开心一刻
一天,楼主在路上碰到了一个很久没见的朋友,找了个餐馆,坐下聊了起来
楼主:在哪上班了 ?
朋友:火葬场啊
楼主:在那上班,一个月多少钱啊 ?
朋友:两万多啊
楼主(不可思议):多少 ?
朋友(非常淡定):两万多
楼主:你们那还要人吗 ?
朋友:要啊,24小时都要
楼主:不是,我的意思是你们那还收人吗
朋友:收,天天都收
楼主:我是说,我能进去不 ?
朋友:那200多斤的胖子都能进去,你进不去 ?
楼主:不是,你是非要把我给炼了是咋地 ? 我能进去不,我能自己进去不 ?
朋友:那有点悬,都是推进去的
楼主:我是说,你们那还招工吗
朋友:招,不分公母,都招
楼主:老板,买单
老板:你还没点菜了
楼主:不点了,再不走就要被炼了

数据结构
对 HashMap 的底层数据结构,相信大家都有所了解,不同的版本,底层数据结构会有所不同
1.7 的底层数据结构

/** * An empty table instance to share when the table is not inflated. */ static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; /** * The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two. */ transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE; static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; int hash; ... }
1.8 的底层数据结构

/** * The table, initialized on first use, and resized as * necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two. * (We also tolerate length zero in some operations to allow * bootstrapping mechanics that are currently not needed.) */ transient Node<K,V>[] table; static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; ... } /** * Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn * extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or * linked node. */ static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red; ... }
但基础结构还是: 数组 + 链表 ,称作 哈希表 或 散列表
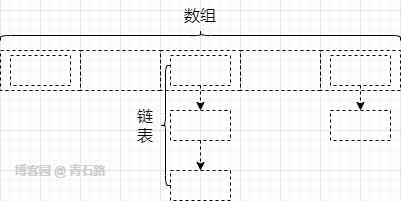
只是 1.8 做了优化,引进了 红黑树 ,来提升链表中元素获取的速度
JDK1.7 头插
只有元素添加的时候,才会出现链表元素的插入,那么我们先来看看 put 方法
put - 添加元素
源码如下

/** * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old * value is replaced. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or * <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>. * (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map * previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.) */ public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
直接看代码可能不够直观,我们结合流程图来看

什么? 还是不够直观? (楼主也这么觉得)

那我们就结合具体案例来看下这个流程
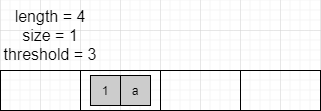
假设 HashMap 初始状态
然后依次往里面添加元素:(2,b), (3,w), (5,e), (9,t), (16,p)
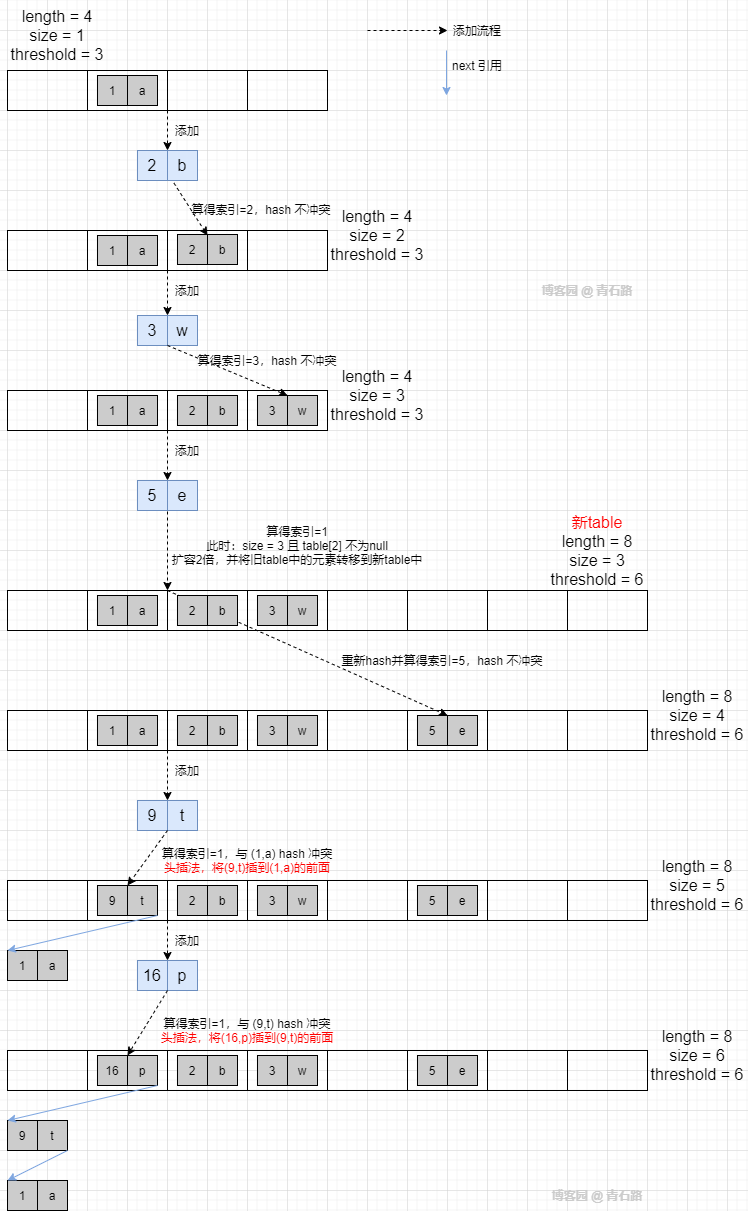
再利用断点调试,我们来看看真实情况
一切都对得上,进展的也挺顺利
resize - 数组扩容
上述提到了扩容,但是没细讲,我们来看看扩容的实现
关键代码如下

/** * Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a * larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the * number of keys in this map reaches its threshold. * * If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not * resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE. * This has the effect of preventing future calls. * * @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two; * must be greater than current capacity unless current * capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value * is irrelevant). */ void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); table = newTable; threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); } /** * Transfers all entries from current table to newTable. */ void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
主要做了两件事:1、创建一个新的 Entry 空数组,长度是原数组的 2 倍,2、遍历原数组,对每个元素重新计算新数组的索引值,然后放入到新数组的对应位置
有意思的是这个转移方法:transfer,我们结合案例来仔细看看
假设扩容之前的状态如下图所示

扩容过程如下
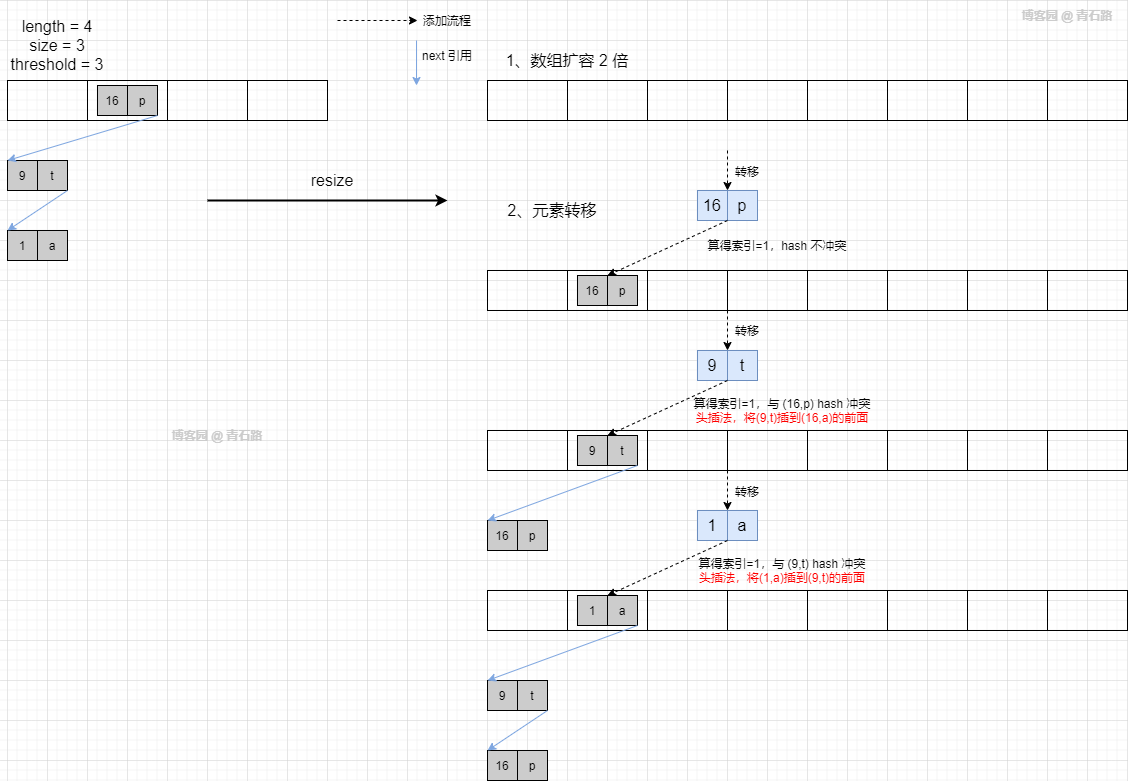
利用断点调试,我们来看看真实情况
链表元素的转移,还是采用的头插法
链表成环
不管是元素的添加,还是数组扩容,只要涉及到 hash 冲突,就会采用头插法将元素添加到链表中
上面讲了那么多,看似风平浪静,实则暗流涌动;单线程下,确实不会有什么问题,那多线程下呢 ? 我们接着往下看
将设扩容之前的的状态如下所示
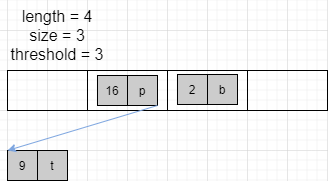
然后,线程 1 添加 (1,a) ,线程 2 添加 (19,n),线程 1 会进行扩容,线程 2 也进行扩容,那么 transfer 的时候就可能出现如下情况

哦豁,链表成环了,这就会导致:Infinite Loop
JDK1.8 尾插
1.8就不讲那么详细了,我们主要来看看 resize 中的元素转移部分

if (oldTab != null) { // 从索引 0 开始逐个遍历旧 table for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) // 链表只有一个元素 newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) // 红黑树,先不管 ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order // 拆链表,拆成两个子链表:索引不变的元素链表和有相同偏移量的元素链表 // 每个链表都保持原有顺序 Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { // 索引不变的元素链表 if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else // 通过尾部去关联 next,维持了元素原有顺序 loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { // 相同偏移量的元素链表 if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else // 通过尾部去关联 next,维持了元素原有顺序 hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } }
通过尾插法,维护了链表元素的原有顺序
在扩容时,头插法会改变链表中元素原本的顺序,以至于在并发场景下导致链表成环的问题,而尾插法,在扩容时会保持链表元素原本的顺序,就不会出现链表成环的问题
相关疑惑
1、JDK 1.7及之前,为什么采用头插法
呃... 这个可能需要问头插法的实现者了;
但有种说法,我觉得挺有道理:缓存的时间局部性原则,最近访问过的数据下次大概率会再次访问,把刚访问过的元素放在链表最前面可以直接被查询到,减少查找次数
2、既然头插法有链表成环的问题,为什么直到 1.8 才采用尾插法来替代头插法
只有在并发情况下,头插法才会出现链表成环的问题,多线程情况下,HashMap 本就非线程安全,这就相当于你在它的规则之外出了问题,那能怪谁?
1.8 采用尾插,是对 1.7 的优化
3、既然 1.8 没有链表成环的问题,那是不是说明可以把 1.8 中的 HashMap 用在多线程中
链表成环只是并发问题中的一种,1.8 虽然解决了此问题,但是还是会有很多其他的并发问题,比如:上秒 put 的值,下秒 get 的时候却不是刚 put 的值;因为操作都没有加锁,不是线程安全的
总结
1、JDK 1.7 采用头插法来添加链表元素,存在链表成环的问题,1.8 中做了优化,采用尾插法来添加链表元素
2、HashMap 不管在哪个版本都不是线程安全的,出了并发问题不要怪 HashMap,从自己身上找原因
