一、Python循环语句
程序一般情况下是按照顺序执行的
编程语言提供了各种控制结构,允许更复杂的执行路径
Python中的循环语句有for和while但没有do while
循环语句允许我们执行一个语句或语句组多次,下面是大多数编程语言中循环语句的一般形式:
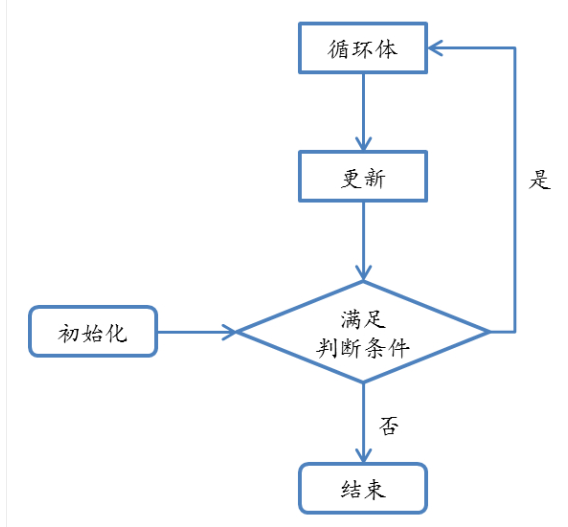
Python提供了for循环和while循环(在Python中没有do while循环)
| 循环类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| [while 循环] "Python WHILE 循环") | 在给定的判断条件为 true 时执行循环体,否则退出循环体。 |
| [for 循环] " Python FOR 循环") | 重复执行语句 |
| [嵌套循环]"Python 循环全套") | 你可以在while循环体中嵌套for循环 |
二、 Python While循环语句
Python编程中while语句用于循环执行程序,即在某条件下,循环执行某段程序,以处理需要重复处理的相同任务,基本形式如下:
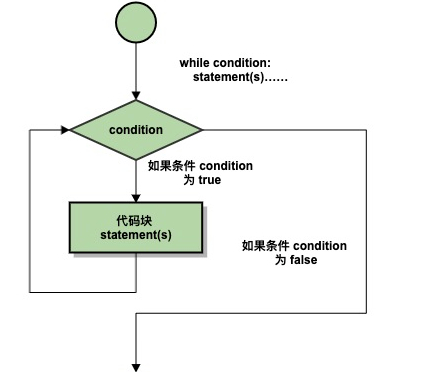
Gif演示Python while语句执行过程

复杂一点

Example1
count = 0
while (count < 9):
print(count,"The count is:"),count
count = count + 1
print('Good bye!')
0 The count is:
1 The count is:
2 The count is:
3 The count is:
4 The count is:
5 The count is:
6 The count is:
7 The count is:
8 The count is:
Good bye!
While 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令continue,breadk来跳过循环,continue用于跳过该次循环,break则用于退出循环,此外“判断条件”还可以是个常值,表示循环必定成立,具体用法如下:
count = 0
while (count < 9):
count = count + 1
if count%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出
continue
print(count)
print('Good bye!')
count = 0
while (count < 9):
count = count + 1
if count > 4: # 当count大于4跳出循环.
break
print(count)
print('Good bye!')
无限循环
var = 1
while var == 1:
num = input('Enter a number ')
print("You enterd:",num)
print("Good bye!")
You enterd:
Enter a number
You enterd:
Enter a number
You enterd:
Enter a number
You enterd:
Enter a number
You enterd:
Enter a number
循环使用else语句
count = 0
while count < 5:
print (count, " is less than 5")
count = count + 1
else:
print (count, " is not less than 5")
0 is less than 5
1 is less than 5
2 is less than 5
3 is less than 5
4 is less than 5
5 is not less than 5
简单语句组
flag = 1
while (flag): print ('Given flag is really true!')
print("Good bye!")
三、For循环
Python for循环可以便利任何序列的项目,如一个列表或者一个字符串
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)

for letter in 'python':
print('当前字母:',letter)
fruits = ['banana','apple','mango']
for fruits in fruits:
print ('当前水果:',fruits)
print("Good bye!")
# 当前实例运行结果为:
当前字母: p
当前字母: y
当前字母: t
当前字母: h
当前字母: o
当前字母: n
当前水果: banana
当前水果: apple
当前水果: mango
Good bye!
3.1 通过序列索引迭代**
fruits = ['banana','apple','mango']
for index in range(len(fruits)):
print ('当前水果:',fruits[index])
print("Good bye!")
当前水果: banana
当前水果: apple
当前水果: mango
Good bye!
# 以上实例我们使用了内置函数len()和range()函数len()返回列表的长度,即元素的个数,range返回一个序列的数.
循环使用else语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这样的意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有区别,else 中的语句会在循环正常执行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下执行,while … else 也是一样。
3.2 Range()函数
- 如果你需要遍历数字序列,可以使用内置range()函数,他会生成数列,例如
for i in range(5):
print(i)
# 你也可以使用range指定区间的值:
for i in range(5,9):
print(i)
5
6
7
8
# 也可以使range以指定数字开始并指定不同的增量(甚至可以是负数,有时这也叫做'步长'):
for i in range(0,10,2):
print(i)
0
2
4
6
8
# 也可以结合range()和len()函数遍历一个序列的索引,如下:
a = ['Google','Baidu','360','JinDong']
for i in range(len(a)):
print(i,a[i])
0 Google
1 Baidu
2 360
3 JinDong
# 还可以使用range()函数来创建一个列表
a=list(range(5))
print(a)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
四、Break和continue语句及循环中的else子句
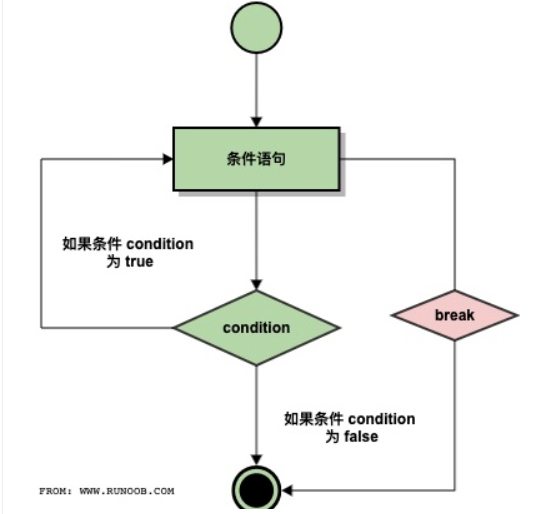
Break执行流程图
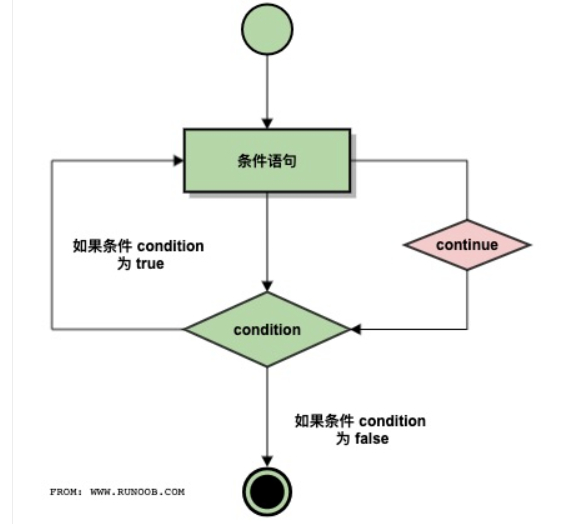
Continue执行流程图
代码执行过程
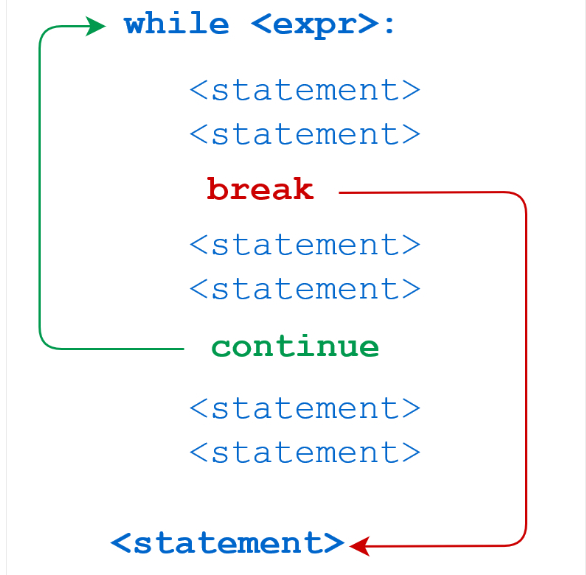
Break语句可以跳出for和while的循环体,如果你从for或while循环中终止,任何对应的else块将不执行
Continue语句被用来告诉Python跳出当前循环块中的剩余语句,然后继续下一轮循环
Example
While中使用Break
n = 5
while n > 0:
n -= 1
if n == 2:
break
print(n)
print('循环结束')
4
3
循环结束
Whie中使用continue
n = 5
while n > 0:
n -= 1
if n == 2:
continue
print(n)
print('循环结束')
4
3
1
0
循环结束
for 循环使用break和continue
for i in 'YouMen':
if i == 'M':
break
print('当前字母为:',i)
print('----------------------')
for i in 'YouMen':
if i == 'M':
continue
print('当前字母为:',i)
当前字母为: Y
当前字母为: o
当前字母为: u
----------------------
当前字母为: Y
当前字母为: o
当前字母为: u
当前字母为: e
当前字母为: n
五、Python Pass语句
Python pass是空语句,是为了保持程序结构的完整性
Pass不做任何事情,一般用作占位语句
最小的类
Python语言pass语句语法格式如下
pass
# Example
for letter in 'python':
if letter == 'h':
pass
print ('这是pass块')
print("当前字母:",letter)
print("Good bye!")
# 上面实例运行结果为:
当前字母: p
当前字母: y
当前字母: t
这是pass块
当前字母: h
当前字母: o
当前字母: n
Good bye!
Exapmle最小的类
class MyEmptyClass:
pass
Example1 打印一个质数
for num in range(10,20):
for i in range(2,num):
if num%i == 0:
j=num/i
print("%d 等于%d * %d" % (num,i,j))
break
else:
print(num)
10 等于2 * 5
11
12 等于2 * 6
13
14 等于2 * 7
15 等于3 * 5
16 等于2 * 8
17
18 等于2 * 9
19
Example2 计算1000以内被7整除的前20个数
count = 0
for i in range(0,1000,7):
print(i)
count += 1
if count >= 20:
break
Example3 给定一个不超过5位的正整数,判断其有几位,依次打印个数,十位数,百位数,千位数.万位数
打印等腰三角形
rows = 10
for i in range(0, rows):
for k in range(0, rows - i):
print ("*",end="") #注意这里的",",一定不能省略,可以起到不换行的作用
k += 1
i += 1
print ()
打印空心菱形
rows = 10
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(rows - i):
print(" ", end=" ")
j += 1
for k in range(2 * i - 1):
if k == 0 or k == 2 * i - 2:
print("*", end=" ")
else:
print(" ", end=" ")
k += 1
print ("
")
i += 1
# 菱形的下半部分
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(i):
# (1,rows-i)
print(" ", end=" ")
j += 1
for k in range(2 * (rows - i) - 1):
if k == 0 or k == 2 * (rows - i) - 2:
print("*", end=" ")
else:
print(" ", end=" ")
k += 1
print("
")
i += 1