代码参考自:https://github.com/DetectionTeamUCAS/FPN_Tensorflow
主要分析fpn多层金字塔结构的输出如何进行预测。
FPN金字塔结构插入在faster_rcnn的特征图获取之后,在rpn结构之前。
具体代码如下所示:
代码结构追溯至FPN部分:
train.py(line 46 :build_whole_detection_network函数)
build_whole_network(line 372: build_whole_detection_network函数)
按照注释分别查看7个步骤:
1. build base network
2. build rpn
3. generate_anchors
4. postprocess rpn proposals. such as: decode, clip, NMS(所得第一次框处理)
5. build Fast-RCNN(5,roipooling 6,inference rois to obtain fc 7,cls reg)
6. postprocess_fastrcnn(最后框处理)
FPN部分在build base network中,得到的plist即为金字塔特征图的集合
build_base_network一步一步回溯找到原函数resnet_base(fpn操作在这里,如下代码)
1 def resnet_base(img_batch, scope_name, is_training=True): 2 ''' 3 this code is derived from light-head rcnn. 4 https://github.com/zengarden/light_head_rcnn 5 6 It is convenient to freeze blocks. So we adapt this mode. 7 ''' 8 if scope_name == 'resnet_v1_50': 9 middle_num_units = 6 10 elif scope_name == 'resnet_v1_101': 11 middle_num_units = 23 12 else: 13 raise NotImplementedError('We only support resnet_v1_50 or resnet_v1_101. Check your network name....yjr') 14 15 blocks = [resnet_v1_block('block1', base_depth=64, num_units=3, stride=2), 16 resnet_v1_block('block2', base_depth=128, num_units=4, stride=2), 17 resnet_v1_block('block3', base_depth=256, num_units=middle_num_units, stride=2), 18 resnet_v1_block('block4', base_depth=512, num_units=3, stride=1)] 19 # when use fpn . stride list is [1, 2, 2] 20 21 with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=False)): 22 with tf.variable_scope(scope_name, scope_name): 23 # Do the first few layers manually, because 'SAME' padding can behave inconsistently 24 # for images of different sizes: sometimes 0, sometimes 1 25 net = resnet_utils.conv2d_same( 26 img_batch, 64, 7, stride=2, scope='conv1') 27 net = tf.pad(net, [[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]]) 28 net = slim.max_pool2d( 29 net, [3, 3], stride=2, padding='VALID', scope='pool1') 30 31 not_freezed = [False] * cfgs.FIXED_BLOCKS + (4-cfgs.FIXED_BLOCKS)*[True] 32 # Fixed_Blocks can be 1~3 33 34 with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=(is_training and not_freezed[0]))): 35 C2, end_points_C2 = resnet_v1.resnet_v1(net, 36 blocks[0:1], 37 global_pool=False, 38 include_root_block=False, 39 scope=scope_name) 40 41 # C2 = tf.Print(C2, [tf.shape(C2)], summarize=10, message='C2_shape') 42 add_heatmap(C2, name='Layer2/C2_heat') 43 44 with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=(is_training and not_freezed[1]))): 45 C3, end_points_C3 = resnet_v1.resnet_v1(C2, 46 blocks[1:2], 47 global_pool=False, 48 include_root_block=False, 49 scope=scope_name) 50 51 # C3 = tf.Print(C3, [tf.shape(C3)], summarize=10, message='C3_shape') 52 add_heatmap(C3, name='Layer3/C3_heat') 53 with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=(is_training and not_freezed[2]))): 54 C4, end_points_C4 = resnet_v1.resnet_v1(C3, 55 blocks[2:3], 56 global_pool=False, 57 include_root_block=False, 58 scope=scope_name) 59 60 add_heatmap(C4, name='Layer4/C4_heat') 61 62 # C4 = tf.Print(C4, [tf.shape(C4)], summarize=10, message='C4_shape') 63 with slim.arg_scope(resnet_arg_scope(is_training=is_training)): 64 C5, end_points_C5 = resnet_v1.resnet_v1(C4, 65 blocks[3:4], 66 global_pool=False, 67 include_root_block=False, 68 scope=scope_name) 69 # C5 = tf.Print(C5, [tf.shape(C5)], summarize=10, message='C5_shape') 70 add_heatmap(C5, name='Layer5/C5_heat') 71 72 feature_dict = {'C2': end_points_C2['{}/block1/unit_2/bottleneck_v1'.format(scope_name)], 73 'C3': end_points_C3['{}/block2/unit_3/bottleneck_v1'.format(scope_name)], 74 'C4': end_points_C4['{}/block3/unit_{}/bottleneck_v1'.format(scope_name, middle_num_units - 1)], 75 'C5': end_points_C5['{}/block4/unit_3/bottleneck_v1'.format(scope_name)], 76 # 'C5': end_points_C5['{}/block4'.format(scope_name)], 77 } 78 79 # feature_dict = {'C2': C2, 80 # 'C3': C3, 81 # 'C4': C4, 82 # 'C5': C5} 83 84 pyramid_dict = {} 85 with tf.variable_scope('build_pyramid'): 86 with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(cfgs.WEIGHT_DECAY), 87 activation_fn=None, normalizer_fn=None): 88 89 P5 = slim.conv2d(C5, 90 num_outputs=256, 91 kernel_size=[1, 1], 92 stride=1, scope='build_P5') 93 if "P6" in cfgs.LEVLES: 94 P6 = slim.max_pool2d(P5, kernel_size=[1, 1], stride=2, scope='build_P6') 95 pyramid_dict['P6'] = P6 96 97 pyramid_dict['P5'] = P5 98 99 for level in range(4, 1, -1): # build [P4, P3, P2] 100 101 pyramid_dict['P%d' % level] = fusion_two_layer(C_i=feature_dict["C%d" % level], 102 P_j=pyramid_dict["P%d" % (level+1)], 103 scope='build_P%d' % level) 104 for level in range(4, 1, -1): 105 pyramid_dict['P%d' % level] = slim.conv2d(pyramid_dict['P%d' % level], 106 num_outputs=256, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="SAME", 107 stride=1, scope="fuse_P%d" % level) 108 for level in range(5, 1, -1): 109 add_heatmap(pyramid_dict['P%d' % level], name='Layer%d/P%d_heat' % (level, level)) 110 111 # return [P2, P3, P4, P5, P6] 112 print("we are in Pyramid::-======>>>>") 113 print(cfgs.LEVLES) 114 print("base_anchor_size are: ", cfgs.BASE_ANCHOR_SIZE_LIST) 115 print(20 * "__") 116 return [pyramid_dict[level_name] for level_name in cfgs.LEVLES] 117 # return pyramid_dict # return the dict. And get each level by key. But ensure the levels are consitant 118 # return list rather than dict, to avoid dict is unordered
观察原特征图的结构C2,C3,C4,C5, 以及特征金字塔的结构P5,P4,P3,P2,为5层的特征金字塔结构 。
操作如图:
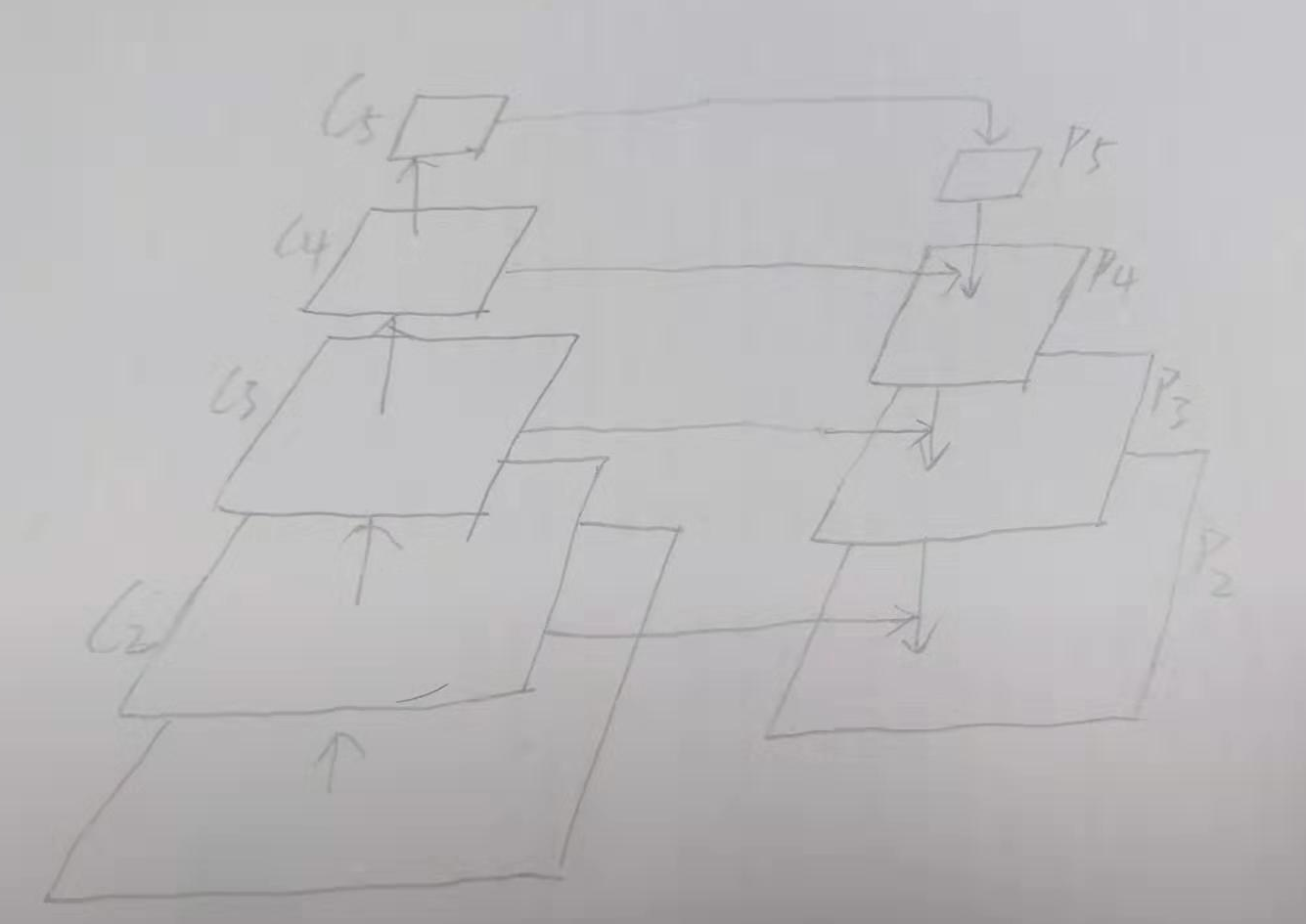
金字塔结构的总层数为(p5,p6,p4,p3,p2)
P5 = conv2d(C5) (因金字塔特征图每层的构造是 上面一层的2x upsaming 和左边的1*1conv后的结果相加)
P6 = max_pool(P5)
核心的融合部分在下面代码中显示:
P4 = C4 + P5
P3 = C3 + P4
P2 = C2 + P3
1 for level in range(4, 1, -1): # build [P4, P3, P2] 2 3 pyramid_dict['P%d' % level] = fusion_two_layer(C_i=feature_dict["C%d" % level], 4 P_j=pyramid_dict["P%d" % (level+1)], 5 scope='build_P%d' % level)
最后的P_LIST共有: LEVLES = ['P2', 'P3', 'P4', 'P5', 'P6']层级
对应每层特征图设置不同大小的anchors
Instead, we assign anchors of a single scale to each level. Formally, we define the anchors to have areas of {32,64,128,256,512} pixels on {P2,P3,P4,P5,P6} respectively.
As in [29] we also use anchors of multiple aspect ratios{1:2, 1:1, 2:1}at each level. So in total there are 15 anchors over the pyramid
后面得到全部金字塔特征图的roi,下一步是要把roi对应到各自层的特征图上取roi特征,不同大小的roi对应不同的特征图,较大的roi对应深层的特征图,按照公式
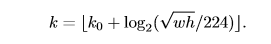
确定对应的层,然后送入roi pooling,统一特征图尺寸。
在roipooling之后的处理过程都基本一样了;
原来是一个map进行predict产生一些proposals;经过处理之后,送入全连接层之后进行cls and reg;
FPN现在是多个map进行predict产生更多不同尺度(更加鲁棒)的proposals,经过处理之后,也是送入全连接层之后进行cls and reg。