复习和练习
复习部分
一、获取数据库连接
1)方式一
// 获取数据库连接
@Test
public void testGetConnection() throws Exception {
// 1.准备获取连接的四个字符串:user,jdbcurl,password,driverClass
String user = "root";
String password = "123456";
String jdbcUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/atguigu";
String driverClass = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user,
password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
2)方式二:解耦合
public Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = JDBCTest.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user,
password);
return connection;
}
二、Statement执行更新数据的操作
我们这里把更新数据的操作。用一个通用的update函数来表示
public void update() {
// 1.获取数据库连接
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection=getConnection();
// 2.调用Connection对象的createStatement()方法获取
// Statement对象
statement=connection.createStatement();
// 3.准备SQL语句
String sql="insert into examstudent values(1,4,'412824195263214584','200523164754000','张峰','郑州',85)";
// 4.发送SQL语句:调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql)方法
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
// 5.关闭数据库资源:由里向外关闭
releaseDB(null, statement, connection);
}
}
三、ResultSet执行查询操作
@Test
public void testResultSet(){
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection=getConnection();
//2.Statement
statement=connection.createStatement();
//3.准备SQL
String sql="select * from customers";
//4.执行SQL,得到结果集
resultSet=statement.executeQuery(sql);
//5.处理结果集
while(resultSet.next()){
int id=resultSet.getInt(1);
String name=resultSet.getString(2);
String email=resultSet.getString(3);
Date birth=resultSet.getDate(4);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(email);
System.out.println(birth);
System.out.println("----------");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
releaseDB(resultSet, statement, connection);
}
}
四、工具类的使用JDBCTools
将获取连接、执行更新操作、释放资源封装在一个JDBCTools类中
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JDBCTools {
// 更新的方法:插入、删除、更新,但是不包含select
public static void update(String sql) {
// 1.获取数据库连接
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
// 2.调用Connection对象的createStatement()方法获取
// Statement对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 4.发送SQL语句:调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql)方法
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 5.关闭数据库资源:由里向外关闭
release(null, statement, connection);
}
}
// 获取数据库连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = JDBCTest.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
Class.forName(driverClass);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user,
password);
return connection;
}
// 释放数据库资源
public static void release(ResultSet rs, Statement statement,
Connection conn) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
练习部分
我们的练习是这样的:
新建一个表:
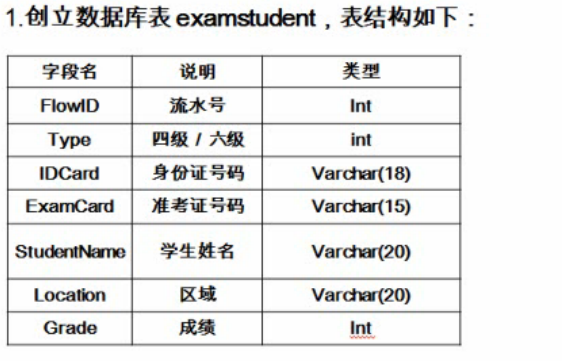
向表中插入数据:
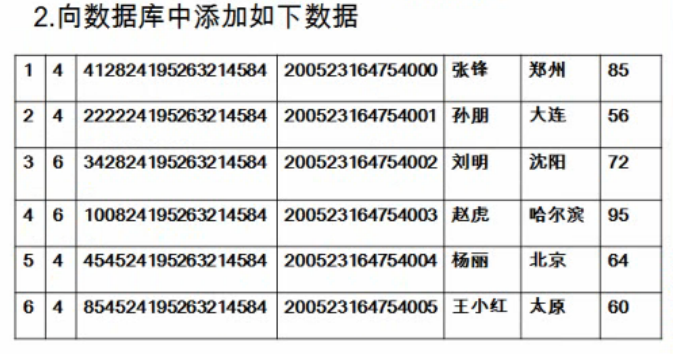
插入成功的话会出现这样的提示(我们从控制台获取要插入的数据):

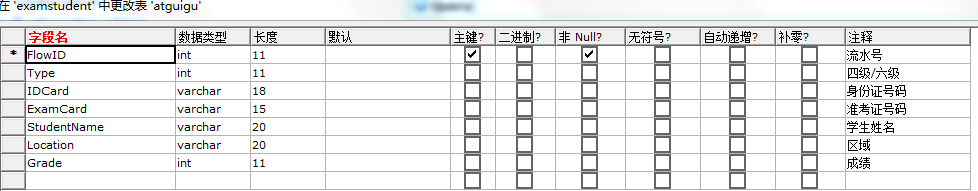
第一步、用图形化界面SQLyog创建一个数据表examstudent
第二步、向数据表中插入数据
面向对象的思想去编程:将插入的数据封装在一个类Student中
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
public class Student {
// 流水号
private int flowId;
// 考试类型
private int type;
// 身份证号
private String idCard;
// 准考证号
private String examCard;
// 学生姓名
private String studentName;
// 学生地址
private String location;
// 考试成绩
private int grade;
public int getFlowId() {
return flowId;
}
public void setFlowId(int flowId) {
this.flowId = flowId;
}
public int getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(int type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getIdCard() {
return idCard;
}
public void setIdCard(String idCard) {
this.idCard = idCard;
}
public String getExamCard() {
return examCard;
}
public void setExamCard(String examCard) {
this.examCard = examCard;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public int getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public Student(int flowId, int type, String idCard, String examCard,
String studentName, String location, int grade) {
super();
this.flowId = flowId;
this.type = type;
this.idCard = idCard;
this.examCard = examCard;
this.studentName = studentName;
this.location = location;
this.grade = grade;
}
public Student() {
}
// 重写Student对象的toString函数
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [flowId=" + flowId + ", type=" + type + ", idCard="
+ idCard + ", examCard=" + examCard + ", studentName="
+ studentName + ", location=" + location + ", grade=" + grade
+ "]";
}
}
从控制台获取输入信息作为插入student对象的相应的字段值,并插入到新创建的表中
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
public class JDBCTestCase {
//单元测试
@Test
public void testAddNewStudent() {
Student student = getStudentFromConsole();
addNewStudent(student);
}
// 从控制台输入学生的信息
private Student getStudentFromConsole() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Student student = new Student();
System.out.print("FlowId:");
student.setFlowId(scanner.nextInt());
System.out.print("Type:");
student.setType(scanner.nextInt());
System.out.print("IdCard:");
student.setIdCard(scanner.next());
System.out.print("ExamCard:");
student.setExamCard(scanner.next());
System.out.print("StudentName:");
student.setStudentName(scanner.next());
System.out.print("Location:");
student.setLocation(scanner.next());
System.out.print("Grade:");
student.setGrade(scanner.nextInt());
return student;
}
public void addNewStudent(Student student) {
String sql = "insert into examstudent" + " values("
+ student.getFlowId() + "," + student.getType() + ",'"
+ student.getIdCard() + "','" + student.getExamCard() + "','"
+ student.getStudentName() + "','" + student.getLocation()
+ "'," + student.getGrade() + ")";
System.out.println(sql);
JDBCTools.update(sql);
}
}
第三步、进行数据的查询(按第三张图片中要求的形式进行查询)
1).从控制台输入一个整数,确定要查询的类型
/*
* 1.身份证查询。 2.用准考证查询 。 3,其他,重新输入
*/
private int getSearchTypeFromConsole() {
System.out.println("请输入查询类型:1.身份证查询. 2.用准考证查询 ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int type = scanner.nextInt();
if (type != 1 && type != 2) {
System.out.println("输入有误,请重新输入!");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
return 0;
}
2).根据查询类型准备sql语句
// searchType:1或者2
private Student searchStudent(int searchType) {
String sql = "select * from examstudent where ";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 1.根据输入的searchType,提示用户输入信息
// 1.1若searchType=1,提示:请输入身份证号
// 1.2若searchType=2,提示:请输入准考证号
// 2/根据searchType确定SQL
if (searchType == 1) {
System.out.print("请输入准考证号:");
String examCard = scanner.next();
sql = sql + "examCard='" + examCard + "'";
} else {
System.out.print("请输入身份证号:");
String IdCard = scanner.next();
sql = sql + "IdCard='" + IdCard + "'";
}
// 3.执行查询
Student student = getStudent(sql);
// 4.若存在结果,将查询结果封装成一个Student对象
return student;
}
执行查询操作,将结果封装成一个Student对象
private Student getStudent(String sql) {
Student student = null;
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()) {
student = new Student(resultSet.getInt(1), resultSet.getInt(2),
resultSet.getString(3), resultSet.getString(4),
resultSet.getString(5), resultSet.getString(6),
resultSet.getInt(7));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCTools.release(resultSet, statement, connection);
}
return student;
}
打印查询结果:
/**
* 打印学生信息:若学生存在则打印具体信息,否则打印:查无此人
*/
private void printStudent(Student student) {
if (student != null) {
System.out.println(student);
} else {
System.out.println("查无此人");
}
}
写一个测试方法测试一下:
@Test
public void testGetStudent() {
// 1.得到查询的类型
int searchType = getSearchTypeFromConsole();
// 2.具体查询信息
Student student = searchStudent(searchType);
// 3.打印学生信息
printStudent(student);
}
运行结果:
请输入查询类型:1.身份证查询. 2.用准考证查询 1 请输入身份证号:3 Student [flowId=1, type=2, idCard=3, examCard=4, studentName=lili, location=dalin, grade=85]
本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/ysw-go/
1、本博客的原创原创文章,都是本人平时学习所做的笔记,如有错误,欢迎指正。
2、如有侵犯您的知识产权和版权问题,请通知本人,本人会即时做出处理文章。
3、本博客的目的是知识交流所用,转载自其它博客或网站,作为自己的参考资料的,感谢这些文章的原创人员