#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h> // bool 类型
int N = 0; // 进程数目
int M = 0; // 资源数目
int* Available; // 可利用资源向量 M
int** Max; // 最大需求矩阵 M * N
int** Allocation; // 分配矩阵 M * N
int** Need; // 需求矩阵 M * N
// 初始化数据结构
void init();
// 销毁数据结构
void destory();
// 安全性检查算法
void security_checks();
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
init();
security_checks();
destory();
return 0;
}
/**
* 初始化数据结构
*/
void init() {
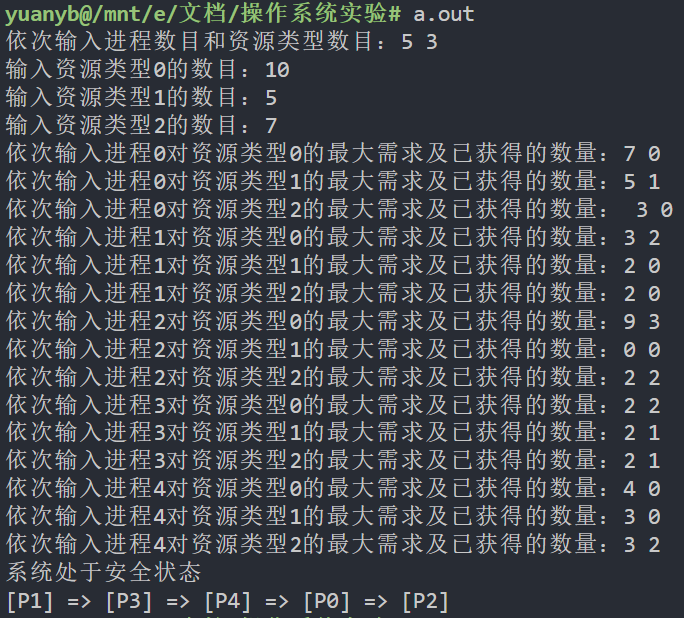
printf("依次输入进程数目和资源类型数目:");
scanf("%d%d", &N, &M);
// 分配内存
Available = malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);
Max = malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);
Allocation = malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);
Need = malloc(sizeof(int*) * N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Max[i] = malloc(sizeof(int) * M);
Allocation[i] = malloc(sizeof(int) * M);
Need[i] = malloc(sizeof(int) * M);
}
// 赋值
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
printf("输入资源类型%d的数目:", i);
scanf("%d", &(Available[i]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
printf("依次输入进程%d对资源类型%d的最大需求及已获得的数量:", i, j);
scanf("%d%d", &(Max[i][j]), &(Allocation[i][j]));
Available[j] -= Allocation[i][j];
Need[i][j] = Max[i][j] - Allocation[i][j];
}
}
}
/**
* 销毁数据结构
*/
void destory() {
free(Available);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
free(Max[i]);
free(Need[i]);
free(Allocation[i]);
}
}
/**
* 安全性检查算法
*/
void security_checks() {
int Work[M];
bool Finish[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Finish[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
Work[i] = Available[i];
}
int finish_count = 0; // 结束任务的进程数目
char security_seq[N][5]; // 安全序列
while (true) {
bool had_allocated = false; // 判断本轮是否分配
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (Finish[i] == false) { // 找一个没有结束的进程
bool all_valid = true;
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) { // 如果对所有资源的Need[i][j]都小于Work[j],则分配
if (Need[i][j] > Work[j]) { // 但凡有一个不满足,则不分配
all_valid = false;
break;
}
}
if (all_valid == true) { // 分配并回收资源
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
Work[j] += Allocation[i][j];
}
Finish[i] = true;
had_allocated = true;
sprintf(security_seq[finish_count++], "P%d�", i);
}
}
}
if (finish_count == N) { // 结束,安全
puts("系统处于安全状态");
printf("进程安全序列为:");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // 输出安全序列
printf("[%s]", security_seq[i]);
if (i != N - 1) printf(" => ");
else puts("");
}
return ;
} else if (had_allocated == false) { // 结束,不安全
puts("系统处于不安全状态");
return ;
}
}
}
