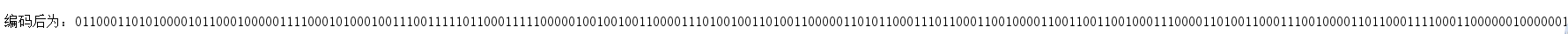20172332 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》Java哈夫曼编码实验--哈夫曼树的建立,编码与解码
哈夫曼树
- 1、路径和路径长度
- 在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子或孙子结点之间的通路,称为路径。通路中分支的数目称为路径长度。若规定根结点的层数为1,则从根结点到第L层结点的路径长度为L-1。
- 2、结点的权及带权路径长度
- 若将树中结点赋给一个有着某种含义的数值,则这个数值称为该结点的权。结点的带权路径长度为:从根结点到该结点之间的路径长度与该结点的权的乘积。
- 3、树的带权路径长度
- 树的带权路径长度规定为所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,记为WPL。
哈夫曼编码
- 问题概述:
在数据传输中,需要将传输的文字换成二进制的字符,用0和1的不同排列来表示字符。然而,在传送报文的时候总希望传输报文的总长度尽可能短。在实际的应用中,各个字符的出现频率或使用次数是不同的,在设计编码时,应使用频率高的用短码,使用频率低的用长码。
- 基本思路
对于数据通信中的报文编码问题,一般采用以下三步来解决:
统计每个报文的出现次数;
以报文字符为叶结点,以字符出现的次数为权重,构造哈夫曼树;
遍历二叉树,求报文字符编码及报文传输长度。
注意:在求文字符编码的时候,假设到每棵左子树的根结点的边为0,到右子树的结点的边为1。
哈夫曼树结点的结构
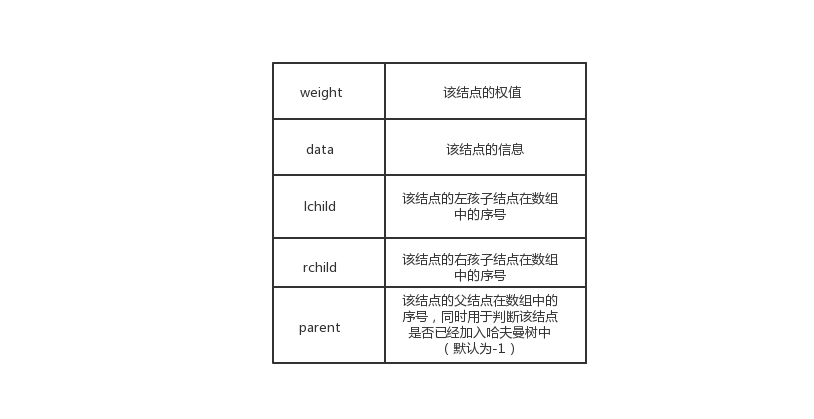
- 可以用一个数组存放原来的n个叶子结点和构造过程中临时生成的结点,数组大小为2n-1。所以,哈夫曼树类中有两个成员字段:data数组用于存放结点集合;leafNum表示哈夫曼树叶子结点的数目。而哈夫曼树结点一共有5个域:
关键代码与解读
- Node类:要实现Comparable接口,比较权重,好确定放的位置(编码是0还是1)。
public class Node<T> implements Comparable<Node<T>> {
@Override
//确定位置
public int compareTo(Node<T> other) {
if(other.getWeight() > this.getWeight()){
return 1;
}
if(other.getWeight() < this.getWeight()){
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
}
- HuffmanTree类:创建树,当还有结点时,对结点进行排序,然后左孩子为数组中的个数-2的结点,右孩子为数组中的个数-1的结点(用数组实现树的那一章说过左右孩子在数组中的索引),赋予左孩子的编码为0,右孩子的编码为1,双亲结点则为左右孩子相加的权重(也就是左右孩子的概率和),把双亲结点加入链表中,从链表中把旧的左右孩子删除,直至链表中的结点只剩一个(也就是根结点)。
public Node<T> createTree(List<Node<T>> nodes) {
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(nodes);
Node<T> left = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 2);
left.setCode(0 + "");
Node<T> right = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 1);
right.setCode(1 + "");
Node<T> parent = new Node<T>(null, left.getWeight() + right.getWeight());
parent.setLeft(left);
parent.setRight(right);
nodes.remove(left);
nodes.remove(right);
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0);
}
public List<Node<T>> breadth(Node<T> root) {
List<Node<T>> list = new ArrayList<Node<T>>();
Queue<Node<T>> queue = new ArrayDeque<Node<T>>();
if (root != null) {
queue.offer(root);
root.getLeft().setCode(root.getCode() + "0");
root.getRight().setCode(root.getCode() + "1");
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
list.add(queue.peek());
Node<T> node = queue.poll();
if (node.getLeft() != null)
node.getLeft().setCode(node.getCode() + "0");
if (node.getRight() != null)
node.getRight().setCode(node.getCode() + "1");
if (node.getLeft() != null) {
queue.offer(node.getLeft());
}
if (node.getRight() != null) {
queue.offer(node.getRight());
}
}
return list;
}
char[] chars = new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's'
, 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', ' ','
'};
int[] number = new int[]{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
- Word类:因为加了空格和回车,所以小于28,得到每个字符出现的次数(类似于累加的形式)
//得到相应字符出现的次数
public void num(String string) {
for (int i = 0; i < 28; i++) {
int temp = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < string.length(); j++) {
if (string.charAt(j) == chars[i])
temp++;
}
number[i] += temp;
}
}
- HuffmanTreeTest:把读入的存进list中并进行排序整理,输出每个字母出现的次数,倒数第二个显示的为空格,最后一个显示的为回车
File file = new File("abc.txt");
Word read = new Word();
String temp = read.txtString(file);
System.out.println(temp);
int[] num = read.getNumber();
char[] chars = read.getChars();
for (int i = 0; i < 28; i++) {
System.out.print(chars[i] + ":" + num[i] + " ");
list.add(new Node<String>(chars[i] + "", num[i]));
}
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println();

- HuffmanTreeTest:计算相应字母、空格与回车出现的概率
HuffmanTree huffmanTree = new HuffmanTree();
Node<String> root = huffmanTree.createTree(list);
list2 = huffmanTree.breadth(root);
for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {
if (list2.get(i).getData() != null) {
list3.add(list2.get(i).getData());
list4.add(list2.get(i).getCode());
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < list2.size(); i++) {
num2 += list2.get(i).getWeight();
}
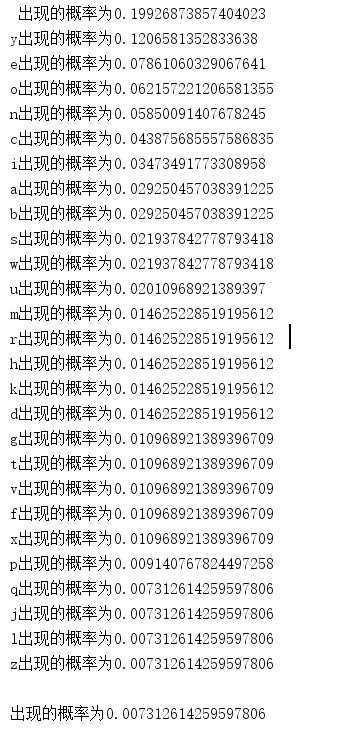
for (int i = 0; i < list3.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list3.get(i) + "出现的概率为" + list2.get(i).getWeight() / num2 + " ");
}
System.out.println();
- HuffmanTreeTest:得到相应字母、空格与回车的对应编码值
for (int i = 0; i < list4.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list3.get(i) + "的编码为" + list4.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();

for (int i = 0; i < temp.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < list3.size(); j++) {
if (temp.charAt(i) == list3.get(j).charAt(0))
result += list4.get(j);
}
}
System.out.println("编码后为:" + result);
for (int i = 0; i < result.length(); i++) {
list5.add(result.charAt(i) + "");
}
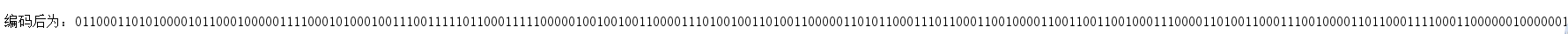
while (list5.size() > 0) {
temp2 = temp2 + "" + list5.get(0);
list5.remove(0);
for (int i = 0; i < list4.size(); i++) {
if (temp2.equals(list4.get(i))) {
temp3 = temp3 + "" + list3.get(i);
temp2 = "";
}
}
}
System.out.println();

File file2 = new File("abc1.txt");
Writer out = new FileWriter(file2);
out.write(temp3);
out.close();