线程池
为什么要用线程池:
1.减少了创建和销毁线程的次数,每个工作线程都可以被重复利用,可执行多个任务。
2.调整线程池中工作线线程的数目,防止因为消耗过多的内存。
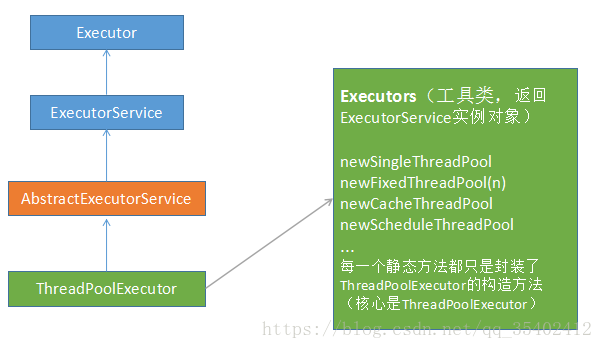
线程池的接口如下:
使用:我们只需要从Executors静态工厂方法获取所需要的线程池即可。
ThreadPoolExecutor的构建参数
/**
* Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial
* parameters and default thread factory.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even
* if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are
* executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable}
* tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br>
* {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br>
* {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br>
* {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue}
* or {@code handler} is null
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}参数解释
corePoolSize - 池中所保存的线程数,包括空闲线程。
maximumPoolSize-池中允许的最大线程数。
keepAliveTime - 当线程数大于核心时,此为终止前多余的空闲线程等待新任务的最长时间。
unit - keepAliveTime 参数的时间单位。
workQueue - 执行前用于保持任务的队列。此队列仅保持由 execute方法提交的 Runnable任务。
threadFactory - 执行程序创建新线程时使用的工厂。
handler - 由于超出线程范围和队列容量而使执行被阻塞时所使用的处理程序。
常见的四种创建线程池的方法:
1. newSingleThreadExecutor
创建一个单线程的线程池。这个线程池只有一个线程在工作,也就是相当于单线程串行执行所有任务。如果这个唯一的线程因为异常结束,那么会有一个新的线程来替代它。此线程池保证所有任务的执行顺序按照任务的提交顺序执行。
2.newFixedThreadPool
创建固定大小的线程池。每次提交一个任务就创建一个线程,直到线程达到线程池的最大大小。线程池的大小一旦达到最大值就会保持不变,如果某个线程因为执行异常而结束,那么线程池会补充一个新线程。
3. newCachedThreadPool(推荐使用)
创建一个可缓存的线程池。如果线程池的大小超过了处理任务所需要的线程,那么就会回收部分空闲(60秒不执行任务)的线程,当任务数增加时,此线程池又可以智能的添加新线程来处理任务。此线程池不会对线程池大小做限制,线程池大小完全依赖于操作系统(或者说JVM)能够创建的最大线程大小。
4.newScheduledThreadPool
创建一个大小无限的线程池。此线程池支持定时以及周期性执行任务的需求。