关于JAVA IO流的学习
1、复习:集合这块最主要掌握什么内容?
1.1、每个集合对象的创建(new)
1.2、向集合中添加元素
1.3、从集合中取出某个元素
1.4、遍历集合
1.5、主要的集合类:
ArrayList
LinkedList
HashSet (HashMap的key,存储在HashMap集合key的元素需要同时重写hashCode + equals)
TreeSet
HashMap
Properties
TreeMap
2、IO流,什么是IO?
I : Input
O : Output
通过IO可以完成硬盘文件的读和写。
3、IO流的分类?
有多种分类方式:
一种方式是按照流的方向进行分类:
以内存作为参照物,
往内存中去,叫做输入(Input)。或者叫做读(Read)。
从内存中出来,叫做输出(Output)。或者叫做写(Write)。
另一种方式是按照读取数据方式不同进行分类:
有的流是按照字节的方式读取数据,一次读取1个字节byte,等同于一次读取8个二进制位。
这种流是万能的,什么类型的文件都可以读取。包括:文本文件,图片,声音文件,视频文件等....
假设文件file1.txt,采用字节流的话是这样读的:
a中国bc张三fe
第一次读:一个字节,正好读到'a'
第二次读:一个字节,正好读到'中'字符的一半。
第三次读:一个字节,正好读到'中'字符的另外一半。
有的流是按照字符的方式读取数据的,一次读取一个字符,这种流是为了方便读取
普通文本文件而存在的,这种流不能读取:图片、声音、视频等文件。只能读取纯
文本文件,连word文件都无法读取。
假设文件file1.txt,采用字符流的话是这样读的:
a中国bc张三fe
第一次读:'a'字符('a'字符在windows系统中占用1个字节。)
第二次读:'中'字符('中'字符在windows系统中占用2个字节。)
综上所述:流的分类
输入流、输出流
字节流、字符流
4、Java中的IO流都已经写好了,我们程序员不需要关心,我们最主要还是掌握,
在java中已经提供了哪些流,每个流的特点是什么,每个流对象上的常用方法有
哪些????
java中所有的流都是在:java.io.*;下。
java中主要还是研究:
怎么new流对象。
调用流对象的哪个方法是读,哪个方法是写。
5、java IO流这块有四大家族:
四大家族的首领:
java.io.InputStream 字节输入流
java.io.OutputStream 字节输出流
java.io.Reader 字符输入流
java.io.Writer 字符输出流
四大家族的首领都是抽象类。(abstract class)
所有的流都实现了:
java.io.Closeable接口,都是可关闭的,都有close()方法。
流毕竟是一个管道,这个是内存和硬盘之间的通道,用完之后一定要关闭,
不然会耗费(占用)很多资源。养成好习惯,用完流一定要关闭。
所有的输出流都实现了:
java.io.Flushable接口,都是可刷新的,都有flush()方法。
养成一个好习惯,输出流在最终输出之后,一定要记得flush()
刷新一下。这个刷新表示将通道/管道当中剩余未输出的数据
强行输出完(清空管道!)刷新的作用就是清空管道。
注意:如果没有flush()可能会导致丢失数据。
注意:在java中只要“类名”以Stream结尾的都是字节流。以“Reader/Writer”结尾的都是字符流。
6、java.io包下需要掌握的流有16个:
文件专属:
java.io.FileInputStream(掌握)

package javase.io1; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; /* * java.io.fileinputstream * 1.文件字符输入流,万能流,任何类型的文件都可以采用这个流来读 * 2.字节的方式,完成输入流的操作,完成读的操作(硬盘-->内存) * */ public class FileInputStreamTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建文件输入流对象 FileInputStream fis=null; try { fis=new FileInputStream("E:\io.txt"); //开始读 3.交互太频繁,不用 while(true){ int readDate =fis.read(); //方法返回值是读取字节本身 if(readDate==-1){ break; } System.out.println(readDate); } /* * while((readDate=fis.read())!=-1){ * System.out.println(readDate); * } */ } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(fis!=null){ //关闭流,前提流不是空 try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }

1 package javase.io1; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 /** 8 *int read(byte[] b) 9 * 一次最多读取b.length个字符 10 * 11 *ieda默认当前路径:当前工程的根目录 12 */ 13 public class FileInputStreamTest02 { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 FileInputStream fis=null; 17 try { 18 // fis=new FileInputStream("E:\io.txt"); 19 fis=new FileInputStream("E:\JAVA\study_day06\src\javase\io\FileInputStreamTest01.java"); 20 //准备一个byte数组 21 byte[] bytes=new byte[4]; 22 // while(true){ 23 // int readCount = fis.read(bytes); 24 // if(readCount==-1){ 25 // break; 26 // } 27 // //把byte数组转换成字符串 28 // System.out.print(new String(bytes, 0,readCount)); 29 // } 30 //改进while 31 int readCount=0; 32 while ((readCount=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ 33 System.out.print(new String(bytes, 0, readCount)); 34 } 35 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 36 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 }finally{ 42 try { 43 fis.close(); 44 } catch (IOException e) { 45 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 } 49 50 51 } 52 53 }

1 package javase.io1; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 /* 8 * FileInputStream 类的常用方法 9 * 10 * int available():返回流当中剩余的没有读写的字节数量 11 * 作用:指定总字节数量,然后再读取就不要循环了 12 * 13 * long skip(long n):跳过几个字节不读 14 * 15 */ 16 public class FileInputStreamTest03 { 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 FileInputStream fis=null; 20 try { 21 fis=new FileInputStream("E:\io.txt"); 22 int available = fis.available(); 23 byte[] bytes=new byte[available]; 24 //不太用于太大的文件,因为byte数组不能太大 25 //跳过几个字节 26 //fis.skip(2); 27 System.out.println(); 28 int read = fis.read(bytes); 29 System.out.println(new String(bytes)); 30 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 31 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 }finally{ 37 try { 38 fis.close(); 39 } catch (IOException e) { 40 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } 43 } 44 45 } 46 47 }
java.io.FileOutputStream(掌握)

1 package javase.io1; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 /* 8 * 文件字节输出流,负责写 9 */ 10 public class FileOutputStreamTest01 { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 FileOutputStream fos=null; 14 15 try { 16 //加true表示在文件后叠加,不然原文件内容会被清空,慎重使用 17 fos=new FileOutputStream("myfile.java",true); 18 byte[] bytes={97,98,99,100}; 19 fos.write(bytes); 20 String s="风萧萧兮易水寒"; 21 //将String转换为byte数组 22 byte[] bytes2 = s.getBytes(); 23 fos.write(bytes2); 24 25 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 26 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 33 } 34 35 }
java.io.FileReader

1 package javase.io1; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileReader; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 /** 8 * FileReader 9 * 文件输入流,只能读取趋同文本 10 * 读取文本内容时,比较方便 数组类型换为char 11 * @author yumu 12 * 13 */ 14 public class FileReaderTest { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 FileReader reader=null; 18 19 try { 20 try { 21 reader=new FileReader("E:\io.txt"); 22 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 23 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 //准备一个char数组 27 char[] chars=new char[4]; 28 int readCount=0; 29 while((readCount=reader.read(chars))!=-1){ 30 System.out.print(new String(chars,0,readCount)); 31 } 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 }finally{ 36 try { 37 reader.close(); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 44 45 } 46 }
java.io.FileWriter

1 package javase.io1; 2 3 import java.io.FileWriter; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 /** 7 * FileWriter: 8 * 文件字符输出,写 9 * 只能输出普通文本 10 * @author yumu 11 * 12 */ 13 public class FileWriterTest01 { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 FileWriter fiw=null; 17 try { 18 fiw=new FileWriter("E:/iop.txt",true); 19 char[] chars={'我','是','中','国','人'}; 20 fiw.write(chars); 21 fiw.write(" "); 22 fiw.write("风萧萧兮易水寒"); 23 fiw.flush(); 24 25 } catch (IOException e) { 26 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 }finally{ 29 if(fiw!=null){ 30 try { 31 fiw.close(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 40 } 41 42 }
练习题:使用上述分别完成文件的拷贝

1 package javase.io1; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 8 /** 9 * 文件拷贝 10 * @author yumu 11 *使用FilInputStream 和FileOutputStream进行复制 12 *适用于任何类型文件的复制 13 */ 14 15 public class Copy1 { 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 FileInputStream fis=null; 19 FileOutputStream fos=null; 20 try { 21 fis=new FileInputStream("C:\Users\ASUS\Desktop\文件\我这一生.mp4"); 22 fos=new FileOutputStream("D://我的一生.MP4"); 23 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024]; 24 int readCount=0; 25 while((readCount=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ 26 fos.write(bytes, 0, readCount); 27 } 28 fos.flush(); 29 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 30 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } catch (IOException e) { 33 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 }finally{ 36 if(fis!=null){ 37 //应分别抛异常,否则一方的异常产生,可能导致另一个流无法关闭 38 try { 39 fis.close(); 40 } catch (IOException e) { 41 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 } 45 if(fos!=null){ 46 try { 47 fos.close(); 48 } catch (IOException e) { 49 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 56 } 57 58 }

package javase.io1; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; /** * 使用FileReader和FileWriter完成拷贝,只能拷贝文本,Word文件不是文本 * @author yumu * */ public class Copy2 { public static void main(String[] args) { FileReader reader=null; FileWriter writer=null; try { reader=new FileReader("E:\case\cy.txt"); writer=new FileWriter("D:\cy111.txt"); char[]chars=new char[4]; int readCount=0; while((readCount=reader.read(chars))!=-1){ System.out.print(new String(chars)); writer.write(chars, 0, readCount); } writer.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(reader!=null){ try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(writer!=null){ try { writer.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
转换流:(将字节流转换成字符流)
java.io.InputStreamReader
java.io.OutputStreamWriter
缓冲流专属:
java.io.BufferedReader
java.io.BufferedWriter

1 package javase.io2; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.FileReader; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 /** 8 * BufferedReader: 9 * 带有缓冲区的字符输入流 10 * //使用 这个流不需要自定义byte,char数组,自带缓冲区 11 * @author yumu 12 * 13 */ 14 public class BufferedReaderTest01 { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 17 FileReader reader=new FileReader("E:\io.txt"); 18 //当一个流的构造方法中需要一个流的时候,这个被传进来的流叫做:节点流 19 //外部负责包装的这个流.叫做:包装流,还有一个名字叫做:处理流 20 //像这样的这个程序来说:FileReader就是一个节点流,BufferReader就是包装流/处理流 21 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(reader); 22 //读一行 23 // String readLine = br.readLine(); 24 // String readLine1= br.readLine(); 25 // System.out.println(readLine); 26 // System.out.println(readLine1); 27 //br,reafLine 读取一整行不带换行符 28 String s=null; 29 while((s=br.readLine())!=null){ 30 System.out.println(s); 31 } 32 33 //关闭流 34 //对于包装流, 35 br.close(); 36 } 37 38 39 }

1 package javase.io2; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 8 9 /** 10 * BufferedReader 如何传入字节流 11 * 通过转换流 12 * 字节流转换为字符流 13 * InputStreamReader 14 * OutputStreamWriter 15 * @author yumu 16 * 17 */ 18 public class BufferedReaderTest02 { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 //字节流 22 try { 23 // FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("E:\io.txt"); 24 // //通过转换流转化 InputStreamReader字节流转换为字符流 25 // //in 是字节流,reader是包装流 26 // InputStreamReader reader=new InputStreamReader(in); 27 // //这个构造方法传一个 28 // //reader是字节流,br是包装流 29 // BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(reader); 30 //合并 31 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("E:/io.txt"))); 32 String s=null; 33 while ((s=br.readLine())!=null){ 34 System.out.println(s); 35 } 36 br.close(); 37 38 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 39 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } catch (IOException e) { 42 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 46 } 47 48 }

1 package javase.io2; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 7 8 /** 9 * BuffWriter:带有缓冲的字符输出流 10 * OutputStreamWriter:转换流 11 * @author yumu 12 * 13 */ 14 public class BufferedWriterTest01 { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 17 //BufferedWriter out=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("E:/io2.txt" )); 18 BufferedWriter out =new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("E:/io2.txt",true))); 19 20 //开始写 21 out.write("你好"); 22 out.write(" "); 23 out.write("世界"); 24 //刷新 25 out.flush(); 26 //关闭 27 out.close(); 28 29 } 30 31 }
java.io.BufferedInputStream
java.io.BufferedOutputStream
数据流专属:
java.io.DataInputStream

1 package javase.io2; 2 import java.io.DataInputStream; 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 /** 6 * DataInputStream 数据字节输入流 7 * 8 * @author yumu 9 * 10 */ 11 public class DataInputStreamTest { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 14 DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:/data")); 15 byte b = dis.readByte(); 16 int i = dis.readInt(); 17 short s = dis.readShort(); 18 System.out.println(b+","+i+","+s); 19 dis.close(); 20 } 21 22 }
java.io.DataOutputStream

1 package javase.io2; 2 3 import java.io.DataOutputStream; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 /** 8 * DataOutputStream 数据字节输出流 9 * @author yumu 10 * 11 */ 12 public class DataOutputStreamTest { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 15 DataOutputStream data =new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/data")); 16 byte b = 40; 17 int i = 412; 18 short s=34; 19 data.writeByte(b); 20 data.writeInt(i); 21 data.writeLong(s); 22 data.flush(); 23 data.close(); 24 } 25 26 }
标准输出流:
java.io.PrintWriter
java.io.PrintStream(掌握)

1 package javase.io2; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.PrintStream; 6 7 /** 8 * PrintStream 标准的字节输出流 9 * 不需要关闭 默认输出到控制台 10 * 可以改变标准输出流的输出方法 11 * @author yumu 12 * 13 */ 14 public class PrintStreamTest { 15 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { 17 /* 18 * 总结System类的属性和方法 19 System.out out是System类的静态变量 20 System.out.println(); println不是System类的,而是printStream类的方法 21 System.gc();建议启动垃圾回收器 22 System.currentTimeMillis() 取自1970年1月1日到现在的毫秒值 23 System.exit(0); 24 System.arraycopy();数组拷贝 25 */ 26 //指向log文件 27 PrintStream print =new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/log.txt")); 28 //将输出方向改为log文件 29 System.setOut(print); 30 System.out.println("出问题了"); 31 32 } 33 34 }
练习题:日志工具

1 package javase.io2; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.PrintStream; 6 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 7 import java.util.Date; 8 9 /** 10 * 日志工具 11 * @author yumu 12 * 13 */ 14 public class logger { 15 public static void log(String msg){ 16 17 try { 18 PrintStream out =new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("E:/log.txt",true)); 19 System.setOut(out); 20 //系统当前时间 21 Date nowTime=new Date(); 22 //格式化时间 23 SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS"); 24 25 String strTime = sdf.format(nowTime); 26 System.out.println(strTime+":"+msg); 27 out.flush(); 28 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 29 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 //将输出方向改为log文件 33 } 34 }

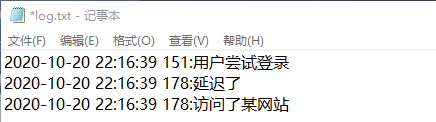
1 package javase.io2; 2 /** 3 * 测试log工具类 4 * 5 * @author yumu 6 * 7 */ 8 public class logTest { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 logger.log("用户尝试登录"); 11 logger.log("延迟了"); 12 logger.log("访问了某网站"); 13 System.out.println("213"); 14 } 15 }
对象专属流:
java.io.ObjectInputStream(掌握)
java.io.ObjectOutputStream(掌握)
第一种:反序列一个

1 package javase.io3; 2 3 import java.io.Serializable; 4 5 public class Student implements Serializable{ 6 private String name; 7 private int no; 8 public Student(String name, int no) { 9 super(); 10 this.name = name; 11 this.no = no; 12 } 13 public Student() { 14 super(); 15 16 } 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 public void setName(String name) { 21 this.name = name; 22 } 23 public int getNo() { 24 return no; 25 } 26 public void setNo(int no) { 27 this.no = no; 28 } 29 @Override 30 public String toString() { 31 return "Student [name=" + name + ", no=" + no + "]"; 32 } 33 34 35 }

1 package javase.io3; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 7 8 /** 9 * 对象 10 * @author yumu 11 *java.io.NotSerializableException: javase.io3.Student 不支持 12 *参与序列化和反序列的对象,必须实现Serializable接口 13 * 其接口通过源码可发现,是一个标志性接口,没有什么内容, 14 * 标志性接口是给java虚拟机参考的,看到后给一个序列化版本号 15 * java语言中采取什么控制类 16 * 类名 17 * 序列化版本号 18 * 缺点:代码一旦确定不能修改 19 * 建议给该类提供一个固定不变的序列号 20 * private static final long serialVersionUID=12322344435L; 21 * 22 * 23 * 如果不用某个属性,加 transient 关键字表示游离,不参与序列化 24 * private transient String name 表示name不参加序列化 25 * 26 */ 27 public class ObjectOutputStreamTest01 { 28 29 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { 30 Student s =new Student("张三",123); 31 //序列化 32 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("students")); 33 //系列化对象 34 oos.writeObject(s); 35 //刷新 36 oos.flush(); 37 //关闭 38 oos.close(); 39 } 40 41 }

1 package javase.io3; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 7 /* 8 * 反序列化 9 */ 10 public class ObjectInputStreamTest01 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 12 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("students")); 13 Object obj = ois.readObject(); 14 //反序列化回来是一个学生对象,所以会调用学生对象toString方法 15 System.out.println(obj); 16 ois.close(); 17 } 18 }
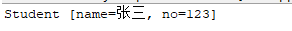
第二种:反序列多个

1 package javase.io3; 2 3 import java.io.Serializable; 4 5 /** 6 * 用户表 7 * @author yumu 8 * 9 */ 10 public class User implements Serializable{ 11 12 private String name; 13 private int age; 14 public User(String name, int age) { 15 super(); 16 this.name = name; 17 this.age = age; 18 } 19 public User() { 20 super(); 21 22 } 23 public String getName() { 24 return name; 25 } 26 public void setName(String name) { 27 this.name = name; 28 } 29 public int getAge() { 30 return age; 31 } 32 public void setAge(int age) { 33 this.age = age; 34 } 35 @Override 36 public String toString() { 37 return "User [name=" + name + " age=" + age + "]"+" "; 38 } 39 40 41 }

1 package javase.io3; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 import java.util.List; 9 10 public class ObjectOutputStreamTest02 { 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { 12 List<User> li=new ArrayList<User>() ; 13 li.add(new User("zhangsan1",1234)); 14 li.add(new User("zhangsan2",1234)); 15 li.add(new User("zhangsan3",1234)); 16 li.add(new User("zhangsan4",1234)); 17 18 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("user")); 19 oos.writeObject(li); 20 oos.flush(); 21 oos.close(); 22 } 23 }

1 package javase.io3; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 7 8 /** 9 * 测试User 10 * @author yumu 11 * 12 */ 13 public class ObjectInputStreamTest02 { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 16 ObjectInputStream ios=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("user")); 17 Object readObject = ios.readObject(); 18 System.out.println(readObject); 19 ios.close(); 20 } 21 22 }

7、java.io.File类。
File类的常用方法。

1 package javase.io.file; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 6 import java.util.Date; 7 8 /** 9 * 1.File 类和四大家族没有关系,不能UI文件进行读写 10 * 2.File对象代表什么? 11 * 文件和目录路径的抽象表现形式 12 * 3.需要掌握file类常用方法 13 * 14 * 15 * @author yumu 16 * 17 */ 18 public class FileTest01 { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 //创建file对象 22 File f1=new File("E:/file"); 23 File f2=new File("E:/file1/a/b"); 24 //判断file 是否存在 25 System.out.println(f1.exists()); 26 27 //如果E:/file不存在,则以文件的形式创造出来 28 if(!f1.exists()){ 29 //以文件形式新建 30 //fl.createNewFile(); 31 //以目录形式新建 32 f1.mkdir(); 33 } 34 if(!f2.exists()){ 35 //以文件形式新建 36 37 //以目录形式新建 38 f2.mkdirs(); 39 } 40 41 File f3=new File("E:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\001-JavaSE课堂笔记+思维导图\01-JavaSE零基础思维导图"); 42 String parent = f3.getParent(); 43 File parentFile = f3.getParentFile(); 44 System.out.println(parent); //获取父目录 45 System.out.println(parentFile.getAbsolutePath()); //获取父目录绝对路径 46 System.out.println(parentFile); 47 //获取文件名 48 System.out.println(f3.getName()); 49 //判断是否是一个目录 50 System.out.println(f3.isDirectory()); 51 //判断是否是一个文件 52 System.out.println(f3.isFile()); 53 54 //获取最后一次修改时间 55 //lastModified() 自1970年到最后一次修改时时间毫秒数 56 //将毫秒数转换为日期 57 long haoMiao = f3.lastModified(); 58 Date time=new Date(haoMiao); 59 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS"); 60 String strTime = sdf.format(time); 61 System.out.println(strTime); 62 //获取文件大小 63 System.out.println(f3.length()); 64 65 //获取当前目前所有的子文件 66 File[] listFiles = f3.listFiles(); 67 for(File f: listFiles){ 68 System.out.println(f); 69 } 70 71 72 } 73 74 }

8、java io这块还剩下什么内容:
第一:ObjectInputStream ObjectOutputStream的使用。
第二:IO流+Properties集合的联合使用。

1 package javase.io3; 2 import java.io.FileReader; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.util.Properties; 5 6 /** 7 * Io和 Properties联合使用 8 * @author yumu 9 * 类似于以上机制的这种文件被称为配置文件 10 * 并且其格式为 11 * key1=value 12 * key2=value 13 * 的时候,我们称为配置文件. 14 * java规范中有要求:属性[配置文件以.preperties结尾,但这不是必须的 15 * 16 */ 17 public class IoPropertiestest { 18 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 19 /* 20 * 将文件数据加载到properties中 21 */ 22 FileReader reader=new FileReader("E:\JAVA\study_day06\userinfo"); 23 //新建Map集合 24 Properties Pro=new Properties(); 25 //调用properties对象的load方法将文件数据加载到Map集合 26 //文件中的数据顺着管道加载到Map集合中,其中等号=左边做Key,右边做value 27 Pro.load(reader); 28 //通过Key获取value 29 String username=Pro.getProperty("username"); 30 System.out.println(username); 31 String password=Pro.getProperty("password"); 32 System.out.println(password); 33 34 } 35 }
1、拷贝目录。

1 package javase.io2; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 9 /** 10 * 拷贝目录 11 * @author yumu 12 * 13 */ 14 /** 15 * @author yumu 16 * 17 */ 18 public class copyAll { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 //拷贝源 22 File srcFile = new File("E:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\001-JavaSE课堂笔记+思维导图1"); 23 //拷贝目标 24 File destFile = new File("E:\a"); 25 //调用拷贝方法 26 copyDir(srcFile,destFile); 27 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * 拷贝目录 32 * @param srcFile 拷贝源 33 * @param destFile 拷贝目录 34 */ 35 36 private static void copyDir(File srcFile, File destFile) { 37 38 if(srcFile.isFile()){ 39 //如果是文件的话,递归结束 40 //一边读,一边写 41 FileInputStream in =null; 42 FileOutputStream out=null; 43 try { 44 in=new FileInputStream(srcFile); 45 //写到这个文件中 46 String path=(destFile.getAbsolutePath().endsWith("\")?destFile.getAbsolutePath():destFile.getAbsolutePath()+"\" )+srcFile.getAbsolutePath().substring(3); 47 out=new FileOutputStream(path); 48 //一边读,一边写 49 byte [] bytes=new byte[1024*1024]; 50 int readCount=0; 51 while((readCount=in.read(bytes))!=-1){ 52 out.write(bytes,0,readCount); 53 } 54 out.flush(); 55 56 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 57 58 e.printStackTrace(); 59 } catch (IOException e) { 60 61 e.printStackTrace(); 62 }finally{ 63 if(out!=null){ 64 try { 65 out.close(); 66 } catch (IOException e) { 67 68 e.printStackTrace(); 69 } 70 }if(in!=null){ 71 try { 72 in.close(); 73 } catch (IOException e) { 74 75 e.printStackTrace(); 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 80 return; 81 } 82 //获取源下面的子目录 83 File[] files = srcFile.listFiles(); 84 //System.out.println(files.length); 85 for(File file:files){ 86 //System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); 87 //递归调用 88 89 if(file.isDirectory()){ 90 //新建对应目录 91 String srcDir = file.getAbsolutePath(); 92 String destDir=(destFile.getAbsolutePath().endsWith("\")?destFile.getAbsolutePath():destFile.getAbsolutePath()+"\" )+srcDir.substring(3); 93 System.out.println(destDir); 94 File newFile = new File(destDir); 95 if(!newFile.exists()){ 96 newFile.mkdirs(); 97 } 98 99 } 100 copyDir(file,destFile); 101 } 102 103 104 } 105 106 }
2、关于对象流
ObjectInputStream
ObjectOutputStream
重点:
参与序列化的类型必须实现java.io.Serializable接口。
并且建议将序列化版本号手动的写出来。
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
3、IO + Properties联合使用。
IO流:文件的读和写。
Properties:是一个Map集合,key和value都是String类型。
