享元模式 FlyWeight
2019-06-21 14:47:30
参考博文:https://blog.csdn.net/zhiduoniu/article/details/18267451 侵权必删
什么是享元模式:以共享的方式高效地支持大量细粒度对象的重用。
适用性:大量细粒度对象存在的场合。(细粒度:相似的对象)
享元模式基本角色:
单例简单工厂:维护一个共享对象池采用HashMap,创建并管理享元对象
抽象享元类:具体享元类的抽象,向外界提供享元对象接口。
具体享元类:实现了抽象享元类,其实例称为享元对象;在具体享元类中为内部状态提供了存储空间。
内部状态和外部状态的概念:
内部状态是共享对象共有的状态,一般作为具体享元类的成员变量
外部状态是受到客户端调用的影响,通过外部注入的方式获得,如方法的参数。
享元模式的代码要点:
单例简单工厂:单例模式,共享对象池,创建并管理享元对象。
抽象享元类:提供方法接口
具体享元类:内部状态,实现抽象方法
享元模式类图:
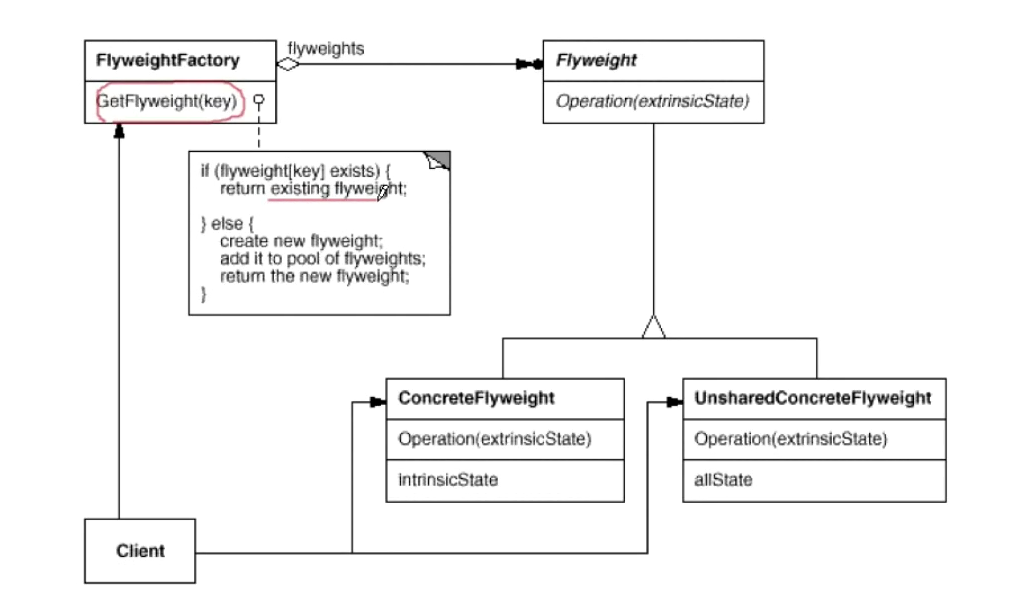
享元模式的基本代码:
package FlyWeightDemo; /** * 抽象享元类 * 需要分离内部状态和外部状态 * 内外部状态的含义:内部状态是所有共享对象共有的相同的状态,一般作为成员变量; * 外部状态是收到客户端调用的影响,不是共享的状态 * */ public abstract class Chessman { //外部状态 //本例中Location作为棋子的位置是收客户端调用的影响故是外部状态,通过方法参数的方式注入 protected abstract String getColor(); public void display(Location l){ System.out.println("x:"+l.getX()+" "+ "y:"+l.getY()); } }
package FlyWeightDemo; /** * 具体共享类 * 成员变量中保存了可以共享内部状态 */ public class ConcreteChessman extends Chessman{ private String color; public ConcreteChessman(String color) { this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } }
package FlyWeightDemo; /** * 外部状态 * 外部状态与内部状态分离,在客户端需要时传给共享对象 * */ public class Location { private int x; private int y; public Location(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public int getX() { return x; } public void setX(int x) { this.x = x; } public int getY() { return y; } public void setY(int y) { this.y = y; } }
package FlyWeightDemo; import java.util.HashMap; /** * 单例简单工厂 * */ public class FlyWeightFactory { private static HashMap<String,Chessman> pool; private FlyWeightFactory(){ pool = new HashMap<>(); } private static class FactoryHolder{ private static FlyWeightFactory factory = new FlyWeightFactory(); } public static FlyWeightFactory getInstance(){ return FactoryHolder.factory; } public Chessman getChessman(String color){ //如果pool中含有该对象则返回该对象的引用 if(pool.containsKey(color)){ System.out.println("get from pool."); return pool.get(color); }else { //如果不含该对象,则先实例化存入pool中,然后返回该对象引用 Chessman c = new ConcreteChessman(color); pool.put(color,c); System.out.println("new a instance"); return c; } } }
package FlyWeightDemo; /** * 测试代码 * 由测试结果可以知道,只有第一次用到某一细粒度对象时才会创建对象并存入对象共享池中 * 通过方法参数的方式,将Location外部状态传给共享对象。 */ public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) { FlyWeightFactory factory = FlyWeightFactory.getInstance(); Chessman black1 = factory.getChessman("black"); Chessman black2 = factory.getChessman("black"); Chessman black3 = factory.getChessman("black"); Chessman white1 = factory.getChessman("white"); Chessman white2 = factory.getChessman("white"); Chessman green1 = factory.getChessman("green"); Chessman green2= factory.getChessman("green"); System.out.println("====================="); System.out.println(black1==black2); System.out.println(black2==black3); System.out.println(white1==white2); System.out.println("====================="); System.out.println(green1.getColor()); green1.display(new Location(1,1)); green2.display(new Location(3,451)); } }
//代码测试结果 new a instance get from pool. get from pool. new a instance get from pool. new a instance get from pool. ===================== true true true ===================== green x:1 y:1 x:3 y:451