使用 Set
Set用于存储不重复的元素集合,它主要提供以下几个方法:
-
将元素添加进Set
:boolean add(E e) -
将元素从Set
删除:boolean remove(Object e) -
判断是否包含元素:boolean contains(Object e)
一个示例:
public class SetMain {
public static void main(String[] args){
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
System.out.println(set.add("abc")); // true
System.out.println(set.add("xyz")); // true
System.out.println(set.add("xyz")); // false,添加失败,因为元素已存在
System.out.println(set.contains("abc")); // true
System.out.println(set.contains("abcd")); // false,元素不存在
System.out.println(set.remove("xyz")); // true
System.out.println(set.remove("hello")); // false,元素不存在
System.out.println(set);
}
}
Set实际上相当于只存储key、不存储value的Map。我们经常用Set用于去除重复元素。
最常用的Set实现类是HashSet,实际上,HashSet仅仅是对HashMap的一个简单封装,它的核心代码如下:
public class HashSet<E> implements Set<E> {
// 持有一个HashMap:
private HashMap<E, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 放入HashMap的value:
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT) == null;
}
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o) == PRESENT;
}
}
Set接口并不保证有序,而SortedSet接口则保证元素是有序的:
-
HashSet是无序的,因为它实现了Set接口,并没有实现SortedSet接口;
-
TreeSet是有序的,因为它实现了SortedSet接口。
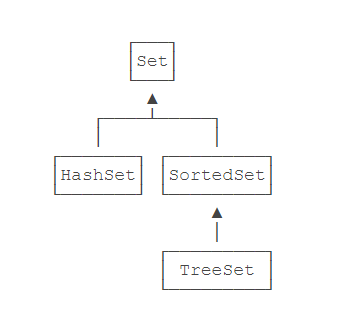
HashSet 与 TreeSet 之间的区别,十分类似与 HashMap 与 TreeMap 之间的区别。
先来看 HashSet 的输出:
public static void main(String[] args){
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("apple");
set.add("pear");
set.add("banana");
for (String s:set){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
输出:
banana
apple
pear
再看 TreeSet 的输出:
public static void main(String[] args){
TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("apple");
set.add("pear");
set.add("banana");
for (String s:set){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
输出:
// 按首字母排序输出
apple
banana
pear
使用TreeSet和使用TreeMap的要求一样,添加的元素必须正确实现Comparable接口。
每天学习一点点,每天进步一点点。