:
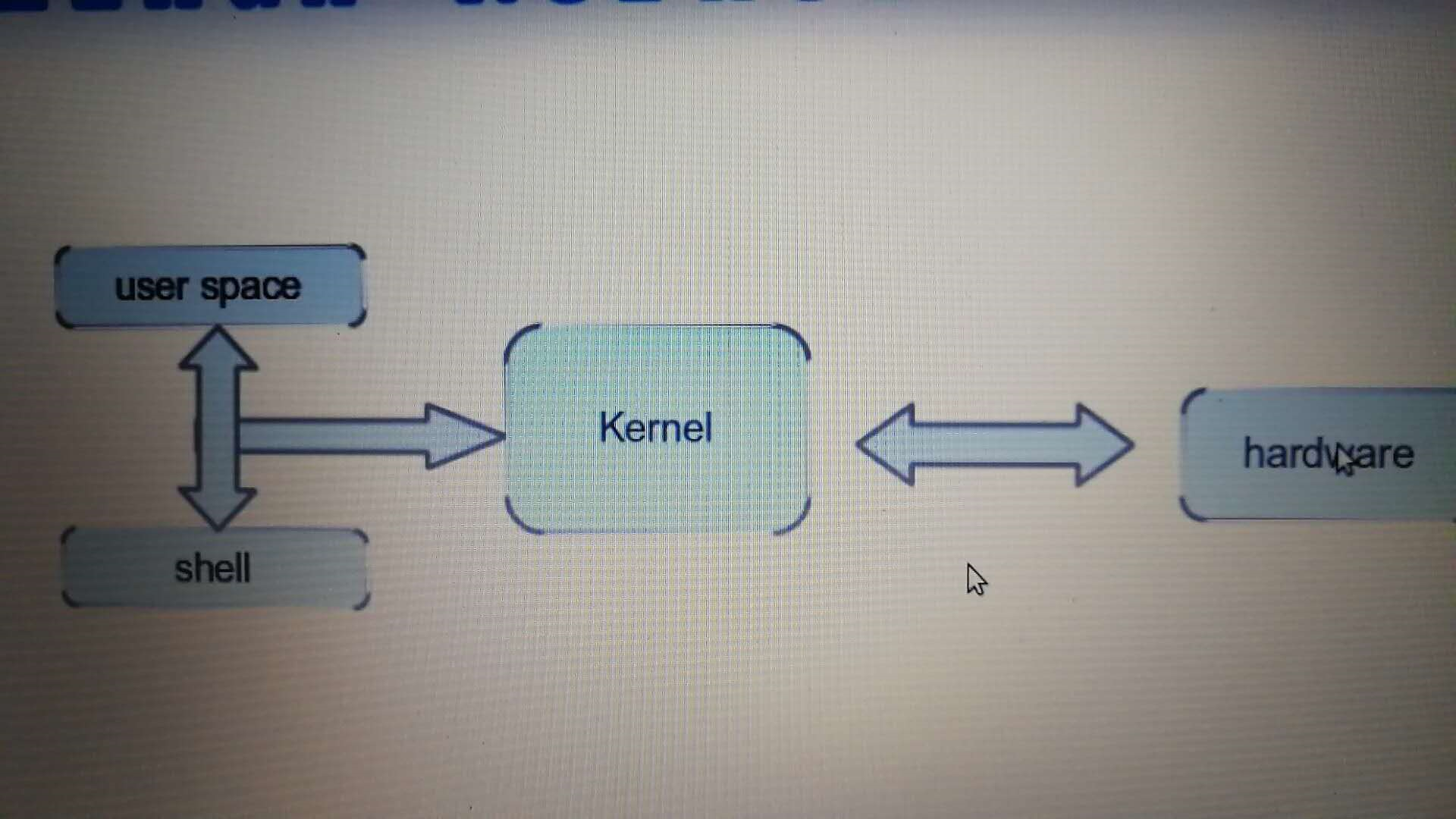
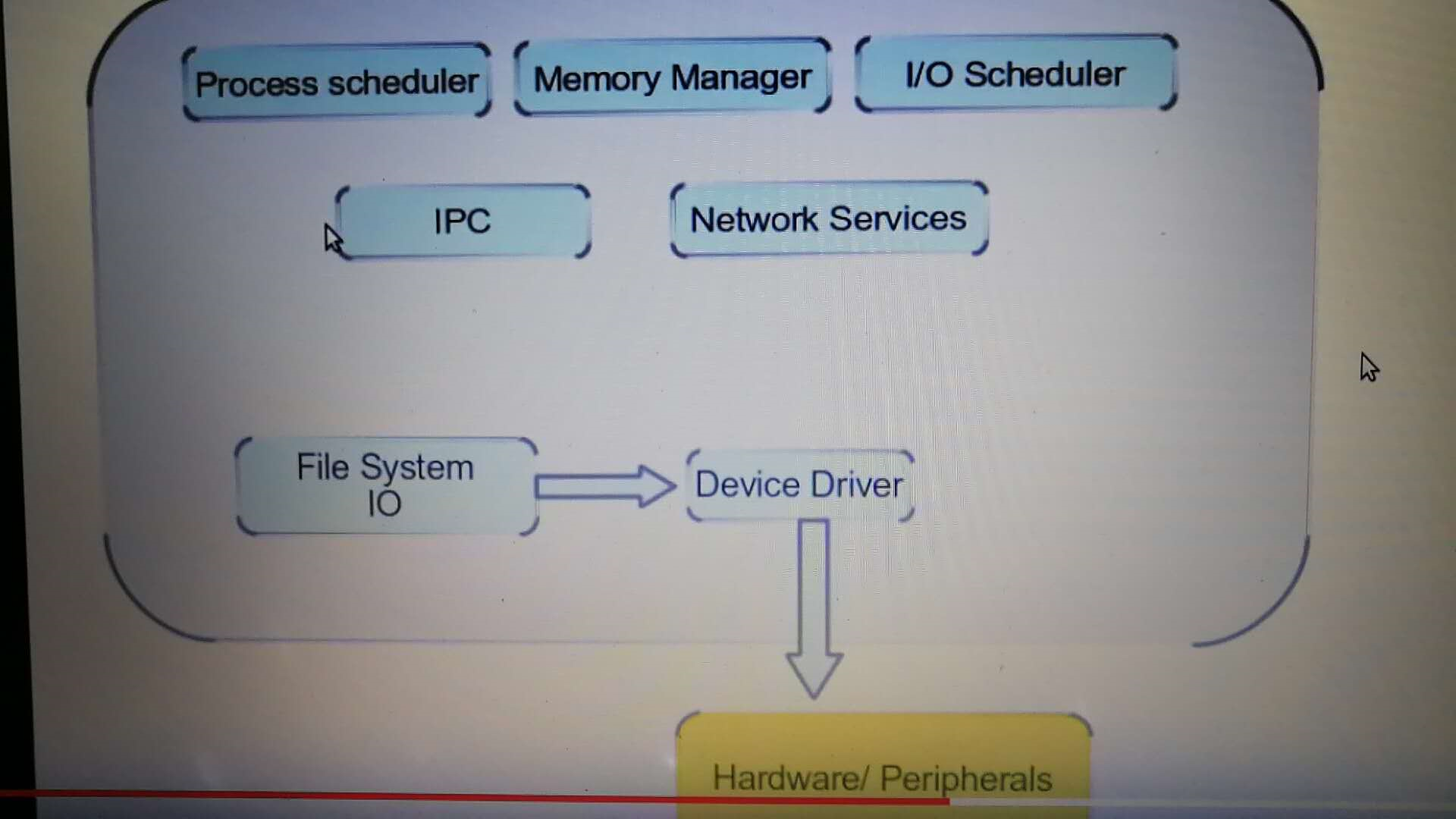
Linux Driver
Device Major and Minor Numbers
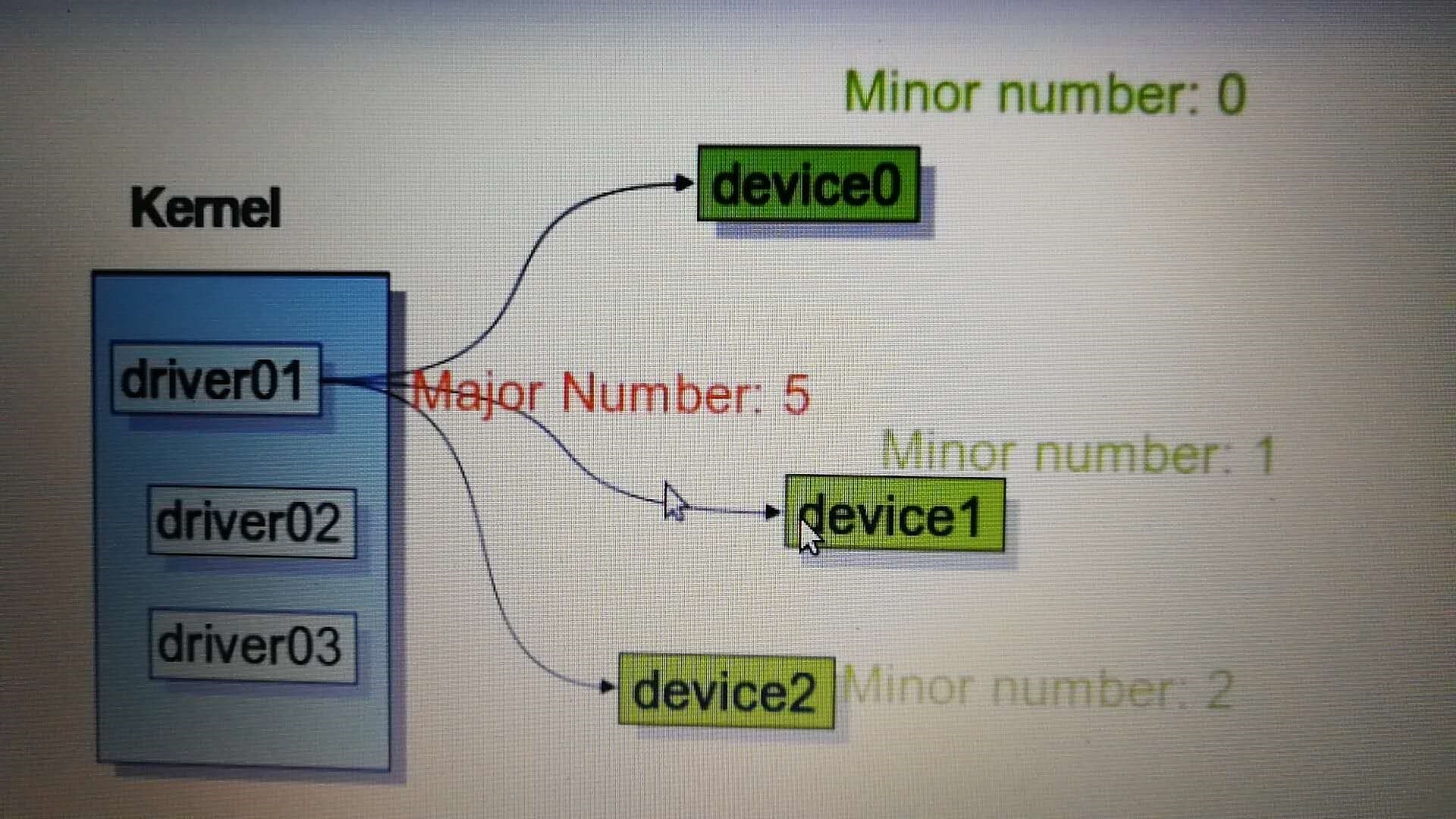
he Internal Representation of Device Numbers Within the kernel, the dev_t type (defined in <linux/types.h>) is used to hold device numbers—both the major and minor parts.
As of Version 2.6.0 of the kernel, dev_t is a 32-bit quantity with 12 bits set aside for the major number and 20 for the minor number. Your code should, of course, never make any assumptions about the internal organization of device numbers; it should, instead, make use of a set of macros found in <linux/kdev_t.h>.
To obtain the major or minor parts of a dev_t, use:
MAJOR(dev_t dev);
MINOR(dev_t dev);
If, instead, you have the major and minor numbers and need to turn them into a dev_t, use:
MKDEV(int major, int minor);
Two Main Types of Device Drivers
Character Device Drivers
Character devices can be compared to normal files in which we can read/write arbitrary bytes at a time. Character device work with a stream of bytes.
The only relevant difference between a char device and a regular file is that you can always move back and forth in the regular file, whereas most char devices are just data channels, which yoiu can only access sequentially.
Examples of character device drivers are:
> Serial port
>Text console
> Mice
> Parallel printer ports
Char devices are accessed by means of filesystem nodes, such as /dev/tty1 and /dev/lp0
writing/reading character by character
operate in blocking mode; synchronous with operations
most common of all device drivers

Find all the devices in the system
$ ls /dev
$ ls -l /dev/tty0
crw--w---- 1 root tty 4, 0 Mar 10 09:17 /dev/tty0
$ ls -l /dev/tty1
crw--w---- 1 gdm tty 4, 1 Mar 10 09:17 /dev/tty1
The major number of tty0 is 4, and the minor number is 0.
Block Device Drivers
writing/reading block by block
CPU intensive and operations take a long time to complete, asynchronous with operations
Block devices, on the other hand, operate on blocks of data, not on arbitrary bytes. The usual block size is 512 bytes or larger powers of two. As a result, block and char devices differ only in the way data managed internally by the kernel. Like a char device, each block device is accessed through a filesystem node, and the difference between them is transparent to the user.
Examples of block device drivers include
> Hard drives
>CD-ROM drives
Create a new device node
mknod [OPTION]... NAME TYPE [MAJOR MINOR]
yubao@yubao-ThinkPad-E560:/dev$ sudo mknod /dev/myDevice c 900 1
[sudo] password for yubao:
yubao@yubao-ThinkPad-E560:/dev$ ls -l myDevice
crw-r--r-- 1 root root 900, 1 Mar 10 10:00 myDevice
Location of Linux Kernel Modules
Usually, all Linux kernel modules (drivers) are stored in the module directory located that /lib/modules/$(uname -r) directory.
To see current modules, type:
yubao@yubao-ThinkPad-E560:~$ ls /lib/modules/$(uname -r)
build modules.alias modules.builtin.bin modules.devname modules.symbols
initrd modules.alias.bin modules.dep modules.order modules.symbols.bin
kernel modules.builtin modules.dep.bin modules.softdep vdso
list all drivers for various devices:
yubao@yubao-ThinkPad-E560:~$ ls /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/kernel/drivers acpi dax hid isdn mmc platform scsi vfio ata dca hsi leds mtd power spi vhost atm dma hv lightnvm net powercap spmi video auxdisplay edac hwmon macintosh nfc pps ssb virtio base extcon hwspinlock mailbox ntb ptp staging vme bcma firewire hwtracing mcb nvdimm pwm target w1 block firmware i2c md nvme rapidio thermal watchdog bluetooth fmc iio media parport regulator thunderbolt xen char fpga infiniband memstick pci remoteproc tty clk fsi input message pcmcia reset uio cpufreq gpio iommu mfd phy rpmsg usb crypto gpu ipack misc pinctrl rtc uwb
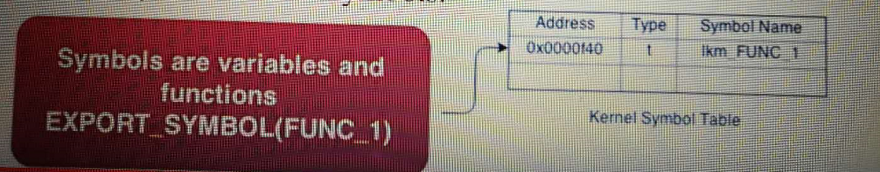
How Symbols are Exported?
Exporting Kernel Symbols is typically done with:
> EXPORT_SYMBOL(), which exports a given symbol to all loadable modules
>EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(), which exports a given symbol to only those modules that have a GPL-compatible license.
Kernal Symbol Table
Definition:
Kernal symbol table is nothing but a look-up table between symbol names and their addresses in memory.
When a module is loaded into Kernel memory using insmod or modprobe utility, any symbol exported by the module becomes part of Kernal Symbol table. Exported symbols will become public Kernel Symbols.
The most common and most frustrating failure in loading an LKM is an unresolved symbol, like:
insmod: error inserting 'XXX.ko": -l Unknown sybol in module
To debug this error:
> use nm utility
$nm XXX.ko will display all the symbol table of this module
> Know symbol definitions
yubao@yubao-ThinkPad-E560:~/MyProjects/Linux/driver/HelloWorld$ nm hello.ko 0000000000000020 T cleanup_module U __fentry__ 0000000000000020 t hello_exit 0000000000000000 t hello_init 0000000000000000 T init_module 0000000000000040 r __module_depends U printk 0000000000000000 D __this_module 0000000000000000 r __UNIQUE_ID_license8 0000000000000049 r __UNIQUE_ID_name9 0000000000000018 r __UNIQUE_ID_srcversion10 0000000000000054 r __UNIQUE_ID_vermagic8
Symbol types in Module
Check https://linux.die.net/man/1/nm for details.
The characters that identify symbol type describe
- A : Global absolute symbol.
- a : Local absolute symbol.
- B : Global bss symbol.
- b : Local bss symbol.
- D : Global data symbol.
- d : Local data symbol.
- f : Source file name symbol.
- L : Global thread-local symbol (TLS).
- l : Static thread-local symbol (TLS).
- T : Global text symbol.
- t : Local text symbol.
- U : Undefined symbol.
How to check all the symbols?
$ cat /proc/kallsyms |more
System.map
In Linux, the System.map file is a symbol table used by the kernel.
yubao@yubao-ThinkPad-E560:~/MyProjects/Linux/driver/SybolError$ locate System.map /boot/System.map-4.13.0-32-generic /boot/System.map-4.13.0-36-generic /boot/System.map-4.4.0-040400-generic /boot/System.map-4.4.0-64-generic /boot/System.map-4.4.64-040464-generic
References
- Linux Device Drivers, Third Edition, https://lwn.net/Kernel/LDD3/