Mysql索引的建立对于Mysql的高效运行是很重要的,索引可以大大提高MySQL的检索速度。大家在使用Mysql的过程中,肯定都使用到了索引,也都知道建立索引的字段通常都是作为查询条件的字段(一般作为WHERE子句的条件),却容易忽略查询语句里包含order by的场景。其实涉及到排序order by的时候,建立适当的索引能够提高查询效率。这里就介绍一下利用索引优化order by的查询语句。
创建测试数据
创建一张测试数据表user_article(用户文章表),有id(主键),user_id(用户ID),title(标题),content(内容),comment_num(评论次数),create_time(创建时间)字段。
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user_article`(
`id` INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` INT UNSIGNED,
`title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`content` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`comment_num` INT UNSIGNED,
`create_time` INT UNSIGNED,
PRIMARY KEY ( `id` )
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
插入测试数据,插入数据多一点,如果数据少mysql会认为走索引效率低,全表扫描效率高:
insert into user_article (user_id,title,content,comment_num,create_time) values(1,'标题1','内容1',10,1582289251);
insert into user_article (user_id,title,content,comment_num,create_time) values(2,'标题2','内容2',20,1582634851);
insert into user_article (user_id,title,content,comment_num,create_time) values(3,'标题3','内容3',30,1582634851);
insert into user_article (user_id,title,content,comment_num,create_time) values(1,'标题4','内容4',40,1584276451);
where+单字段order by
形如SELECT [column1],[column2],…. FROM [TABLE] WHERE [columnX] = [value] ORDER BY [sort]
explain select * from user_article where user_id=10000 order by comment_num desc;
结果:
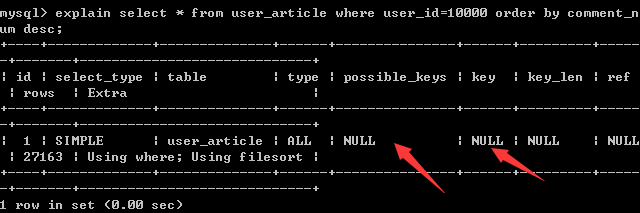
查询未使用索引,可建立一个联合索引(user_id,comment_num)来优化。
create index a on user_article(user_id,comment_num);
show index from user_article;
explain select * from user_article where user_id=10000 order by comment_num desc;
结果:

查询已经使用了建立的索引,如果只对user_id建立索引,会是什么情况呢?
drop index a on user_article;
create index user_id on user_article(user_id);
show index from user_article;
explain select * from user_article where user_id=10000 order by comment_num desc;
结果:
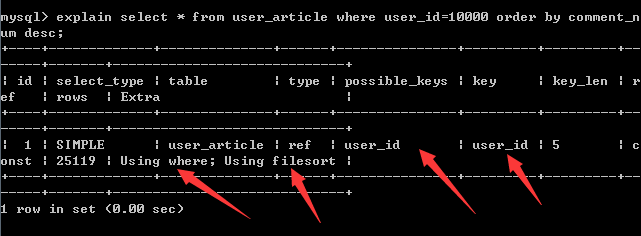
查询同样使用了索引,区别在于extra里多了using filesort,多了排序操作,查看执行时间,联合索引的查询效率高于单索引,不对user_id建立索引,只对comment_num建立索引会是什么情况呢?
drop index user_id on user_article;
create index comment_num on user_article(comment_num);
show index from user_article;
explain select * from user_article where user_id=10000 order by comment_num desc;
结果:
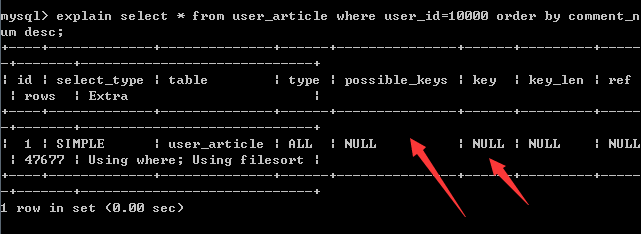
如果对where条件字段未建索引,只对排序字段建索引,是不会使用索引的。
where+多字段order by
形如SELECT * FROM [table] WHERE uid=1 ORDER x,y
create index b on user_article(user_id,comment_num,create_time);
explain select * from user_article where user_id=10000 order by comment_num,create_time;
结果:

建立索引(user_id,comment_num,create_time)实现order by的优化,只对user_id建立索引,与单字段order by一样,会使用索引,但是查询效率不及联合索引。
从上面测试可以看出,走不走索引还是跟where条件里的字段是否建立索引有关,如果where条件里字段未建立索引,那查询不会使用索引,建立联合索引,减少了using_filesort的排序操作,可以提高查询效率。