一.概述
卷积神经网络【Convolutional Neural Networks,CNN】是一类包含卷积计算且具有深度结构的前馈神经网络【Feedforward Neural Networks】是深度学习的代表算法之一。卷积神经网络具有表征学习【representation learning】能力,能够按其阶层结构对输入信息进行平移不变分类。
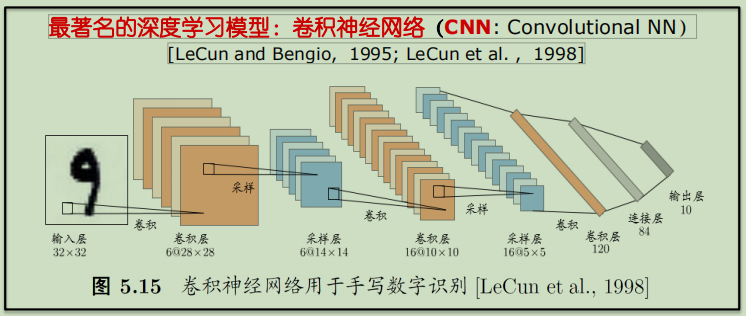
神经网络实质上是多层函数嵌套形成的数学模型。1998年Yann LeCun等人推出了LeNet-5架构,广泛用于手写字体识别,包含全连接层和sigmoid激活函数,还有卷积层和池化层。
二.代码实现
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 Created on Wed Nov 21 17:32:28 2018 4 5 @author: zhen 6 """ 7 8 import tensorflow as tf 9 from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data 10 11 mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('C:/Users/zhen/MNIST_data_bak/', one_hot=True) 12 sess = tf.InteractiveSession() 13 14 def weight_variable(shape): 15 initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) 16 return tf.Variable(initial) 17 18 def bias_variable(shape): 19 initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape) 20 return tf.Variable(initial) 21 22 def conv2d(x, W): 23 return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') 24 25 def max_pool_2x2(x): 26 return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') 27 28 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) 29 y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) 30 x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) 31 32 # 第一层卷积核 33 W_conv = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 16]) 34 b_conv = bias_variable([16]) 35 h_conv = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv) + b_conv) 36 h_pool = max_pool_2x2(h_conv) 37 38 # 第二层卷积核 39 W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 16, 32]) 40 b_conv2 = bias_variable([32]) 41 h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool, W_conv2) + b_conv2) 42 h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) 43 44 # 全连接层 45 W_fc = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 32, 512]) 46 b_fc = bias_variable([512]) 47 h_pool_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 32]) 48 h_fc = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool_flat, W_fc) + b_fc) 49 50 # 防止过拟合,使用Dropout层 51 keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) 52 h_fc_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc, keep_prob) 53 54 # Softmax分类 55 W_fc2 = weight_variable([512, 10]) 56 b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) 57 y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2) 58 59 # 定义损失函数 60 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y * tf.log(y_conv), reduction_indices=[1])) 61 train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) 62 correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1)) 63 accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) 64 65 # 训练 66 tf.global_variables_initializer().run() 67 for i in range(20): 68 batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50) 69 train_step.run(feed_dict={x:batch[0], y:batch[1], keep_prob:0.5}) 70 71 print("test accuracy %g" % accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y:mnist.test.labels, keep_prob:1.0}))
三.结果
1.算法模型不变,增大训练集数据【隐藏一层16个卷积核,隐藏二层32个卷积核,全连接层512,10分类】:
数据集为1000条:

数据集为10000条:
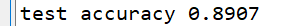
数据集为100000条:

2.训练集数据不变,增大卷积核数【数据集为10000,全连接层512,10分类】:
隐藏一层16个卷积核,隐藏二层32个卷积核:
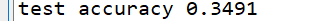
隐藏一层32个卷积核,隐藏二层64个卷积核:

隐藏一层64个卷积核,隐藏二层128个卷积核:

四.分析
在训练集较小时,一味增加卷积核的数量对预测性能的提升十分有限,在相同模型的情况下,适当的提升训练集的数据对模型的提升十分明显,当然为了达到更高的性能可以两者兼得!