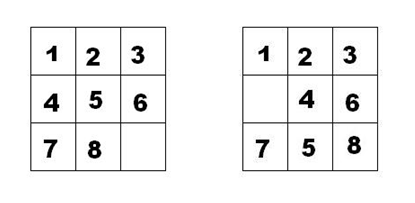
如下面第一个图的九宫格中,放着 1~8 的数字卡片,还有一个格子空着。与空格子相邻的格子中的卡片可以移动到空格中。经过若干次移动,可以形成第二个图所示的局面。
我们把第一个图的局面记为:12345678.
输入
输入第一行包含九宫的初态,第二行包含九宫的终态。
输出
输出最少的步数,如果不存在方案,则输出-1。
样例输入
12345678.
123.46758样例输出
3
题目要求的是 求起始状态转移到最终状态最少的步数,并且涉及迷宫问题。这类求迷宫最优解,我第一反应就是广搜,废话不多说,上code。
//单向bfs代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
struct node
{
string origin;
int step;
};
string last;//终点状态
queue<node>p;
set<string>vis;//判重
int dx[4] = {0,1,0,-1};//四个方向拓展
int dy[4] = {1,0,-1,0};
void bfs()
{
while(!p.empty())
{
node head = p.front();
p.pop();// bfs 队首出列,队首结点可拓展的点入队,完成从起点状态到终点状态的状态迁移
if(head.origin == last)//判断终止条件
{
cout<<head.step<<endl;
return;
}
//找到 head.origin中'.'的位置
int pos;
for(int i=0;i<head.origin.size();i++)
{
if(head.origin[i] == '.')
{
pos = i;
break;
}
}
int x = pos/3;
int y = pos%3;//将string对象origin模拟地转化为3*3的字符数组,方便判断是否出界
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)//四个方向拓展
{
int x1 = x+dx[i];
int y1 = y+dy[i];
if(x1<3&&x1>=0&&y1>=0&&y1<3)
{
node temp = head;
//这里要用一个temp临时结点保存住head,因为在对head向四周拓展时有可能会改变它的origin属性,但是这种改变显然是我们在四个方向并列拓展时不希望产生的
int newpos = x1*3+y1;
swap(temp.origin[newpos],temp.origin[pos]);
if(!vis.count(temp.origin))
//如果这种状态没有之前没有出现过,就完成相应的入队操作
{
temp.step++;//移动次数加1;
vis.insert(temp.origin);
p.push(temp);
}
}
}
}
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
node t;
cin>>t.origin>>last;
t.step = 0;//初始移动次数那肯定为0
vis.insert(t.origin);
p.push(t);
bfs();
return 0;
}
运行结果截图