 代码
代码
1 int array[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
2 #define TOTAL_ELEMENTS (sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]))
3
4 #include <iostream>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 class Base{
8 public:
9 explicit Base(int i=0):ival(i)
10 {
11 cout << "Class Base's constructure is called" << endl;
12 }
13 Base(const Base& b)
14 {
15 cout << "Class Base's copy constructure is called" << endl;
16 }
17 public:
18 int ival;
19 };
20
21 void fun(Base b)
22 {
23 cout << "fun is called" << endl;
24 }
25
26 Base fn1()
27 {
28 Base b;
29 return b;
30 }
31
32 Base fn2()
33 {
34 return Base();
35 }
36
37 void main()
38 {
39 int val = 5;
40 fun(Base(val));
41 Base myb;
42 fun(myb);
43 cout << endl;
44
45 int d = -1;
46 if(d < (unsigned char)1)
47 cout << "int -1 < unsigned char 1" << endl;
48 if(d < (unsigned int)1)
49 cout << "int -1 < unsigned int 1" << endl;
50
51 if(d <= TOTAL_ELEMENTS)
52 cout << "int -1 < TOTAL_ELEMENTS" << endl;
53
54 cout << endl;
55
56 fn1(); cout << endl;
57 fn2(); cout << endl;
58
59 Base b1 = fn1(); cout << endl;
60 Base b2 = fn2(); cout << endl;
61
62 getchar();
63 }
2 #define TOTAL_ELEMENTS (sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]))
3
4 #include <iostream>
5 using namespace std;
6
7 class Base{
8 public:
9 explicit Base(int i=0):ival(i)
10 {
11 cout << "Class Base's constructure is called" << endl;
12 }
13 Base(const Base& b)
14 {
15 cout << "Class Base's copy constructure is called" << endl;
16 }
17 public:
18 int ival;
19 };
20
21 void fun(Base b)
22 {
23 cout << "fun is called" << endl;
24 }
25
26 Base fn1()
27 {
28 Base b;
29 return b;
30 }
31
32 Base fn2()
33 {
34 return Base();
35 }
36
37 void main()
38 {
39 int val = 5;
40 fun(Base(val));
41 Base myb;
42 fun(myb);
43 cout << endl;
44
45 int d = -1;
46 if(d < (unsigned char)1)
47 cout << "int -1 < unsigned char 1" << endl;
48 if(d < (unsigned int)1)
49 cout << "int -1 < unsigned int 1" << endl;
50
51 if(d <= TOTAL_ELEMENTS)
52 cout << "int -1 < TOTAL_ELEMENTS" << endl;
53
54 cout << endl;
55
56 fn1(); cout << endl;
57 fn2(); cout << endl;
58
59 Base b1 = fn1(); cout << endl;
60 Base b2 = fn2(); cout << endl;
61
62 getchar();
63 }
运行结果:
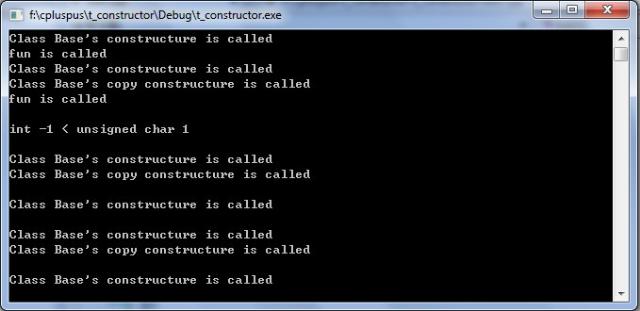
注意40行,用一个无名对象作为实参,调用函数fun,但编译器用实参初始化形参的时候,并没有如用普通对象调用fun一样,调用拷贝构造函数。无名对象的初始化,也就是形参的初始化。
这个技术还可以用于函数的return语句。如:return Student("Lucy"); 或者 Student st("Lucy"); return st; 前者好于后者。(例子fn1、fn2函数的调用)
对于后者,st对象被创建,同时调用构造函数完成初始化,然后调用拷贝构造函数,把st拷贝到保存返回值的外部存储单元中。最后,st对象在函数结束时被销毁。对于前者,编译器可以直接把临时对象创建并初始化在外部存储单元中,省去了拷贝和析构函数的开销。
关于比较的说明:当一个表达式的操作数类型不同,就会发生转换。数据类型一般朝着浮点精度更高、占用内存空间更长的方向转化。当int -1和unsigned char 1 比较的时候,后者隐式转换为int类型的1,所以前者小于后者,关系成立。
当int -1 和unsigned int 1比叫大小,前者转换为unsigned int,但-1转化为unsigned int为很大很大的值。所以前者小于后者,关系不成立。这个解释同样适用于TOTAL_ELEMENTS句子,sizeof返回的是无符号整形。
