任意门:http://codeforces.com/contest/652/problem/D
D. Nested Segments
You are given n segments on a line. There are no ends of some segments that coincide. For each segment find the number of segments it contains.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of segments on a line.
Each of the next n lines contains two integers li and ri ( - 109 ≤ li < ri ≤ 109) — the coordinates of the left and the right ends of the i-th segment. It is guaranteed that there are no ends of some segments that coincide.
Print n lines. The j-th of them should contain the only integer aj — the number of segments contained in the j-th segment.
4
1 8
2 3
4 7
5 6
3
0
1
0
3
3 4
1 5
2 6
0
1
1
题意概括:
有 N 个区间,求每个区间有多少个存在的子区间。
例如第一个样例:
4
1 8
2 3
4 7
5 6
【1,8】有 3 个,他们发别是 【2,3】,【4,7】,【5,6】;
【2,3】没有;
【4,7】有 1 个,【5,6】;【5,6】没有;
注意:
一、只是有部分相交的区间不在考虑范围内,模拟一下样例二就明白了。
3
3 4
1 5
2 6
二、端点不重合,这个很重要!!!
解题思路:
由题意可知这是离线操作,涉及区间查询和修改,线段树或树状数组。
其次数据范围不小,要考虑离散化。
这道题如何离散化?
二维 pair 储存原数据 + vector 排序&&去重;
树状数组要维护一些什么呢?我们怎么记录区间内有几个符合条件的线段呢?
一开始自己模拟样例一后是想到标记左端点,然后求其区间和,刚好区间和 减去他自己就是答案,不够这种想法是很片面的。
因为有只有部分相交的情况:例如样例二
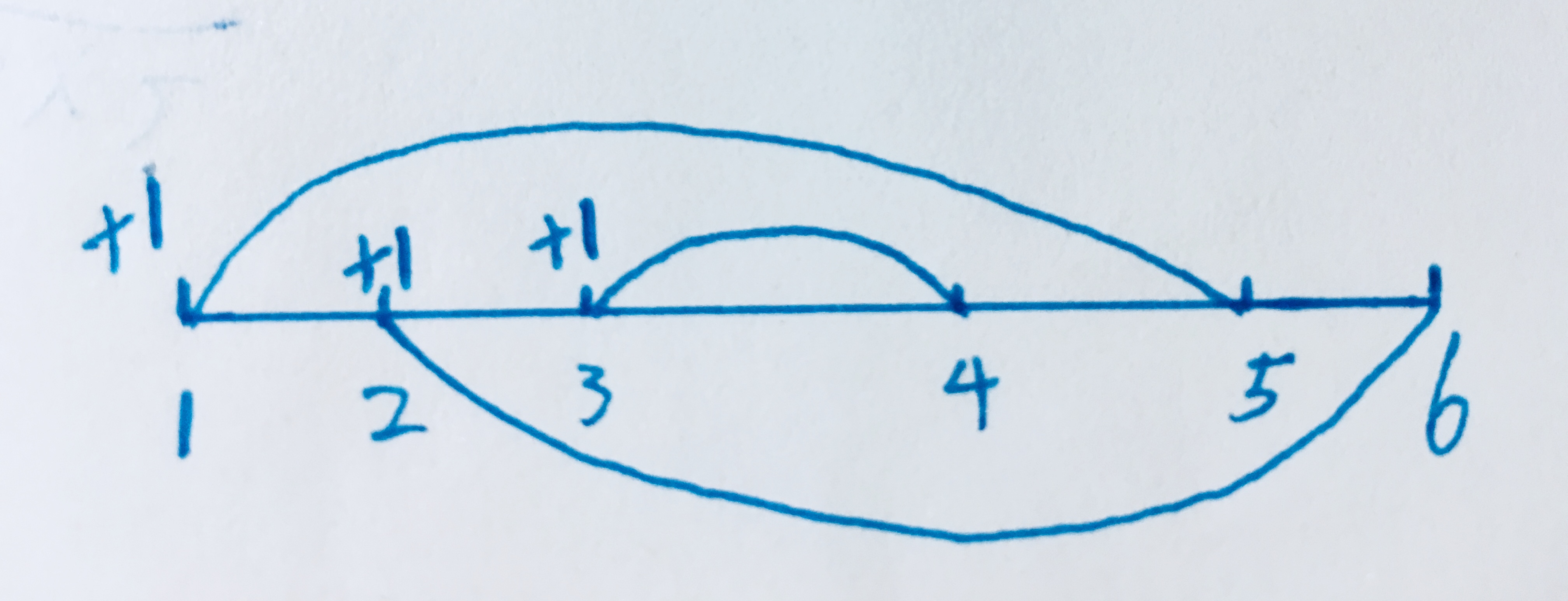
【1,5】= 1+1+1-1 = 2 答案错误(把部分相交的考虑进去了)
但这道题的解决方法就是标记一个端点,如果标记左端点则按右端点顺序遍历,如果标记右端点则按左端点顺序遍历。
固定其中一个端点后求区间和,并且在查询完毕之后要消除当前区间对后面区间的影响,因为我们按照其中一个端点的顺序遍历,如果不消除当前固定端点区间的影响,那么后面就会有部分相交了。
例如说我标记左端点,按照右端点的顺序遍历,如果我遍历右端点为 6 之后没有把【2, 6】的影响消除,那么当我遍历到右端点为 5 的时候就会把只有部分相交的区间也记录进去了。
解决了以上两个大问题,剩下的就是代码实现的事了。
AC code:

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <cmath> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <vector> 8 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 9 #define LL long long 10 using namespace std; 11 const int MAXN = 4e5+10; 12 13 int t[MAXN]; //树状数组 14 pair< pair<int, int>, int> p[MAXN]; //记录区间左右端点和 15 vector<int> Q; 16 map<int, int> mmp; 17 int ans[MAXN]; 18 int N; 19 20 int lowbit(int x){return x&(-x);} 21 void Update(int x, int val) 22 { 23 for(int i = x; i < MAXN; i+=lowbit(i)){ 24 t[i]+=val; 25 } 26 } 27 28 int query(int x) 29 { 30 int res = 0; 31 for(int i = x; i; i-=lowbit(i)) 32 res+=t[i]; 33 return res; 34 } 35 36 int main() 37 { 38 scanf("%d", &N); 39 for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){ 40 scanf("%d %d", &p[i].first.first, &p[i].first.second); 41 Q.push_back(p[i].first.first); 42 Q.push_back(p[i].first.second); 43 p[i].second = i; 44 } 45 sort(Q.begin(), Q.end()); //离散化 46 Q.erase(unique(Q.begin(),Q.end()), Q.end()); //去重 47 for(int i = 0; i < Q.size(); i++){ 48 mmp[Q[i]] = i+1; //新旧端点的映射关系 49 } 50 for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){ 51 p[i].first.first = mmp[p[i].first.first]; //更新区间的左右端点 52 p[i].first.second = mmp[p[i].first.second]; 53 Update(p[i].first.second, 1); //更新区间!!!精妙之处在于标记的该区间的其中一个端点!!!(题目条件端点不重合) 54 } 55 sort(p+1, p+1+N); //排序等级:左端点 > 右端点 > 区间编号 56 for(int i = 1, j = 1; i < MAXN; i++){ //遍历左端点,注意范围是 1~MAXN 57 while(j <= N && p[j].first.first == i){ //左端点相同的区间 58 ans[p[j].second] = query(p[j].first.second); 59 Update(p[j].first.second, -1); //消除当前区间对后面区间的影响 60 j++; 61 } 62 if(j == N+1) break; //遍历完成 63 } 64 for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) 65 printf("%d ", ans[i]-1); 66 return 0; 67 }
