1.例一
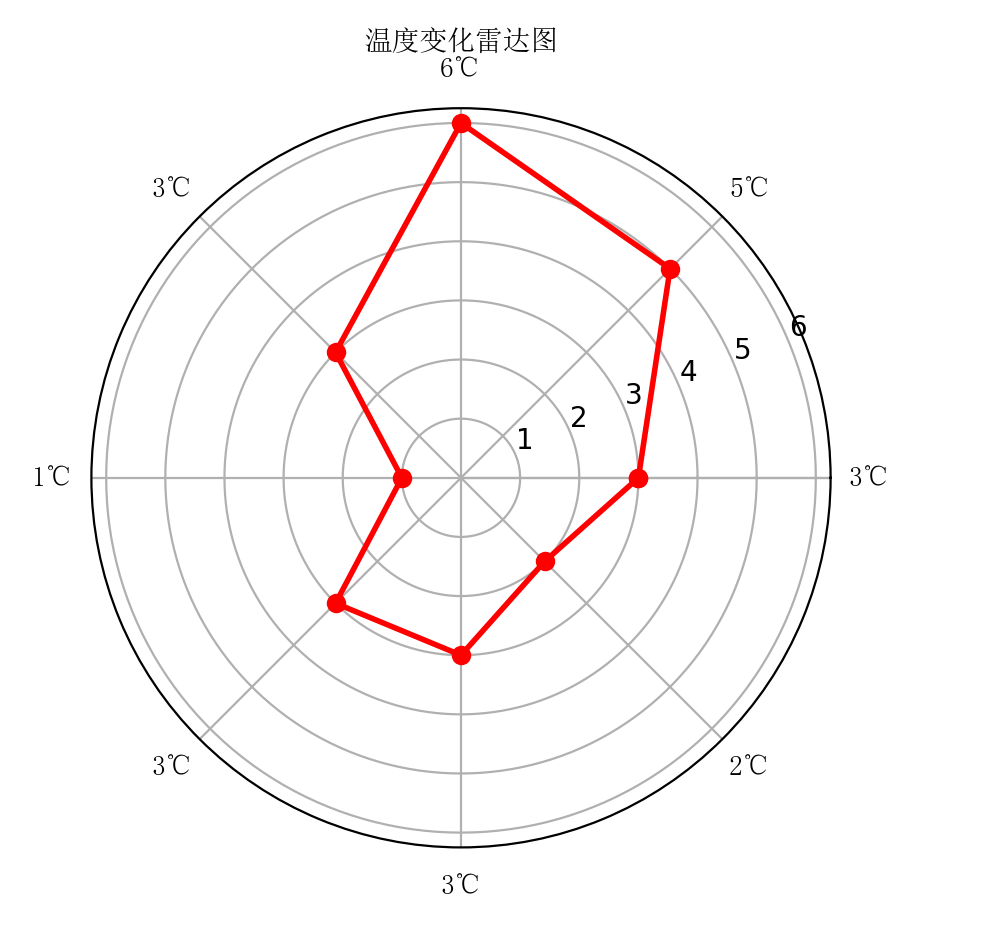
图1
代码1

#第1步:导出模块 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import font_manager # 中文字体设置第1步,导出模块 #中文字体设置第2步:引出字体模块和位置 my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="/usr/share/fonts/truetype/noto/simsun.ttf") #数据来源,单独设定,非文件来源 #dataLenth = 8 #数据个数,8组数据 #标签 labels = np.array(['3℃','5℃','6℃','3℃','1℃','3℃','3℃','2℃']) data = np.array([3,5,6,3,1,3,3,2]) #数据值,与上面labels有对应关系 #雷达图的数据格式,基本固定 #angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, dataLenth, endpoint=False) #如果没有dataLenth = 8==len(labels),也可以这样 angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, len(labels), endpoint=False) data = np.concatenate((data, [data[0]])) angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]])) #导出fig图片设置,雷达图这种格式基本固定 fig = plt.figure() #polar=true,就是ax.set_thetagrids可以显示 ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True) #数据线的宽度2,ro-代表red-;bo-代表blue-;yo-代表yellow-;o-代表深蓝deepblue- ax.plot(angles, data, 'ro-', linewidth=2) #ax.set_thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, labels, fontproperties="SimHei") #bug,本机报错 ax.set_thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, labels, fontproperties=my_font) #fig标题设置,中文字体设置 #中文字体设置第3步,在显示中文的地方,增加u和fontproperties=my_font #ax.set_title("温度变化雷达图", va='bottom', fontproperties="SimHei") ax.set_title(u"温度变化雷达图", va='bottom', fontproperties=my_font) ax.grid(True) #显示雷达图的一圈一圈的线,8个圈线 #显示图片 plt.show()
2.例二
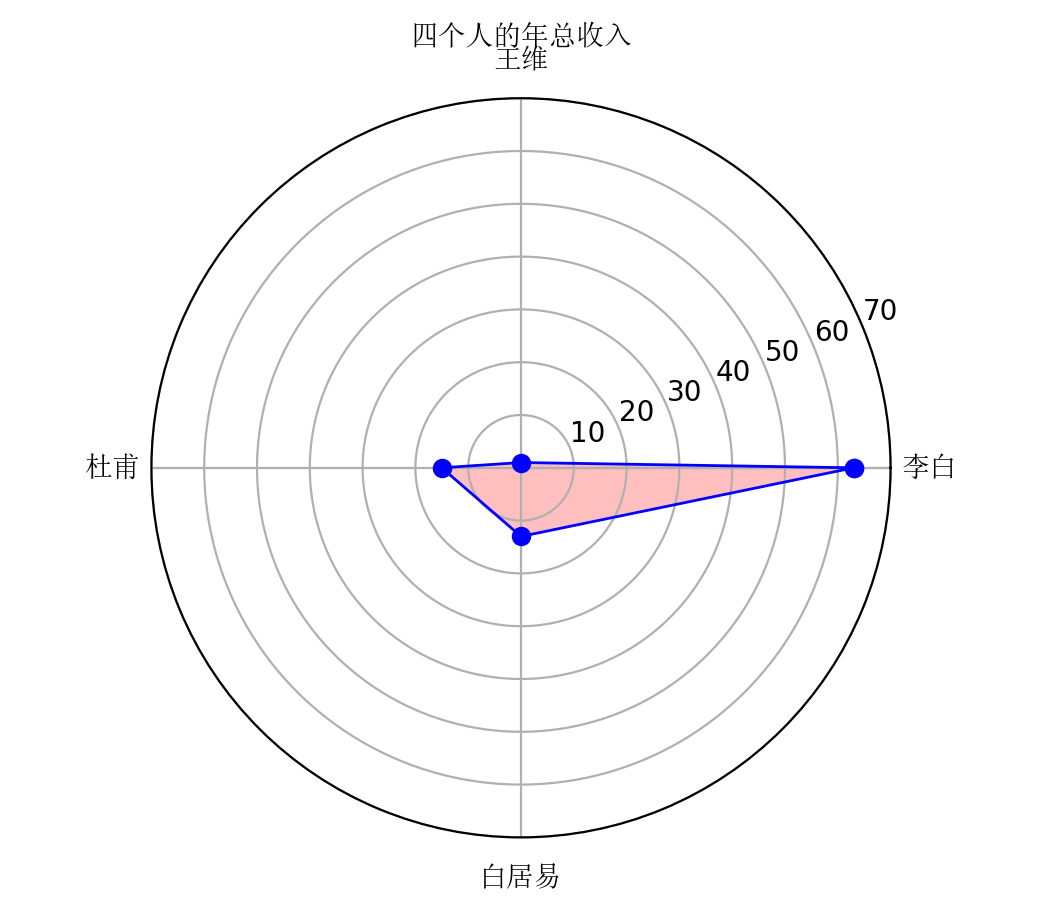
图2
代码二

#导出模块 import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import font_manager # 中文字体设置第1步,导出模块 #中文字体设置 #plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['KaiTi'] # 显示中文,本机不行 #中文字体设置第2步:引出字体模块和位置 my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="/usr/share/fonts/truetype/noto/simsun.ttf") #中文字体设置第3步,在显示中文的地方,在这里增加u labels = np.array([u'李白', u'王维', u'杜甫',u'白居易']) # 这种中文字体设置很难,分2个地方 #dataLenth = 4 # 数据长度 data_radar = np.array([63, 1, 15, 13]) # 数据 #angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, dataLenth, endpoint=False) # 分割圆周长 #如果不设置dataLenth = 4,也可以len(labels)=4,代表4组数据 angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, len(labels), endpoint=False) # 分割圆周长 data_radar = np.concatenate((data_radar, [data_radar[0]])) # 闭合 angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]])) # 闭合 plt.polar(angles, data_radar, 'bo-', linewidth=1) # 做极坐标系 # 中文设置的labels,在这里加fontproperties=my_font plt.thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, labels,fontproperties=my_font) plt.fill(angles, data_radar, facecolor='r', alpha=0.25)# 填充 plt.ylim(0, 70) #中文字体设置第3步,在显示中文的地方,增加u和fontproperties=my_font #va='bottom',默认这个;top可能与王维重叠 plt.title(u'四个人的年总收入', fontproperties=my_font) #标题设置 plt.show()
3.例三
3.1 读取csv数据
L R F M C
customer0 -0.18851 0.701298 -0.66178 -0.68228 -0.43681
customer1 0.050142 -0.33906 0.092392 0.065064 0.09756
customer2 -0.05403 -0.03271 -0.30585 -0.33106 0.011589
customer3 0.309113 -0.64527 1.378002 1.4691 0.3989
customer4 -0.12259 0.332883 -0.53543 -0.54537 -0.08043

3.2 图3
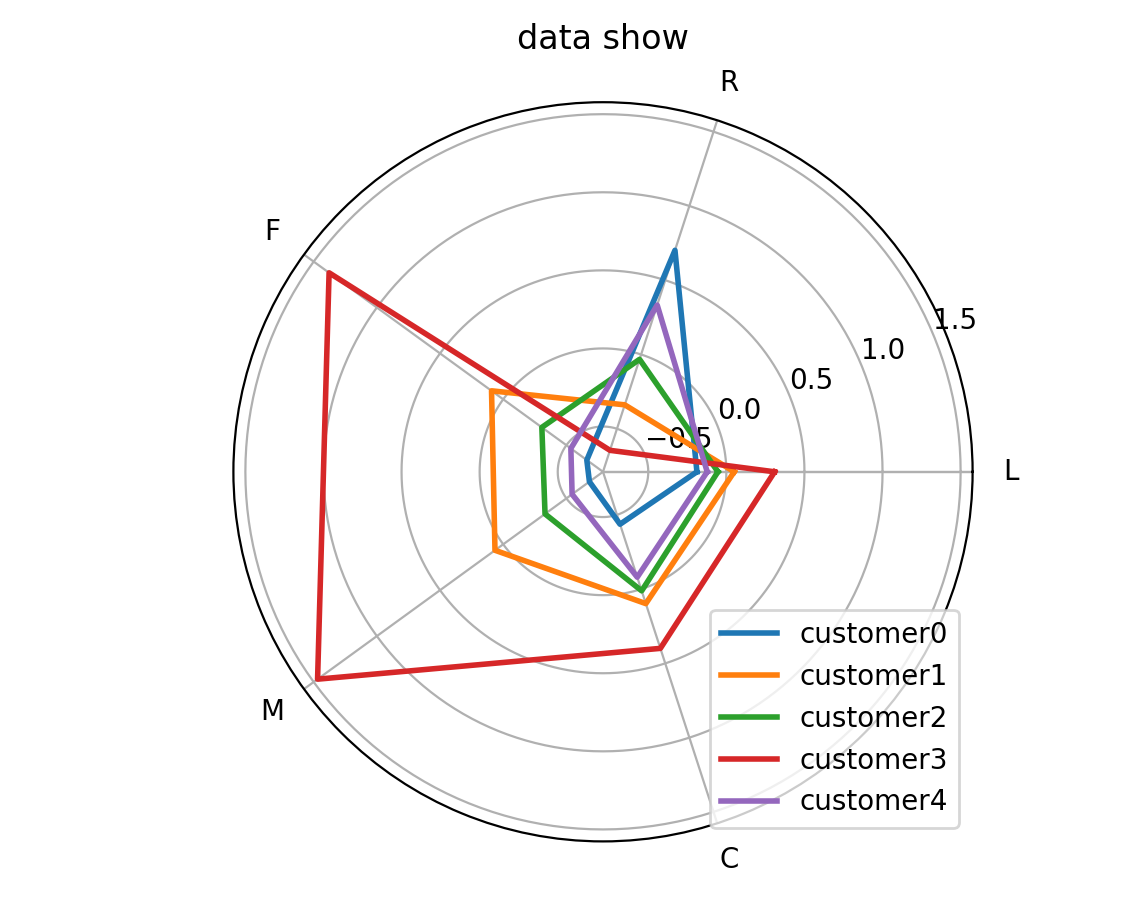
3.3 代码3

#导出模块 import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #定义 def result_pic(result): # 解析出类别标签和种类 labels = ['L', 'R', 'F', 'M', 'C'] kinds = list(result.iloc[:, 0]) # 由于在雷达图中,要保证数据闭合,这里就再添加L列,并转换为 np.ndarray result = pd.concat([result, result[['L']]], axis=1) centers = np.array(result.iloc[:, 1:]) angle = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, len(labels), endpoint=False) angle = np.concatenate((angle, [angle[0]])) # 绘图 fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True) # 参数polar, 以极坐标的形式绘制图形 # 画线 for i in range(len(kinds)): ax.plot(angle, centers[i], linewidth=2, label=kinds[i]) # 添加属性标签 ax.set_thetagrids(angle * 180 / np.pi, labels) plt.title('data show') plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': result = pd.read_csv('data2.csv', sep=',') result_pic(result) #注意细节:一般我们都是喜欢用excel或者wps表格进行数据的输入 #但是在保存数据时,喜欢直接更改文件的属性,导致数据读不出来 #应该是将文件另存为.csv格式
