1、作用
在树型结构的模型中,有两种节点:叶子节点、中间节点,其中叶子节点不能再接节点,中间节点可以接叶子节点和中间节点。这个模型用组合模式能够很好的实现,在组合模式中分为3个类:component(抽象构件)、composite(容器构件)、leaf(叶子构件)。其中component是composite和leaf共同的抽象基类,这样统一了叶子节点也中间节点的区别,方便用户使用;composite是一个容器构件,可以继续容纳composite和leaf构件;leaf构件不能容纳leaf构件和compsite构件。
文件系统是compsite模式的一个很好的例子:把文件和文件夹抽象成component类、文件夹则为compsite的容器类、文件为leaf类。
2、实现方式
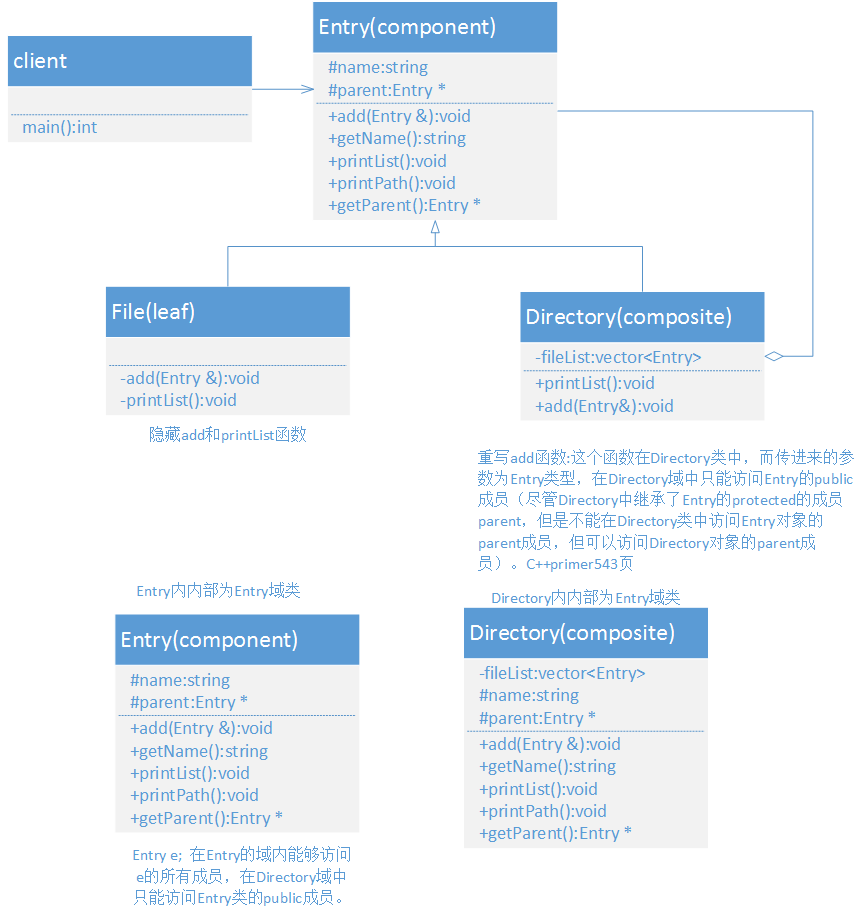
下面是使用组合模式抽象出的文件系统的UML图:
先是将文件(File)和目录(Directory)抽象成目录(Entry)类,类中包含三个函数:
add:这个函数用于添加子节点,Entry中默认实现为抛出异常的形式,这样File继承这个方法后,不需要修改,因为File是叶子节点不能添加子节点,当调用该方法时抛出异常(在File类中,最好还是将这个方法隐藏起来,不对用户可见,覆盖为private的或者定位为delete的)。Directory类中要对这方法进行重写,实现添加子节点的功能。
getName:获取节点名字
printList:打印该节点下子节点的所有名字,在File类中这个函数需要被隐藏,应为File没有子节点。Directory中要重新该函数,因为基类Entry中这个函数是抽象的。
特别需要注意的是,Directory与Entry的关系是组合关系,这样能够保证在Directory中添加Entry(file和Directory),这个结构中,我树做成了双向树,既可以从根节点到叶节点,也可以从叶节点到根节点,目的是为了获取路径(这个功能也可以添加一个路径path变量为Entry的成员),同时可以实现返回上一层目录的功能。
name:文件夹或者文件的名字
parent:文件或者文件夹上一层目录对象指针。
add():添加文件或者文件夹到当前文件夹中,文件的add函数是隐藏起来的。
getName():获取文件或者文件夹的名字。
printList():打印文件夹下所有文件或者文件夹的名字,文件的这个函数是隐藏的。
printPath():打印当前文件夹或者文件所在的路径。
getParent():获取文件或文件夹的上一层目录的Entry对象指针(这个类本应该隐藏的,设置为protected的,但是由于在Directory中要访问Entry对象的parent成员,做不到,不知道还有没有其他的好办法。)
3、C++代码
fileSys.h
#include <vector> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <exception> #include <stack> #ifndef __FILESYS__H__ #define __FILESYS__H__ using namespace std; class Entry { public: Entry(const string &name) : name (name) ,parent(nullptr){} virtual void add(Entry &) { throw exception(); } virtual string getName() const { return name; } virtual void printList() const {}; void setParent(Entry *e) { parent = e; } virtual void printPath() const { stack<string> s; const Entry *node = this; do { s.push(node->getName()); node = node->parent; } while(node != nullptr); while(!s.empty()) { cout<<"/"<<s.top(); s.pop(); } cout<<endl; } protected: string name; Entry *parent; }; class File : public Entry { public: File(const string &name):Entry(name){} private: using Entry::add; // 隐藏add函数,定义为delete的方式是阻止生成默认的构造函数。 using Entry::printList; // 隐藏printLinst函数 }; class Directory : public Entry { public: Directory(const string &name):Entry(name){} void add(Entry &e) { e.setParent(this); // Directory域中只能访问Entry域中的public成员, 不能直接访问proteted的parent成员 //e.parent = this; filelist.push_back(e); } void printList() const { for(const auto &v : filelist) cout<<v.getName()<<endl; } private: vector<Entry> filelist; //(用map存储会更好,其中名字为键,方便获取目录下的某个文件) }; #endif
test.cc
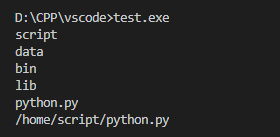
生成如下目录结构

#include "FileSys.h" int main() { Entry *fileSys = new Directory("home"); auto tmp1 = Directory("script"); auto tmp2 = Directory("data"); auto tmp3 = Directory("bin"); auto tmp4 = Directory("lib"); auto tmp5 = File("python.py"); tmp1.add(tmp5); fileSys->add(tmp1); fileSys->add(tmp2); fileSys->add(tmp3); fileSys->add(tmp4); fileSys->printList(); // 打印home目录下所有文件和文件夹名 tmp1.printList(); // 打印script目录下的所有文件和文件夹名字 tmp5.printPath(); // 打印python.py的全路径 return 0; }
输出:
使用了Map的版本
FileSys.h
#include <vector> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include <exception> #include <stack> #include <map> #ifndef __FILESYS__H__ #define __FILESYS__H__ using namespace std; class Entry { public: Entry(const string &name) : name (name) ,parent(nullptr){} virtual void add(Entry &) { throw exception(); } virtual string getName() const { return name; } virtual void printList() const {}; void setParent(Entry *e) { parent = e; } virtual void printPath() const { stack<string> s; const Entry *node = this; do { s.push(node->getName()); node = node->parent; } while(node != nullptr); while(!s.empty()) { cout<<"/"<<s.top(); s.pop(); } cout<<endl; } protected: string name; Entry *parent; }; class File : public Entry { public: File(const string &name):Entry(name){} private: using Entry::add; // 隐藏add函数,定义为delete的方式是阻止生成默认的构造函数。 using Entry::printList; // 隐藏printLinst函数 }; class Directory : public Entry { public: Directory(const string &name):Entry(name){} void add(Entry &e) { e.setParent(this); // Directory域中只能访问Entry域中的public成员, 不能直接访问proteted的parent成员 auto ret = fileList.insert({e.getName(), e}); if(!ret.second) // 已经存在map中 throw runtime_error(e.getName() + " is in " + name + " Directory"); } void printList() const { for(const auto &v : fileList) cout<<v.first<<endl; //cout<<v.second.getName()<<endl; } private: map<string,Entry> fileList; }; #endif
test.cc
#include "FileSys.h" int main() { Entry *fileSys = new Directory("home"); auto tmp1 = Directory("script"); auto tmp2 = Directory("data"); auto tmp3 = Directory("bin"); auto tmp4 = Directory("lib"); auto tmp5 = File("python.py"); tmp1.add(tmp5); fileSys->add(tmp1); fileSys->add(tmp2); fileSys->add(tmp3); fileSys->add(tmp4); fileSys->printList(); tmp1.printList(); tmp5.printPath(); try { fileSys->add(tmp1); // 加入相同的文件夹或文件,会产生异常 } catch(runtime_error err) { cout<<err.what()<<endl; } return 0; }
输出:
