24 for(int k=1;k<n;k++)///进行n-1次松弛操作 25 { 26 bool flag = false; 27 for(int i=0;i<2*m;i++) 28 { 29 if(path[i].type == 0)//大道 30 { 31 if(dist[path[i].cj] > dist[path[i].ci]+path[i].cij) 32 { 33 dist[path[i].cj] = dist[path[i].ci]+path[i].cij; 34 pro[path[i].cj] = path[i].ci; 35 flag = true; 36 } 37 } else{//小道 38 //首先要计算出连续走小路多长时间 39 int con = path[i].cij; 40 int temp = i; 41 if(pro[path[i].ci] != -1 && pro[path[i].ci] != 0)//已经加入,有前驱 42 { 43 44 int pathnum = Edge[pro[path[temp].ci]][path[temp].ci]; 45 while( path[pathnum].type == 1)//连续走小道 46 { 47 con += path[pathnum].cij; 48 temp = Edge[pro[path[temp].ci]][path[temp].ci]; 49 if(pro[path[pathnum].ci] == 0) break;//到达起始结点 50 pathnum = Edge[pro[path[temp].ci]][path[temp].ci]; 51 } 52 53 } 54 if(dist[path[i].cj]>dist[path[temp].ci] + con*con) 55 { 56 dist[path[i].cj]=dist[path[temp].ci] + con*con; 57 pro[path[i].cj] = path[i].ci; 58 flag = true; 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 if(!flag) break; 63 } 64 } 65 66 int main() 67 { 68 69 while(cin>>n>>m) 70 { 71 for(int i=0;i<2*m;i++) 72 { 73 cin>>path[i].type>>path[i].ci>>path[i].cj>>path[i].cij; 74 i++; 75 path[i].ci = path[i-1].cj;path[i].cj = path[i-1].ci; 76 path[i].cij = path[i-1].cij;path[i].type = path[i-1].type; 77 Edge[path[i].ci][path[i].cj] = i; 78 Edge[path[i].cj][path[i].ci] = i-1; 79 } 80 81 bellman(); 82 cout<<dist[n]<<endl; 83 } 84 return 0; 85 }