经过前两篇的介绍,我们对整个redis的动作流程已经有比较清晰的认识。
接下来就是到具体的命令处理方式的理解了,想来我们用这些工具的意义也是在此。虽然没有人觉得,一个set/get方法会有难度,但是我们毕竟不是很清楚,否则也不至于在谈到深处就懵逼了。
我觉得本文的一个重要意义就是: 让set/get还原成它本来样子,和写"hello world"一样简单。
框架性质的东西,我们前面已经讲解,就直接进入主题: set/get 的操作。
set/get 对应的两个处理函数 (redisCommand) 定义是这样的:
// rF 代表 getCommand 是只读命令,又快又准,时间复杂度 O(1)或者O(log(n)) // wm 代表 setCommand 是个写命令,当心空间问题 {"get",getCommand,2,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0} {"set",setCommand,-3,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0}
所以,我们只要理解了, setCommand,getCommand 之后,就可以完全自信的说,set/get 就是和 "hello world" 一样简单了。
零、hash 算法
很显然,kv型的存储一定是hash相关算法的实现。那么redis中如何使用这个hash算法的呢?
redis 中许多不同场景的hash算法,其原型是在 dictType 中定义的。
typedef struct dictType { // hash 算法原型 unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key); void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj); } dictType;
针对大部分场景,我们的key一般都是 string 类型的,但是还是会稍微有不一样的。这里我们就两个场景来说明下:
1. 命令集构建的hash算法
即是 server.commands 中的key的hash算法,这里元素是有限的。其定义如下:
/* Command table. sds string -> command struct pointer. */ dictType commandTableDictType = { // 即 dictSdsCaseHash 是 command 的hash算法实现 dictSdsCaseHash, /* hash function */ NULL, /* key dup */ NULL, /* val dup */ dictSdsKeyCaseCompare, /* key compare */ dictSdsDestructor, /* key destructor */ NULL /* val destructor */ }; // server.c, 不区分大小写的key hash unsigned int dictSdsCaseHash(const void *key) { return dictGenCaseHashFunction((unsigned char*)key, sdslen((char*)key)); } // dict.c, 不区分大小写的key-hash算法: hash * 33 + c /* And a case insensitive hash function (based on djb hash) */ unsigned int dictGenCaseHashFunction(const unsigned char *buf, int len) { // static uint32_t dict_hash_function_seed = 5381; unsigned int hash = (unsigned int)dict_hash_function_seed; while (len--) hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + (tolower(*buf++)); /* hash * 33 + c */ return hash; }
2. 针对普通kv查询的hash算法
整个nosql就是kv的增删改查,所以这是个重要的算法。
/* Db->dict, keys are sds strings, vals are Redis objects. */ dictType dbDictType = { // k 的hash算法实现 dictSdsHash, /* hash function */ NULL, /* key dup */ NULL, /* val dup */ dictSdsKeyCompare, /* key compare */ dictSdsDestructor, /* key destructor */ dictObjectDestructor /* val destructor */ }; // server.c, 调用 dict 的实现 unsigned int dictSdsHash(const void *key) { return dictGenHashFunction((unsigned char*)key, sdslen((char*)key)); } // dict.c, 数据key的hash算法,或者通用的 string 的hashCode 算法 /* MurmurHash2, by Austin Appleby * Note - This code makes a few assumptions about how your machine behaves - * 1. We can read a 4-byte value from any address without crashing * 2. sizeof(int) == 4 * * And it has a few limitations - * * 1. It will not work incrementally. * 2. It will not produce the same results on little-endian and big-endian * machines. */ unsigned int dictGenHashFunction(const void *key, int len) { /* 'm' and 'r' are mixing constants generated offline. They're not really 'magic', they just happen to work well. */ uint32_t seed = dict_hash_function_seed; const uint32_t m = 0x5bd1e995; const int r = 24; /* Initialize the hash to a 'random' value */ uint32_t h = seed ^ len; /* Mix 4 bytes at a time into the hash */ const unsigned char *data = (const unsigned char *)key; // 核心算法: step1. *m, ^k>>r, *m, *m, ^k, 每4位做一次运算 while(len >= 4) { uint32_t k = *(uint32_t*)data; k *= m; k ^= k >> r; k *= m; h *= m; h ^= k; data += 4; len -= 4; } /* Handle the last few bytes of the input array */ // step2. 倒数第三位 ^<<16, 第二位 ^<<8, 第一位 ^, 然后 *m switch(len) { case 3: h ^= data[2] << 16; case 2: h ^= data[1] << 8; case 1: h ^= data[0]; h *= m; }; /* Do a few final mixes of the hash to ensure the last few * bytes are well-incorporated. */ // step3. 再混合 ^>>13, *m, ^>>15 h ^= h >> 13; h *= m; h ^= h >> 15; return (unsigned int)h; }
可以看到,针对普通的字符串的hash可是要复杂许多呢,因为这里数据远比 command 的数据多,情况更复杂,这样的算法唯一的目标就是尽量避免hash冲突。(虽然不知道为啥这么干,但它就是牛逼)
redis中还有其他的hash算法,比如dictObjHash,dictEncObjHash, 后续有接触我们再聊。
接下来,我们正式来看看 set/get 到底如何?
一、getCommand 解析
很显然,get 会是个最简单的命令,自然要检软柿子捏了。
// t_string.c void getCommand(client *c) { getGenericCommand(c); } int getGenericCommand(client *c) { robj *o; // 如果在kv里找不到,则直接响应空,shared.nullbulk 作为全局常量的优势就体现出来了 // shared.nullbulk = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnew("$-1 ")); if ((o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.nullbulk)) == NULL) return C_OK; // 找到对应的数据,但是类型不匹配,说明不能使用 get 命令,响应错误信息 // shared.wrongtypeerr = "-WRONGTYPE Operation against a key holding the wrong kind of value " if (o->type != OBJ_STRING) { addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr); return C_ERR; } else { // 正常情况则直接响应结果即可 addReplyBulk(c,o); return C_OK; } }
整个处理流程果然是异常简单,感觉人生已经达到了巅峰!但是,我们还没有看到关键,那就是查找 key 的过程。我们通过之前的介绍,知道有个叫做 redisDb 的东西,看起来它是负责所有的数据管理。它应该不会因为简单而不存储某些数据吧。
// db.c, 查找某个key对应的元素或者直接响应客户端 robj *lookupKeyReadOrReply(client *c, robj *key, robj *reply) { // 使用 c->db 对应的数据库进行查询,所以要求客户端必须针对某db进行操作,且不能跨库操作是原理决定 robj *o = lookupKeyRead(c->db, key); // 如果没有查到数据就直接使用默认的 reply, 响应客户端了 if (!o) addReply(c,reply); return o; } // db.c, 读取key 对应值 robj *lookupKeyRead(redisDb *db, robj *key) { robj *val; // 检查过期情况,如果过期,则不用再查了 if (expireIfNeeded(db,key) == 1) { /* Key expired. If we are in the context of a master, expireIfNeeded() * returns 0 only when the key does not exist at all, so it's save * to return NULL ASAP. */ if (server.masterhost == NULL) return NULL; /* However if we are in the context of a slave, expireIfNeeded() will * not really try to expire the key, it only returns information * about the "logical" status of the key: key expiring is up to the * master in order to have a consistent view of master's data set. * * However, if the command caller is not the master, and as additional * safety measure, the command invoked is a read-only command, we can * safely return NULL here, and provide a more consistent behavior * to clients accessign expired values in a read-only fashion, that * will say the key as non exisitng. * * Notably this covers GETs when slaves are used to scale reads. */ if (server.current_client && server.current_client != server.master && server.current_client->cmd && server.current_client->cmd->flags & CMD_READONLY) { return NULL; } } // 然后从db中查找对应的key值,其实就是一个 hash 查找 // 缓存命中统计 val = lookupKey(db,key); if (val == NULL) server.stat_keyspace_misses++; else server.stat_keyspace_hits++; return val; } // db.c, 过期的处理有点复杂,我们稍后再看,先看 db 的查找key过程 robj *lookupKey(redisDb *db, robj *key) { // 直接在 db->dict 中进行hash查找即可,前面已经介绍完成,关键优化点在增量rehash dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr); if (de) { robj *val = dictGetVal(de); /* Update the access time for the ageing algorithm. * Don't do it if we have a saving child, as this will trigger * a copy on write madness. */ if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1) val->lru = LRU_CLOCK(); return val; } else { return NULL; } } // db.c, 接下来看下,检查过期情况 int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) { mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key); mstime_t now; if (when < 0) return 0; /* No expire for this key */ /* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */ if (server.loading) return 0; /* If we are in the context of a Lua script, we claim that time is * blocked to when the Lua script started. This way a key can expire * only the first time it is accessed and not in the middle of the * script execution, making propagation to slaves / AOF consistent. * See issue #1525 on Github for more information. */ now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime(); /* If we are running in the context of a slave, return ASAP: * the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will * send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys. * * Still we try to return the right information to the caller, * that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if * we think the key is expired at this time. */ if (server.masterhost != NULL) return now > when; /* Return when this key has not expired */ // 如果还没到期就直接返回 if (now <= when) return 0; /* Delete the key */ server.stat_expiredkeys++; // key过期,是一个写动作,需要传播到 AOF 或者 slaves... propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire); // pub/sub 监控通知 notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED, "expired",key,db->id); // 同步删除或者异步删除, 稍后讨论 return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) : dbSyncDelete(db,key); } /* Return the expire time of the specified key, or -1 if no expire * is associated with this key (i.e. the key is non volatile) */ long long getExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key) { dictEntry *de; /* No expire? return ASAP */ // 查找过期队列, 数据量小 if (dictSize(db->expires) == 0 || (de = dictFind(db->expires,key->ptr)) == NULL) return -1; /* The entry was found in the expire dict, this means it should also * be present in the main dict (safety check). */ serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr) != NULL); // 返回到期时间戳, union 的应用 return dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de); } // 删除过期数据key的两种方式,同步+异步 // db.c, 同步删除, 删除 expires 队列和 dict 数据 /* Delete a key, value, and associated expiration entry if any, from the DB */ int dbSyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) { /* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of * the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */ if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr); if (dictDelete(db->dict,key->ptr) == DICT_OK) { if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key); return 1; } else { return 0; } } // lazyfree.c, 异步删除过期数据, 一看就很复杂 /* Delete a key, value, and associated expiration entry if any, from the DB. * If there are enough allocations to free the value object may be put into * a lazy free list instead of being freed synchronously. The lazy free list * will be reclaimed in a different bio.c thread. */ #define LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD 64 int dbAsyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) { /* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of * the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */ if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr); /* If the value is composed of a few allocations, to free in a lazy way * is actually just slower... So under a certain limit we just free * the object synchronously. */ dictEntry *de = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr); if (de) { robj *val = dictGetVal(de); // 判断删除的数据的影响范围,与 数据类型有关,string为1,hash/set则计算count,list计算length size_t free_effort = lazyfreeGetFreeEffort(val); /* If releasing the object is too much work, let's put it into the * lazy free list. */ if (free_effort > LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD) { // 将相关的数据放入队列中,后台任务慢慢删除 atomicIncr(lazyfree_objects,1,&lazyfree_objects_mutex); bioCreateBackgroundJob(BIO_LAZY_FREE,val,NULL,NULL); // 自身则立即设置为 NULL dictSetVal(db->dict,de,NULL); } } /* Release the key-val pair, or just the key if we set the val * field to NULL in order to lazy free it later. */ if (dictDelete(db->dict,key->ptr) == DICT_OK) { if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key); return 1; } else { return 0; } }
怎么样?是不是有一首歌叫凉凉~
可以说,get操作本身是相当简单的,在无hash冲突前提下,O(1)的复杂度搞定。然而它还要处理过期的数据问题,就不那么简单了。
我们用一个时序图整体体会下get的流程:

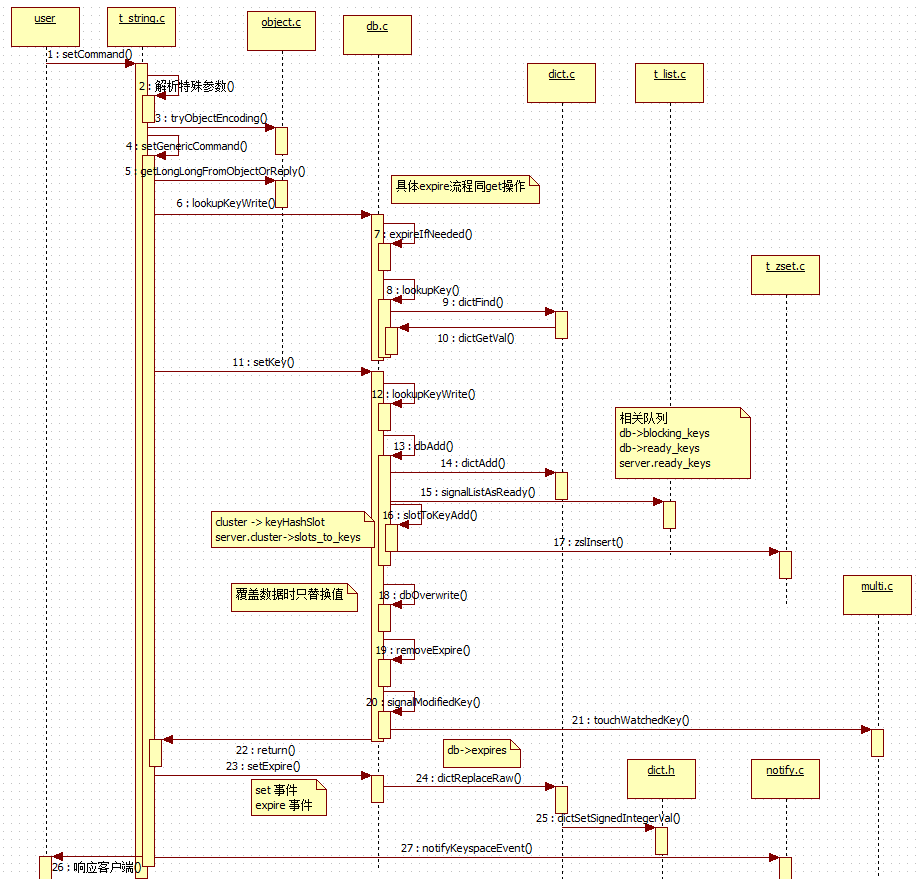
二、setCommand 解析
setCommand 是个写操作,就不是 get 那么简单了。
// t_string.c, set 的所有用法都统一 setCommand, 多个参数共同解析为 flags /* SET key value [NX] [XX] [EX <seconds>] [PX <milliseconds>] */ void setCommand(client *c) { int j; robj *expire = NULL; int unit = UNIT_SECONDS; int flags = OBJ_SET_NO_FLAGS; for (j = 3; j < c->argc; j++) { char *a = c->argv[j]->ptr; robj *next = (j == c->argc-1) ? NULL : c->argv[j+1]; // NX 与 XX 互斥 if ((a[0] == 'n' || a[0] == 'N') && (a[1] == 'x' || a[1] == 'X') && a[2] == '�' && !(flags & OBJ_SET_XX)) { flags |= OBJ_SET_NX; } else if ((a[0] == 'x' || a[0] == 'X') && (a[1] == 'x' || a[1] == 'X') && a[2] == '�' && !(flags & OBJ_SET_NX)) { flags |= OBJ_SET_XX; } // PX 与 EX 互斥 else if ((a[0] == 'e' || a[0] == 'E') && (a[1] == 'x' || a[1] == 'X') && a[2] == '�' && !(flags & OBJ_SET_PX) && next) { flags |= OBJ_SET_EX; unit = UNIT_SECONDS; expire = next; j++; } else if ((a[0] == 'p' || a[0] == 'P') && (a[1] == 'x' || a[1] == 'X') && a[2] == '�' && !(flags & OBJ_SET_EX) && next) { flags |= OBJ_SET_PX; unit = UNIT_MILLISECONDS; expire = next; j++; } else { addReply(c,shared.syntaxerr); return; } } // 尝试压缩 value 值以节省空间 (原始命令: set key value) c->argv[2] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[2]); setGenericCommand(c,flags,c->argv[1],c->argv[2],expire,unit,NULL,NULL); } // object.c, 压缩字符串 /* Try to encode a string object in order to save space */ robj *tryObjectEncoding(robj *o) { long value; sds s = o->ptr; size_t len; /* Make sure this is a string object, the only type we encode * in this function. Other types use encoded memory efficient * representations but are handled by the commands implementing * the type. */ serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,o,o->type == OBJ_STRING); /* We try some specialized encoding only for objects that are * RAW or EMBSTR encoded, in other words objects that are still * in represented by an actually array of chars. */ if (!sdsEncodedObject(o)) return o; /* It's not safe to encode shared objects: shared objects can be shared * everywhere in the "object space" of Redis and may end in places where * they are not handled. We handle them only as values in the keyspace. */ if (o->refcount > 1) return o; /* Check if we can represent this string as a long integer. * Note that we are sure that a string larger than 21 chars is not * representable as a 32 nor 64 bit integer. */ len = sdslen(s); // 针对小于21个字符串的字符,尝试转为 long 型 if (len <= 21 && string2l(s,len,&value)) { /* This object is encodable as a long. Try to use a shared object. * Note that we avoid using shared integers when maxmemory is used * because every object needs to have a private LRU field for the LRU * algorithm to work well. */ if ((server.maxmemory == 0 || (server.maxmemory_policy != MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_LRU && server.maxmemory_policy != MAXMEMORY_ALLKEYS_LRU)) && value >= 0 && value < OBJ_SHARED_INTEGERS) { decrRefCount(o); incrRefCount(shared.integers[value]); return shared.integers[value]; } else { if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_RAW) sdsfree(o->ptr); o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_INT; o->ptr = (void*) value; return o; } } /* If the string is small and is still RAW encoded, * try the EMBSTR encoding which is more efficient. * In this representation the object and the SDS string are allocated * in the same chunk of memory to save space and cache misses. */ // 44 if (len <= OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT) { robj *emb; if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR) return o; // 使用 EMBSTR 编码转换,实际就是同一个 s 返回 emb = createEmbeddedStringObject(s,sdslen(s)); decrRefCount(o); return emb; } /* We can't encode the object... * * Do the last try, and at least optimize the SDS string inside * the string object to require little space, in case there * is more than 10% of free space at the end of the SDS string. * * We do that only for relatively large strings as this branch * is only entered if the length of the string is greater than * OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT. */ if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_RAW && sdsavail(s) > len/10) { o->ptr = sdsRemoveFreeSpace(o->ptr); } /* Return the original object. */ return o; } // sds.c, 去除无用空间占用 /* Reallocate the sds string so that it has no free space at the end. The * contained string remains not altered, but next concatenation operations * will require a reallocation. * * After the call, the passed sds string is no longer valid and all the * references must be substituted with the new pointer returned by the call. */ sds sdsRemoveFreeSpace(sds s) { void *sh, *newsh; // s[-1] 指针不越界, 它是在新建一个 sds 对象时,在该指针前一位写入的值,确定sds类型 char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK; int hdrlen; size_t len = sdslen(s); // sdsHdrSize: sds头部大小 sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype); type = sdsReqType(len); hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type); if (oldtype==type) { newsh = s_realloc(sh, hdrlen+len+1); if (newsh == NULL) return NULL; s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen; } else { newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+len+1); if (newsh == NULL) return NULL; memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1); s_free(sh); s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen; s[-1] = type; sdssetlen(s, len); } sdssetalloc(s, len); return s; } // t_string.c, expire 为超时时间设置 void setGenericCommand(client *c, int flags, robj *key, robj *val, robj *expire, int unit, robj *ok_reply, robj *abort_reply) { long long milliseconds = 0; /* initialized to avoid any harmness warning */ if (expire) { // 解析 expire 到 milliseconds 中 if (getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(c, expire, &milliseconds, NULL) != C_OK) return; if (milliseconds <= 0) { addReplyErrorFormat(c,"invalid expire time in %s",c->cmd->name); return; } if (unit == UNIT_SECONDS) milliseconds *= 1000; } // 语法限制检测, NX 要求不存在, XX 要求存在 if ((flags & OBJ_SET_NX && lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key) != NULL) || (flags & OBJ_SET_XX && lookupKeyWrite(c->db,key) == NULL)) { addReply(c, abort_reply ? abort_reply : shared.nullbulk); return; } // 切实存储 kv setKey(c->db,key,val); server.dirty++; // 设置超时 if (expire) setExpire(c->db,key,mstime()+milliseconds); // 通知pub/sub变更 notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_STRING,"set",key,c->db->id); // 通知expire事件 if (expire) notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC, "expire",key,c->db->id); addReply(c, ok_reply ? ok_reply : shared.ok); } // object.c, int getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(client *c, robj *o, long long *target, const char *msg) { long long value; if (getLongLongFromObject(o, &value) != C_OK) { if (msg != NULL) { addReplyError(c,(char*)msg); } else { addReplyError(c,"value is not an integer or out of range"); } return C_ERR; } *target = value; return C_OK; } // object.c, int getLongLongFromObject(robj *o, long long *target) { long long value; if (o == NULL) { value = 0; } else { serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,o,o->type == OBJ_STRING); // 将字符串转换为 long 型,得到超时时间 if (sdsEncodedObject(o)) { if (strict_strtoll(o->ptr,&value) == C_ERR) return C_ERR; } else if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INT) { value = (long)o->ptr; } else { serverPanic("Unknown string encoding"); } } if (target) *target = value; return C_OK; }
看完了超时及各标识位的解析,及set框架流程,我们来看下具体核心的kv存储: setKey(), setExpire();
// db.c, set kv /* High level Set operation. This function can be used in order to set * a key, whatever it was existing or not, to a new object. * * 1) The ref count of the value object is incremented. * 2) clients WATCHing for the destination key notified. * 3) The expire time of the key is reset (the key is made persistent). */ void setKey(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) { // 先查找,再更新 if (lookupKeyWrite(db,key) == NULL) { // 新增 kv dbAdd(db,key,val); } else { // 覆盖 kv dbOverwrite(db,key,val); } // 增加 value 的引用计数 incrRefCount(val); // 新增的元素,移出过期队列 removeExpire(db,key); signalModifiedKey(db,key); } robj *lookupKeyWrite(redisDb *db, robj *key) { // 先尝试过期处理,再查找db (hash 查找 db->dic) expireIfNeeded(db,key); return lookupKey(db,key); } // db.c, 添加kv /* Add the key to the DB. It's up to the caller to increment the reference * counter of the value if needed. * * The program is aborted if the key already exists. */ void dbAdd(redisDb *db, robj *key, robj *val) { sds copy = sdsdup(key->ptr); // 添加到 db->dict 中 int retval = dictAdd(db->dict, copy, val); serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,retval == C_OK); // list 类型的数据,进行特殊处理(阻塞) if (val->type == OBJ_LIST) signalListAsReady(db, key); // 集群添加 if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyAdd(key); } // db.c /* Slot to Key API. This is used by Redis Cluster in order to obtain in * a fast way a key that belongs to a specified hash slot. This is useful * while rehashing the cluster. */ void slotToKeyAdd(robj *key) { // hash 定位 slot, 下面我们简单看下该算法 unsigned int hashslot = keyHashSlot(key->ptr,sdslen(key->ptr)); sds sdskey = sdsdup(key->ptr); // 添加key 到 server.cluster->slots_to_keys 的 跳表中 zslInsert(server.cluster->slots_to_keys,hashslot,sdskey); } // cluster.c, slot 定位算法, 其实就是 crc16算法与上 0x3FFF,该算法决定了 slot 最多只能有 16383 个 /* We have 16384 hash slots. The hash slot of a given key is obtained * as the least significant 14 bits of the crc16 of the key. * * However if the key contains the {...} pattern, only the part between * { and } is hashed. This may be useful in the future to force certain * keys to be in the same node (assuming no resharding is in progress). */ unsigned int keyHashSlot(char *key, int keylen) { int s, e; /* start-end indexes of { and } */ for (s = 0; s < keylen; s++) if (key[s] == '{') break; /* No '{' ? Hash the whole key. This is the base case. */ if (s == keylen) return crc16(key,keylen) & 0x3FFF; /* '{' found? Check if we have the corresponding '}'. */ for (e = s+1; e < keylen; e++) if (key[e] == '}') break; /* No '}' or nothing betweeen {} ? Hash the whole key. */ if (e == keylen || e == s+1) return crc16(key,keylen) & 0x3FFF; /* If we are here there is both a { and a } on its right. Hash * what is in the middle between { and }. */ return crc16(key+s+1,e-s-1) & 0x3FFF; } // db.c, 设置key的超时标识 void setExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key, long long when) { dictEntry *kde, *de; /* Reuse the sds from the main dict in the expire dict */ kde = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr); serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,kde != NULL); // 将需要超时检测的 key 添加到 db->expires 队列中 de = dictReplaceRaw(db->expires,dictGetKey(kde)); // 设置超时时间为 when dictSetSignedIntegerVal(de,when); } // dict.h #define dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry, _val_) do { entry->v.s64 = _val_; } while(0)
总体来说,set操作会分为几步:
1. 判断出多重参数,如是否是NX/EX/PX/XX, 是否超时设置;
2. 编码转换数据, 如将字符串转换为long型;
3. 解析超时字段;
4. set kv, 添加或者覆盖数据库值, 同时清理过期队列;
5. 设置超时时间;
6. 触发事件监听;
7. 响应客户端;
最后,我们以set的整个时序图作为结尾,也让我们明白一点,不是每个hello world 都很简单: