每篇一句
牛逼架构师:把复杂问题简单化,把简单问题搞没
菜逼架构师:把简单问题复杂化
前言
不知这个标题能否勾起你的好奇心和求知欲?在Spring MVC的使用中,若我说@RequestMapping是最为常用的一个注解你应该没啥意见吧。若你细心的话你能发现它有一个name属性(Spring4.1后新增),大概率你从来都没有使用过且鲜有人知。
我本人搜了搜相关文章,也几乎没有一篇文章较为系统化的介绍它。可能有人会说搜不到就代表不重要/不流行嘛,我大部分统一这个观点,但这块知识点我觉得还挺有意思,因此本文就针对性的弥补市面的空白,带你了解name属性的作用和使用。更为重要的是借此去了解学习Spring MVC非常重要的URI Builder模式
@RequestMapping的name属性
首先看此属性在@RequestMapping中的定义:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
// @since 4.1
String name() default "";
...
}
javadoc描述:为此映射分配名称,它可以使用在类上,也可以标注在方法上。
在分析RequestMappingHandlerMapping源码的时候指出过:它的createRequestMappingInfo()方法会把注解的name封装到RequestMappingInfo.name属性里。因为它既可以在类上又可以在方法上,因此一样的它需要combine,但是它的combine逻辑稍微特殊些,此处展示如下:
RequestMappingInfo:
// 此方法来自接口:RequestCondition
@Override
public RequestMappingInfo combine(RequestMappingInfo other) {
String name = combineNames(other);
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.combine(other.patternsCondition);
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.combine(other.methodsCondition);
...
return new RequestMappingInfo( ... );
}
@Nullable
private String combineNames(RequestMappingInfo other) {
if (this.name != null && other.name != null) {
String separator = RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy.SEPARATOR;
return this.name + separator + other.name;
} else if (this.name != null) {
return this.name;
} else {
return other.name;
}
}
逻辑不难,就是类+"#"+方法的拼接,但是我们知道其实绝大部分情况下我们都从来没有指定过name属性,那么此处就不得不提这个策略接口:HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy了,它用于缺省的名字生成策略器
HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy
为处理程序HandlerMethod方法分配名称的策略接口。此接口可以在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping里配置生成name,然后这个name可以用于AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerMethodsForMappingName(String)方法进行查询~
// @since 4.1
@FunctionalInterface // 函数式接口
public interface HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> {
// Determine the name for the given HandlerMethod and mapping.
// 根据HandlerMethod 和 Mapping拿到一个name
String getName(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, T mapping);
}
它的唯一实现类是:RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy(目前而言RequestMappingInfo的唯一实现只有@RequestMapping,但设计上是没有强制绑定必须是这个注解~)
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy
此类提供name的默认的生成规则(若没指定的话)的实现
// @since 4.1
public class RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy implements HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<RequestMappingInfo> {
// 类级别到方法级别的分隔符(当然你也是可以改的)
public static final String SEPARATOR = "#";
@Override
public String getName(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, RequestMappingInfo mapping) {
if (mapping.getName() != null) { // 若使用者自己指定了,那就以指定的为准
return mapping.getName();
}
// 自动生成的策略
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// 1、拿到类名
// 2、遍历每个字母,拿到所有的大写字母
// 3、用拿到的大写字母拼接 # 拼接方法名。如:TestController#getFoo()最终结果是:TC#getFoo
String simpleTypeName = handlerMethod.getBeanType().getSimpleName();
for (int i = 0; i < simpleTypeName.length(); i++) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(simpleTypeName.charAt(i))) {
sb.append(simpleTypeName.charAt(i));
}
}
sb.append(SEPARATOR).append(handlerMethod.getMethod().getName());
return sb.toString();
}
}
简单总结这部分逻辑如下:
- 类上的name值 + '#' + 方法的name值
- 类上若没指定,默认值是:类名所有大写字母拼装
- 方法上若没指定,默认值是:方法名
name属性有什么用(如何使用)?
说了这么多,小伙伴可能还是一头雾水?有什么用?如何用?
其实在接口的JavaDoc里有提到了它的作用:应用程序可以在下面这个静态方法的帮助下按名称构建控制器方法的URL,它借助的是MvcUriComponentsBuilder的fromMappingName方法实现:
MvcUriComponentsBuilder:
// 静态方法:根据mappingName,获取到一个MethodArgumentBuilder
public static MethodArgumentBuilder fromMappingName(String mappingName) {
return fromMappingName(null, mappingName);
}
public static MethodArgumentBuilder fromMappingName(@Nullable UriComponentsBuilder builder, String name) {
...
Map<String, RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping> map = wac.getBeansOfType(RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.class);
...
for (RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping mapping : map.values()) {
// 重点:根据名称找到List<HandlerMethod> handlerMethods
// 依赖的是getHandlerMethodsForMappingName()这个方法,它是从MappingRegistry里查找
handlerMethods = mapping.getHandlerMethodsForMappingName(name);
}
...
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = handlerMethods.get(0);
Class<?> controllerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType();
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod();
// 构建一个MethodArgumentBuilder
return new MethodArgumentBuilder(builder, controllerType, method);
}
说明:
MethodArgumentBuilder是MvcUriComponentsBuilder的一个public静态内部类,持有controllerType、method、argumentValues、baseUrl等属性...
它的使用场景,我参考了Spring的官方文档,截图如下:
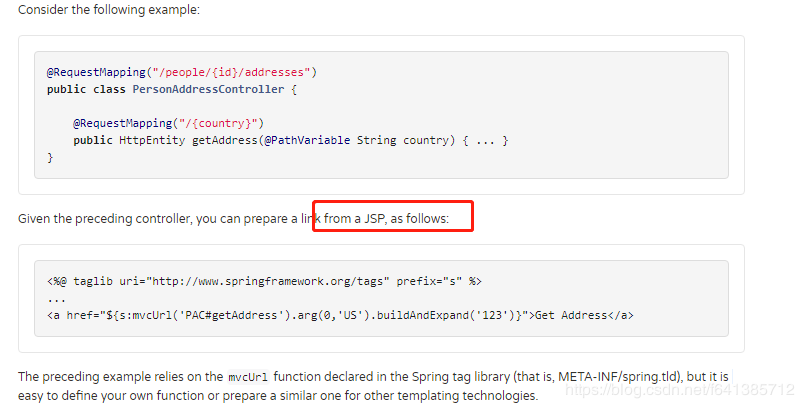
官方文档说:它能让你非常方便的在JSP页面上使用它,形如这样子:
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="s" %>
...
<a href="${s:mvcUrl('PAC#getAddress').arg(0,'US').buildAndExpand('123')}">Get Address</a>
这么写至少感觉比你这样拼装URL:pageContext.request.contextPath//people/1/addresses/china 要更加靠谱点,且更加面向对象点吧~
说明:使用此
s:mvcUrl函数是要求你导入Spring标签库的支持的~
此处应有疑问:JSP早就过时了,现在谁还用呢?难道Spring4.1新推出来的name属性这么快就寿终正寝了?
当然不是,Spring作为这么优秀的框架,设计上都是功能都是非常模块化的,该功能自然不是和JSP强耦合的(Spring仅是提供了对JSP标签库而顺便内置支持一下下而已~)。
在上面我截图的最后一段话也讲到了,大致意思是:
示例依赖于Spring标记库(即META-INF/Spring.tld)中申明的mvcUrl函数,此函数的声明如下:
<function>
<description>Helps to prepare a URL to a Spring MVC controller method.</description>
<name>mvcUrl</name>
<function-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MvcUriComponentsBuilder</function-class>
<function-signature>org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MvcUriComponentsBuilder.MethodArgumentBuilder fromMappingName(java.lang.String)</function-signature>
</function>
可见它最终的处理函数是MvcUriComponentsBuilder.fromMappingName(java.lang.String)()这个方法而已(文末有详细介绍,请关联起来看本文)~
因为,如果你是其它模版技术(如Thymeleaf)也是很容易自定义一个这样类似的函数的,那么你就依旧可以使用此便捷、强大的功能来帮助你开发。
通过name属性的引入,就顺利过渡到了接下来要将的重点,也是本文的重中之重:Spring MVC支持的强大的URI Builder模式。
URI Builder
Spring MVC作为一个web层框架,避免不了处理URI、URL等和HTTP协议相关的元素,因此它提供了非常好用、功能强大的URI Builder模式来完成,这就是本文重点需要讲述的脚手架~
Spring MVC从3.1开始提供了一种机制,可以通过UriComponentsBuilder和UriComponents面向对象的构造和编码URI。
UriComponents
它表示一个不可变的URI组件集合,将组件类型映射到字符串值。
URI:统一资源标识符。 URL:统一资源定位符。
还是傻傻分不清楚?这里我推荐一篇通俗易懂的 文章 供你参考
它包含用于所有组件的方便getter,与java.net.URI类似,但具有更强大的编码选项和对URI模板变量的支持。
// @since 3.1 自己是个抽象类。一般构建它我们使用UriComponentsBuilder构建器
public abstract class UriComponents implements Serializable {
// 捕获URI模板变量名
private static final Pattern NAMES_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\{([^/]+?)\}");
@Nullable
private final String scheme;
@Nullable
private final String fragment;
// 唯一构造,是protected 的
protected UriComponents(@Nullable String scheme, @Nullable String fragment) {
this.scheme = scheme;
this.fragment = fragment;
}
... // 省略它俩的get方法(无set方法)
@Nullable
public abstract String getSchemeSpecificPart();
@Nullable
public abstract String getUserInfo();
@Nullable
public abstract String getHost();
// 如果没有设置port,就返回-1
public abstract int getPort();
@Nullable
public abstract String getPath();
public abstract List<String> getPathSegments();
@Nullable
public abstract String getQuery();
public abstract MultiValueMap<String, String> getQueryParams();
// 此方法是public且是final的哦~
// 注意它的返回值还是UriComponents
public final UriComponents encode() {
return encode(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
public abstract UriComponents encode(Charset charset);
// 这是它最为强大的功能:对模版变量的支持
// 用给定Map映射中的值替换**所有**URI模板变量
public final UriComponents expand(Map<String, ?> uriVariables) {
return expandInternal(new MapTemplateVariables(uriVariables));
}
// 给定的是变量数组,那就按照顺序替换
public final UriComponents expand(Object... uriVariableValues) {...}
public final UriComponents expand(UriTemplateVariables uriVariables) { ... }
// 真正的expand方法,其实还是子类来实现的
abstract UriComponents expandInternal(UriTemplateVariables uriVariables);
// 规范化路径移除**序列**,如“path/…”。
// 请注意,规范化应用于完整路径,而不是单个路径段。
public abstract UriComponents normalize();
// 连接所有URI组件以返回完全格式的URI字符串。
public abstract String toUriString();
public abstract URI toUri();
@Override
public final String toString() {
return toUriString();
}
// 拷贝
protected abstract void copyToUriComponentsBuilder(UriComponentsBuilder builder);
... // 提供静态工具方法expandUriComponent和sanitizeSource
}
它包含有和Http相关的各个部分:如schema、port、path、query等等。此抽象类有两个实现类:OpaqueUriComponents和HierarchicalUriComponents
Hierarchical:分层的Opaque:不透明的
由于在实际使用中会使用构建器来创建实例,所以都是面向抽象类编程,并不需要关心具体实现,因此实现类部分此处省略~
UriComponentsBuilder
从命名中就可以看出,它使用了Builder模式,用于构建UriComponents。实际应用中我们所有的UriComponents都应是通过此构建器构建出来的~
// @since 3.1
public class UriComponentsBuilder implements UriBuilder, Cloneable {
... // 省略所有正则(包括提取查询参数、scheme、port等等等等)
... // 它所有的构造函数都是protected的
// ******************鞋面介绍它的实例化静态方法(7种)******************
// 创建一个空的bulder,里面schema,port等等啥都木有
public static UriComponentsBuilder newInstance() {
return new UriComponentsBuilder();
}
// 直接从path路径里面,分析出一个builder。较为常用
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromPath(String path) {...}
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromUri(URI uri) {...}
// 比如这种:/hotels/42?filter={value}
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromUriString(String uri) {}
// 形如这种:https://example.com/hotels/42?filter={value}
// fromUri和fromHttpUrl的使用方式差不多~~~~
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromHttpUrl(String httpUrl) {}
// HttpRequest是HttpMessage的子接口。它的原理是:fromUri(request.getURI())(调用上面方法fromUri)
// 然后再调用本类的adaptFromForwardedHeaders(request.getHeaders())
// 解释:从头Forwarded、X-Forwarded-Proto等拿到https、port等设置值~~
// 详情请参见http标准的Forwarded头~
// @since 4.1.5
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromHttpRequest(HttpRequest request) {}
// origin 里面放的是跨域访问的域名地址。比如 www.a.com 访问 www.b.com会形成跨域
// 这个时候访问 www.b.com 的时候,请求头里会携带 origin:www.a.com(b服务需要通过这个来判断是否允许a服务跨域访问)
// 方法可以获取到协议,域名和端口。个人觉得此方法没毛卵用~~~
// 和fromUriString()方法差不多,不过比它精简(因为这里只需要关注scheme、host和port)
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromOriginHeader(String origin) {}
// *******************下面都是实例方法*******************
// @since 5.0.8
public final UriComponentsBuilder encode() {
return encode(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
public UriComponentsBuilder encode(Charset charset) {}
// 调用此方法生成一个UriComponents
public UriComponents build() {
return build(false);
}
public UriComponents build(boolean encoded) {
// encoded=true,取值就是FULLY_ENCODED 全部编码
// 否则只编码模版或者不编码
return buildInternal(encoded ? EncodingHint.FULLY_ENCODED :
(this.encodeTemplate ? EncodingHint.ENCODE_TEMPLATE : EncodingHint.NONE)
);
}
// buildInternal内部就会自己new子类:OpaqueUriComponents或者HierarchicalUriComponents
// 以及执行UriComponents.expand方法了(若指定了参数的话),使用者不用关心了
// 显然这就是个多功能方法了:设置好参数。build后立马Expand
public UriComponents buildAndExpand(Map<String, ?> uriVariables) {
return build().expand(uriVariables);
}
public UriComponents buildAndExpand(Object... uriVariableValues) {}
//build成为一个URI。注意这里编码方式是:EncodingHint.ENCODE_TEMPLATE
@Override
public URI build(Object... uriVariables) {
return buildInternal(EncodingHint.ENCODE_TEMPLATE).expand(uriVariables).toUri();
}
@Override
public URI build(Map<String, ?> uriVariables) {
return buildInternal(EncodingHint.ENCODE_TEMPLATE).expand(uriVariables).toUri();
}
// @since 4.1
public String toUriString() { ... }
// ====重构/重新设置Builder====
public UriComponentsBuilder uri(URI uri) {}
public UriComponentsBuilder uriComponents(UriComponents uriComponents) {}
@Override
public UriComponentsBuilder scheme(@Nullable String scheme) {
this.scheme = scheme;
return this;
}
@Override
public UriComponentsBuilder userInfo(@Nullable String userInfo) {
this.userInfo = userInfo;
resetSchemeSpecificPart();
return this;
}
public UriComponentsBuilder host(@Nullable String host){ ... }
... // 省略其它部分
// 给URL后面拼接查询参数(键值对)
@Override
public UriComponentsBuilder query(@Nullable String query) {}
// 遇上相同的key就替代,而不是直接在后面添加了(上面query是添加)
@Override
public UriComponentsBuilder replaceQuery(@Nullable String query) {}
@Override
public UriComponentsBuilder queryParam(String name, Object... values) {}
... replaceQueryParam
// 可以先单独设置参数,但不expend哦~
public UriComponentsBuilder uriVariables(Map<String, Object> uriVariables) {}
@Override
public Object clone() {
return cloneBuilder();
}
// @since 4.2.7
public UriComponentsBuilder cloneBuilder() {
return new UriComponentsBuilder(this);
}
...
}
API都不难理解,此处我给出一些使用案例供以参考:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url;
UriComponents uriComponents = UriComponentsBuilder.newInstance()
//.encode(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)
.scheme("https").host("www.baidu.com").path("/test").path("/{template}") //此处{}就成 不要写成${}
//.uriVariables(传一个Map).build();
.build().expand("myhome"); // 此效果同上一句,但推荐这么使用,方便一些
url = uriComponents.toUriString();
System.out.println(url); // https://www.baidu.com/test/myhome
// 从URL字符串中构造(注意:toUriString方法内部是调用了build和expend方法的~)
System.out.println(UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(url).toUriString()); // https://www.baidu.com/test/myhome
System.out.println(UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString(url).toUriString()); // https://www.baidu.com/test/myhome
// 给URL中放添加参数 query和replaceQuery
uriComponents = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(url).query("name=中国&age=18").query("&name=二次拼接").build();
url = uriComponents.toUriString();
// 效果描述:&test前面这个&不写也是木有问题的。并且两个name都出现了哦~~~
System.out.println(uriComponents.toUriString()); // https://www.baidu.com/test/myhome?name=中国&name=二次拼接&age=18
uriComponents = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(url).query("name=中国&age=18").replaceQuery("name=二次拼接").build();
url = uriComponents.toUriString();
// 这种够狠:后面的直接覆盖前面“所有的”查询串
System.out.println(uriComponents.toUriString()); // https://www.baidu.com/test/myhome?name=二次拼接
//queryParam/queryParams/replaceQueryParam/replaceQueryParams
// queryParam:一次性指定一个key,queryParams一次性可以搞多个key
url = "https://www.baidu.com/test/myhome"; // 重置一下
uriComponents = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(url).queryParam("name","中国","美国").queryParam("age",18)
.queryParam("name","英国").build();
url = uriComponents.toUriString();
// 发现是不会有repalace的效果的~~~~~~~~~~~~~
System.out.println(uriComponents.toUriString()); // https://www.baidu.com/test/myhome?name=中国&name=美国&name=英国&age=18
// 关于repalceParam相关方法,交给各位自己去试验吧~~~
// 不需要domain,构建局部路径,它也是把好手
uriComponents = UriComponentsBuilder.fromPath("").path("/test").build();
// .fromPath("/").path("/test") --> /test
// .fromPath("").path("/test") --> /test
// .fromPath("").path("//test") --> /test
// .fromPath("").path("test") --> /test
System.out.println(uriComponents.toUriString()); // /test?name=fsx
}
使用这种方式来构建URL还是非常方便的,它的容错性非常高,写法灵活且不容易出错,完全面向模块化思考,值得推荐。
- URI构建的任意部分(包括查询参数、scheme等等)都是可以用
{}这种形式的模版参数的 - 被替换的模版中还支持这么来写:
/myurl/{name:[a-z]}/show,这样用expand也能正常赋值
它还有个子类:ServletUriComponentsBuilder,是对Servlet容器的适配,也非常值得一提
ServletUriComponentsBuilder
它主要是扩展了一些静态工厂方法,用于创建一些相对路径(相当于当前请求HttpServletRequest )。
// @since 3.1
public class ServletUriComponentsBuilder extends UriComponentsBuilder {
@Nullable
private String originalPath;
// 不对外提供public的构造函数
// initFromRequest:设置schema、host、port(HTTP默认80,https默认443)
public static ServletUriComponentsBuilder fromContextPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
ServletUriComponentsBuilder builder = initFromRequest(request);
// 注意:此处路径全部替换成了ContextPath
builder.replacePath(request.getContextPath());
return builder;
}
// If the servlet is mapped by name, e.g. {@code "/main/*"}, the path
// 它在UriComponentsBuilderMethodArgumentResolver中有用
public static ServletUriComponentsBuilder fromServletMapping(HttpServletRequest request) {}
public static ServletUriComponentsBuilder fromRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) {
ServletUriComponentsBuilder builder = initFromRequest(request);
builder.initPath(request.getRequestURI());
return builder;
}
private void initPath(String path) {
this.originalPath = path;
replacePath(path);
}
public static ServletUriComponentsBuilder fromRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {}
// fromCurrentXXX方法...
public static ServletUriComponentsBuilder fromCurrentContextPath() {}
// 生路其它Current方法
// @since 4.0 移除掉originalPath的后缀名,并且把此后缀名return出来~~
// 此方法必须在UriComponentsBuilder.path/pathSegment方法之前调用~
@Nullable
public String removePathExtension() { }
}
说明:
Spring5.1后不推荐使用它来处理X-Forwarded-*等请求头了,推荐使用ForwardedHeaderFilter来处理~
使用UriComponentsBuilder类的最大好处是方便地注入到Controller中,在方法参数中可直接使用。详见UriComponentsBuilderMethodArgumentResolver,它最终return的是:ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromServletMapping(request),这样我们在Controller内就可以非常容易且优雅的得到URI的各个部分了(不用再自己通过request慢慢get)~
MvcUriComponentsBuilder
此类效果类似于ServletUriComponentsBuilder,它负责从Controller控制器标注有@RequestMapping的方法中获取UriComponentsBuilder,从而构建出UriComponents。
// @since 4.0
public class MvcUriComponentsBuilder {
// Bean工厂里·UriComponentsContributor·的通用名称
// 关于UriComponentsContributor,RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver和PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver都是它的子类
public static final String MVC_URI_COMPONENTS_CONTRIBUTOR_BEAN_NAME = "mvcUriComponentsContributor";
// 用于创建动态代理对象
private static final SpringObjenesis objenesis = new SpringObjenesis();
// 支持Ant风格的Path
private static final PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
// 参数名
private static final ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
// 课件解析查询参数、path参数最终是依赖于我们的MethodArgumentResolver
// 他们也都实现了UriComponentsContributor接口~~~
private static final CompositeUriComponentsContributor defaultUriComponentsContributor;
static {
defaultUriComponentsContributor = new CompositeUriComponentsContributor(new PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver(), new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver(false));
}
// final的,只能通过构造器传入
private final UriComponentsBuilder baseUrl;
// 此构造方法是protected的
protected MvcUriComponentsBuilder(UriComponentsBuilder baseUrl) {
this.baseUrl = baseUrl;
}
// 通过BaseUrl创建一个实例
public static MvcUriComponentsBuilder relativeTo(UriComponentsBuilder baseUrl) {
return new MvcUriComponentsBuilder(baseUrl);
}
// 从控制器里。。。
// 这个一个控制器类里有多个Mapping,那么只会有第一个会被生效
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromController(Class<?> controllerType) {
return fromController(null, controllerType);
}
// 注意此方法也是public的哦~~~~ builder可以为null哦~~
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromController(@Nullable UriComponentsBuilder builder, Class<?> controllerType) {
// 若builder为null,那就用它ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentServletMapping(),否则克隆一个出来
builder = getBaseUrlToUse(builder);
// 拿到此控制器的pathPrefixes。
// 关于RequestMappingHandlerMapping的pathPrefixes,出门右拐有详细说明来如何使用
String prefix = getPathPrefix(controllerType);
builder.path(prefix);
// 找到类上的RequestMapping注解,若没标注,默认就是'/'
// 若有此注解,拿出它的mapping.path(),若是empty或者paths[0]是empty,都返回'/'
// 否则返回第一个:paths[0]
String mapping = getClassMapping(controllerType);
builder.path(mapping);
return builder;
}
// 这个方法应该是使用得最多的~~~~ 同样的借用了MethodIntrospector.selectMethods这个方法
// 它的path是结合来的:String path = pathMatcher.combine(typePath, methodPath);
// fromMethodInternal方法省略,但最后一步调用了applyContributors(builder, method, args)这个方法
// 它是使用`CompositeUriComponentsContributor`来处理赋值URL的template(可以自己配置,也可以使用默认的)
// 默认使用的便是PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver和RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver
// 当在处理请求的上下文之外使用MvcUriComponentsBuilder或应用与当前请求不匹配的自定义baseurl时,这非常有用。
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromMethodName(Class<?> controllerType, String methodName, Object... args) {
Method method = getMethod(controllerType, methodName, args);
// 第一个参数是baseUrl,传的null 没传就是ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentServletMapping()
return fromMethodInternal(null, controllerType, method, args);
}
// @since 4.2
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromMethod(Class<?> controllerType, Method method, Object... args) {}
// @since 4.2
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromMethod(UriComponentsBuilder baseUrl, @Nullable Class<?> controllerType, Method method, Object... args) {}
// info必须是MethodInvocationInfo类型
// Create a {@link UriComponentsBuilder} by invoking a "mock" controller method. 用于mock
// 请参见on方法~~
public static UriComponentsBuilder fromMethodCall(Object info) {}
public static <T> T on(Class<T> controllerType) {
return controller(controllerType);
}
// 此方法是核心:ControllerMethodInvocationInterceptor是个私有静态内部类
// 实现了org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor接口以及
// org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor接口
// org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MvcUriComponentsBuilder.MethodInvocationInfo接口
// ReflectionUtils.isObjectMethod(method)
public static <T> T controller(Class<T> controllerType) {
Assert.notNull(controllerType, "'controllerType' must not be null");
return ControllerMethodInvocationInterceptor.initProxy(controllerType, null);
}
// @since 4.1
// 请看上面对@RequestMapping注解中name属性的介绍和使用
// ${s:mvcUrl('PC#getPerson').arg(0,"123").build()
// 这个标签s:mvcUrl它对应的解析函数其实就是MvcUriComponentsBuilder.fromMappingName
// 也就是这个方法`PC#getPerson`就二十所谓的mappingName,若不指定它由HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy生成
// 底层依赖方法:RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getHandlerMethodsForMappingName
public static MethodArgumentBuilder fromMappingName(String mappingName) {
return fromMappingName(null, mappingName);
}
// **************以上都是静态工厂方法,下面是些实例方法**************
// 调用的是静态方法fromController,See class-level docs
public UriComponentsBuilder withController(Class<?> controllerType) {
return fromController(this.baseUrl, controllerType);
}
// withMethodName/withMethodCall/withMappingName/withMethod等都是依赖于对应的静态工厂方法,略
}
MvcUriComponentsBuilder提供的功能被广泛应用到Mock接口中,并且它提供的MvcUriComponentsBuilder#fromMappingName的API是集成模版引擎的关键,我个人认为所想深入了解Spring MVC或者在此基础上扩展,了解它的URI Builder模式的必要性还是较强的。
总结
本文所叙述的内容整体生可能比较冷,可能大多数人没有接触过甚至没有听过,但并不代表它没有意义。
你和同伴都使用Spring MVC,差异化如何体现出来呢?我觉得有一个方向就是向他/她展示这些"真正的技术"~
== 若对Spring、SpringBoot、MyBatis等源码分析感兴趣,可加我wx:fsx641385712,手动邀请你入群一起飞 ==
== 若对Spring、SpringBoot、MyBatis等源码分析感兴趣,可加我wx:fsx641385712,手动邀请你入群一起飞 ==