1. 两数之和
题目:
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素不能使用两遍。
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
思路(3条):
-
暴力破解
通过双重循环,找出两个符合条件的索引值,将其拼凑成列表进行返回。
代码如下:
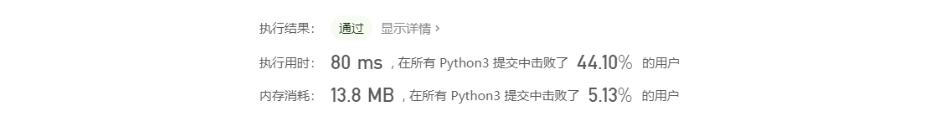
class Solution: def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]: ''' 通过双重循环寻找合适的索引值 然后返回 时间复杂度O(n^2) 空间复杂度O(n) ''' result = [] for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(i+1, len(nums)): if nums[i] == target - nums[j]: result = [i,j] return result效果好像不太好。
-
使用python的切片来做
切片是python的一个特定的语法,可以使用比较少的代码量实现相同的功能,但是很难看得懂。
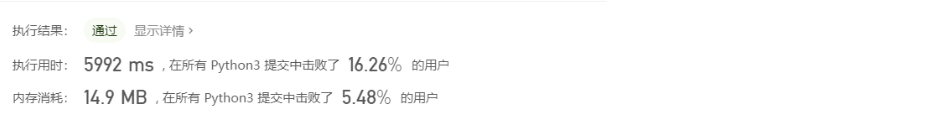
class Solution: def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]: ''' 使用python特有的切片来寻找 虽然代码不体现两重循环,但其实还是两重循环 时间复杂度O(n^2) 空间复杂度O(n) ''' for i in range(len(nums)): if target - nums[i] in nums[i+1:]: #nums[i+1:]就是从i+1到列表末尾 return (i, nums.index(target-nums[i],i+1))效果跟上一个差不多。
-
使用hash函数来做
hash函数可以更快地找到符合要求的值,但是我不太懂。
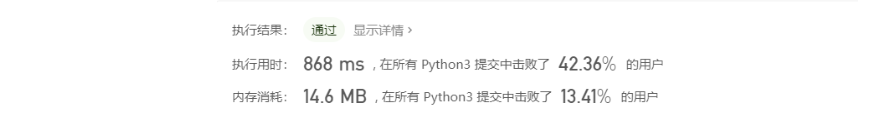
class Solution: def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]: ''' Hash函数计算结果 时间复杂度O(n) 空间复杂度O(n) ''' dic = {} for i, num in enumerate(nums): if num in dic: return [dic[num], i] else: dic[target - num] = i时间复杂度明显变短,但是空间复杂度没啥变化。

2. 两数相加
题目:
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807
思路:
使用链表去装载两链表各元素的和,同时判定是否要进位。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
"""
carry = 0
total = 0
l3 = ListNode(0)
head = l3
while l1 is not None or l2 is not None or carry > 0:
total = carry
if l1 is not None:
total += l1.val
l1 = l1.next
if l2 is not None:
total += l2.val
l2 = l2.next
node = ListNode(total % 10)
l3.next = node
l3 = l3.next
carry = total // 10 #"//"代表整除
return head.next
执行结果如下: