第一:安装前准备:
声明我用的是ubuntu 16.04的系统
1.修改主机名,并保证两台机器可以互相ping同主机名
ip1 master_hostname
ip2 slave_hostname
第二:安装
服务器安装 yum install salt-master -y
客户端安装 yum install salt-minion -y
ubuntu16.04的安装完会自动启动
第三:配置:
更改minion端的
master: master的ip地址(注意: “:后面有一个空格”)
第四:认证:
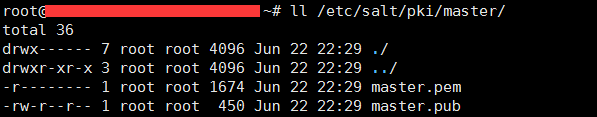
master创建的key:
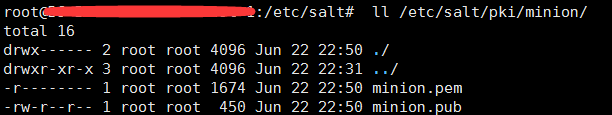
minion创建的key:
等待认证的key:

查看等待同意的key:

执行接受操作:

查看key的位置,原本在pre下面,现在跑到了minion下面了

以上是简单的查看了key的认证,下面我们看下salt-key的详细用法:

# salt-key -h Usage: salt-key [options] Salt key is used to manage Salt authentication keys Options: --version show program's version number and exit --versions-report show program's dependencies version number and exit -h, --help show this help message and exit --saltfile=SALTFILE Specify the path to a Saltfile. If not passed, one will be searched for in the current working directory -c CONFIG_DIR, --config-dir=CONFIG_DIR Pass in an alternative configuration directory. Default: /etc/salt -u USER, --user=USER Specify user to run salt-key --hard-crash Raise any original exception rather than exiting gracefully Default: False -q, --quiet Suppress output -y, --yes Answer Yes to all questions presented, defaults to False --rotate-aes-key=ROTATE_AES_KEY Setting this to False prevents the master from refreshing the key session when keys are deleted or rejected, this lowers the security of the key deletion/rejection operation. Default is True. Logging Options: Logging options which override any settings defined on the configuration files. --log-file=LOG_FILE Log file path. Default: /var/log/salt/key. --log-file-level=LOG_LEVEL_LOGFILE Logfile logging log level. One of 'all', 'garbage', 'trace', 'debug', 'profile', 'info', 'warning', 'error', 'critical', 'quiet'. Default: 'warning'. Output Options: Configure your preferred output format --out=OUTPUT, --output=OUTPUT Print the output from the 'salt-key' command using the specified outputter. The builtins are 'key', 'yaml', 'overstatestage', 'highstate', 'newline_values_only', 'pprint', 'txt', 'raw', 'virt_query', 'compact', 'json', 'nested', 'quiet', 'no_return'. --out-indent=OUTPUT_INDENT, --output-indent=OUTPUT_INDENT Print the output indented by the provided value in spaces. Negative values disables indentation. Only applicable in outputters that support indentation. --out-file=OUTPUT_FILE, --output-file=OUTPUT_FILE Write the output to the specified file --out-file-append, --output-file-append Append the output to the specified file --no-color, --no-colour Disable all colored output --force-color, --force-colour Force colored output --state-output=STATE_OUTPUT, --state_output=STATE_OUTPUT Override the configured state_output value for minion output. One of full, terse, mixed, changes or filter. Default: full. --state-verbose=STATE_VERBOSE, --state_verbose=STATE_VERBOSE Override the configured state_verbose value for minion output. Set to True or FalseDefault: True Actions: -l ARG, --list=ARG List the public keys. The args "pre", "un", and "unaccepted" will list unaccepted/unsigned keys. "acc" or "accepted" will list accepted/signed keys. "rej" or "rejected" will list rejected keys. "den" or "denied" will list denied keys. Finally, "all" will list all keys. -L, --list-all List all public keys. (Deprecated: use "--list all") #查看认证信息 -a ACCEPT, --accept=ACCEPT Accept the specified public key (use --include-all to match rejected keys in addition to pending keys). Globs are supported. -A, --accept-all Accept all pending keys #接受全部的pending 状态的minion -r REJECT, --reject=REJECT Reject the specified public key (use --include-all to match accepted keys in addition to pending keys). Globs are supported. -R, --reject-all Reject all pending keys --include-all Include non-pending keys when accepting/rejecting -p PRINT, --print=PRINT Print the specified public key -P, --print-all Print all public keys -d DELETE, --delete=DELETE Delete the specified key. Globs are supported. -D, --delete-all Delete all keys #删除指定key -f FINGER, --finger=FINGER Print the specified key's fingerprint -F, --finger-all Print all keys' fingerprints Key Generation Options: --gen-keys=GEN_KEYS Set a name to generate a keypair for use with salt --gen-keys-dir=GEN_KEYS_DIR Set the directory to save the generated keypair, only works with "gen_keys_dir" option; default=. --keysize=KEYSIZE Set the keysize for the generated key, only works with the "--gen-keys" option, the key size must be 2048 or higher, otherwise it will be rounded up to 2048; ; default=2048 --gen-signature Create a signature file of the masters public-key named master_pubkey_signature. The signature can be send to a minion in the masters auth-reply and enables the minion to verify the masters public-key cryptographically. This requires a new signing-key- pair which can be auto-created with the --auto-create parameter --priv=PRIV The private-key file to create a signature with --signature-path=SIGNATURE_PATH The path where the signature file should be written --pub=PUB The public-key file to create a signature for --auto-create Auto-create a signing key-pair if it does not yet exist You can find additional help about salt-key issuing "man salt-key" or on http://docs.saltstack.com #更多查看官网
第五:saltstack远程执行命令:
1.测试与minion的通信是否正常

出现如上图所示的情况,解决办法:
/etc/salt/master的配置文件中,将file_ignore_glob组的注释全部打开,重启master即可

2.远程执行命令:
salt '*' cmd.run 'ls -l /etc'

3.查看磁盘信息:

# salt '*' disk.usage host-minion: ---------- /: ---------- 1K-blocks: 94326644 available: 87738788 capacity: 2% filesystem: /dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-root used: 1773216 /boot: ---------- 1K-blocks: 482922 available: 399773 capacity: 13% filesystem: /dev/sda1 used: 58215 /dev: ---------- 1K-blocks: 4067252 available: 4067252 capacity: 0% filesystem: udev used: 0 /dev/shm: ---------- 1K-blocks: 4087280 available: 4087268 capacity: 1% filesystem: tmpfs used: 12 /run: ---------- 1K-blocks: 817460 available: 773752 capacity: 6% filesystem: tmpfs used: 43708 /run/lock: ---------- 1K-blocks: 5120 available: 5120 capacity: 0% filesystem: tmpfs used: 0 /run/user/1000: ---------- 1K-blocks: 817460 available: 817460 capacity: 0% filesystem: tmpfs used: 0 /sys/fs/cgroup: ---------- 1K-blocks: 4087280 available: 4087280 capacity: 0% filesystem: tmpfs used: 0
4.查看网络信息 salt '*' network.interfaces
5.查看帮助文档信息 salt '*' sys.doc
6.匹配相关minion:
salt -G 'os:Ubuntu' test.ping
salt -E 'minion[0-9]' test.ping
salt -L 'minion1,minion2' test.ping
更多模块的用法请查看官网文档:
https://docs.saltstack.com
第六:列举几个常用的模块:
列出当前版本支持的模块:

# salt '*' sys.list_modules host: - acl - aliases - alternatives - archive - artifactory - at - beacons - bigip - blockdev - btrfs - buildout - cloud - cmd - composer - config - consul - container_resource - cp - cpan - cron - data - debconf - defaults - devmap - dig - disk - django - dnsmasq - dnsutil - drbd - elasticsearch - environ - etcd - event - extfs - file - gem - genesis - git - grains - group - grub - hashutil - hg - hipchat - hosts - http - img - incron - ini - introspect - ip - iptables - jboss7 - jboss7_cli - key - keyboard - kmod - locale - locate - logrotate - lowpkg - lvm - match - mine - modjk - mount - mysql - nagios_rpc - network - node - nspawn - openstack_config - pagerduty - pagerduty_util - partition - pillar - pip - pkg - pkg_resource - pkgbuild - publish - pushover - pyenv - raid - random - random_org - rbenv - rest_sample_utils - ret - rsync - runit - rvm - s3 - saltutil - schedule - scsi - sdb - seed - serverdensity_device - service - shadow - slack - slsutil - smbios - smtp - splay - sqlite3 - ssh - state - status - supervisord - sys - sysctl - syslog_ng - system - temp - test - timezone - tls - udev - uptime - user - vbox_guest - virtualenv - xfs - zfs
test.ping的api调用方式:
import salt.client client = salt.client.LocalClient() ret = client.cmd('*','test.ping') print(ret)
cmd模块:远程执行命令(上面已经列出)
#获取所欲被控主机的内存使用情况
salt '*' cmd.run 'free -m'
API调用方式:
import salt.client client = salt.client.LocalClient() free = client.cmd('*','cmd.run',['free -m']) print(free)
crontab 模块
#为指定被控主机、root用户添加计划任务/usr/local/weekly任务 salt '*' cron.set_job root '*' '*' '*' '*' 1 /usr/local/weekly #删除指定被控主机、root用户crontab的/usr/local/weekly任务 salt '*' cron.rm_job root /usr/local/weekly
crontab的api调用:
增加crontab方式: client.cmd('*','cron.set_job',['root','*','*','*','*',1,'/usr/local/weekly']) 删除crontab的方式: client.cmd('*','cron.rm_job',['root','/usr/local/weekly'])
file模块:
#校验所有被控主机/etc/fstab文件的md5值是否为xxxxxxxxxxxxx,一致则返回True值 salt '*' file.check_hash /etc/fstab md5:a4e398d752713d5f12880a92c7dfd557 #校验所有被控主机文件的加密信息,支持md5、sha1、sha224、shs256、sha384、sha512加密算法 salt '*' file.get_sum /etc/passwd md5 #修改所有被控主机/etc/passwd文件的属组、用户权限、等价于chown root:root /etc/passwd salt '*' file.chown /etc/passwd root root #复制所有被控主机/path/to/src文件到本地的/path/to/dst文件 salt '*' file.copy /path/to/src /path/to/dst #检查所有被控主机/etc目录是否存在,存在则返回True,检查文件是否存在使用file.file_exists方法 salt '*' file.directory_exists /etc #获取所有被控主机/etc/passwd的stats信息 salt '*' file.stats /etc/passwd #获取所有被控主机/etc/passwd的权限mode,如755,644 salt '*' file.get_mode /etc/passwd #修改所有被控主机/etc/passwd的权限mode为0644 salt '*' file.set_mode /etc/passwd 0644 #在所有被控主机创建/opt/test目录 salt '*' file.mkdir /opt/test #将所有被控主机/etc/httpd/httpd.conf文件的LogLevel参数的warn值修改为info salt '*' file.sed /etc/httpd/httpd.conf 'LogLevel warn' 'LogLevel info' #给所有被控主机的/tmp/test/test.conf文件追加内容‘maxclient 100’ salt '*' file.append /tmp/test/test.conf 'maxclient 100' #删除所有被控主机的/tmp/foo文件 salt '*' file.remove /tmp/foo
service服务模块:
#开启(enable)、禁用(disable)nginx开机自启动脚本 salt '*' service.enable nginx salt '*' service.disable nginx #针对nginx服务的reload、restart、start、stop、status操作 salt '*' service.reload nginx salt '*' service.restart nginx salt '*' service.start nginx salt '*' service.stop nginx salt '*' service.status nginx
service的API调用:
client.cmd('*','service.stop',['nginx'])
cp模块:
# cp /opt/getfile.txt /srv/salt/ # salt '*' cp.get_file salt://getfile.txt /opt/getfile.txt salt-client: /opt/getfile.txt
