生物信息学数据分析过程中熟练使用Linux Shell命令可以大大提高工作效率。
1.1 查看文件的前/后n行
-
Linux
下面的命令显示文件名为
filename的文件的前/后5行:12head filename -n5tail filename -n5设置
-n后面的数字,可以指定要查看的行数。如果省略-n参数,则默认显示10行。
另外,-n参数的位置是比较灵活的,而且后面的数值可以加一个空格区分,所以,下面几种形式都是可以的:12345head filenamehead -n5 filenametail -n5 filenamehead filename -n 5tail filename -n 5 -
Mac
Mac下的head/tail命令是BSD平台的实现,-n参数必须在文件名前面,放在文件名后面会被当做一个新的文件名。如果省略-n参数,则默认也显示10行。
下面几种形式都是可以的:1234head -n5 filenametail -n5 filenamehead -n 5 filenametail -n 5 filename
1.2 查看文件的行数
|
1
|
wc -l filename |
上面的命令会把把名为filename文件的行数以及文件名本身一起列出来。有时候我们想要同时看很多个文件的行数。可以使用:
|
1
|
wc -l filename1 filename2 |
这条命令输出为:
|
1
2
3
|
281 filename1281 filename2562 total |
分别为filename1,filename2的行数,以及他们行数的和。当然,也可以直接查看当前文件夹下所有的文件行数:
|
1
|
wc -l * |
1.3 查看文件的列数
在提取完特征之后,检查特征文件的列数是必须要做的,所以查看文件列数的命令也非常常见:
|
1
|
cat filename | awk -F ',' '{print NF}' | head -n1 |
这里假定filename是以,分割的文件,如果是以空格或者别的标记分割的文件,可以自行修改','中的符号。
另外,awk -F ',' '{print NF}'中输出的结果,实际上是每一行的列数,我们假定这里处理的是特征文件,因此每一行的列数都是相同的,所以我们只需要使用head -n1查看第一行的列数就可以了。
1.4 查看序列文件中的序列数
|
1
|
grep -c '>' filename |
因为序列文件中每条序列都是以>开头的,因此统计>的个数就可以知道序列数目。
1.5 文件合并
-
上下合并:
12cat file1 file2 > file3cat file1 file2 file3 > newfile很容易扩展到多个文件合并
-
左右合并
12paste file1 file2 > file3paste file1 file2 file3 > newfile一样可以扩展到多个文件合并。
默认情况下,
paste合并文件之间使用空格或者tab分开,如果你合并的是csv文件,就需要显示指定用,分开:1paste -d "," file1 file2 file3 > newfile
1.6 单个文件去掉重复的行
-
重复的多行只留一行
1sort filename | uniq > newfile -
重复的行全部去掉,只留下文件中的非重复行
1sort filename | uniq -u > newfile
1.7 文件的交集,并集
下面的操作很容易可以扩展到多个文件。
-
文件的并集(重复的行只保留一份)
12cat file1 file2 | sort | uniq > newfilecat file1 file2 file3 | sort | uniq > newfile -
取出两个文件的交集(只留下同时存在于两个文件中的文件)
12cat file1 file2 | sort | uniq -d > newfilecat file1 file2 file3 | sort | uniq -d > newfile -
删除交集,留下其他的行
12cat file1 file2 | sort | uniq -u > newfilecat file1 file2 file3 | sort | uniq -u > newfile
1.7 查看及关闭端口
通常在
tomcat没能正常退出的情况下,8080端口就会被占用,这时就无法重新启动tomcat。因此经常需要查看端口使用情况,并在端口被占用时关闭端口。
在Mac下
-
查看端口
80801lsof -i:8080 -
关闭
80801kill -9 8080
*******************************************************************************
1. 统计fasta文件
grep '>' filename.fasta | wc -l
2. 在文件中的每一行之前加上一个字符串,比如:aaa
sed 's/^/aaa/g' filename.txt > outputfile.txt
3. 遍历整个文件夹,把所有txt文件中的aaa替换成bbb
find . -name '*.txt' | xargs perl -pi -e 's/aaa/bbb/g'
4.其他目录下运行一个软件时候,command no find,如;
[root@node3 bin]# metabing
bash: metabing: command not found
解决方法:
切换到root权限
vim /etc/profile ,添加环境变量: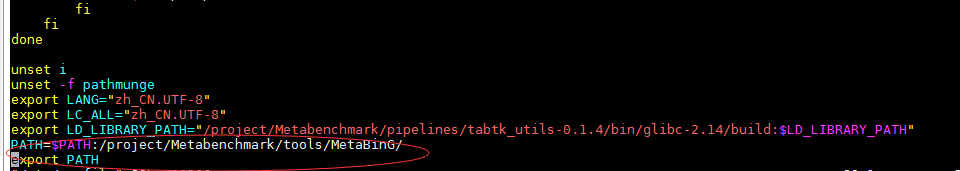
[root@node3 bin]# source /etc/profile
查看效果:
[root@node3 bin]# metabing
Usage: ./metabing <FASTA file> <db>(optional)
success!
5.Linux中我们经常遇到需要批量该文件名字的操作:
[biostack@node3 tmp]$ touch tmp_{1..10}.txt #创建十个空文件
[biostack@node3 tmp]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-10.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-3.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-4.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-5.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-6.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-7.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-8.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 02:31 tmp-9.txt
将当前文件夹中所有的“_”改为“-”
[biostack@node3 tmp]$ find ./ -name "*_*" | while read id; do mv $id ${id/_/-}; done
[biostack@node3 tmp]$ ll
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-1.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-10.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-2.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-3.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-4.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-5.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-6.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-7.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-8.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 biostack users 0 Mar 23 2017 tmp-9.txt
6.libc.so.6: version `GLIBC_2.14' not found
百度网盘下载glibc-2.14.tar http://pan.baidu.com/s/1qYNgSTA
tar glibc-2.14.tar.gz
cd glibc-2.14
mkdir build
cd build
../configure
make && make install
最后,将其添加到环境变量中即可(注意:不要在root权限下)
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/project/Metabenchmark/pipelines/tabtk_utils-0.1.4/bin/glibc-2.14/build:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"
编译本来并不复杂,都是configure & make & make install的老三步,问题在于遇到的各种错误。下面总结了一下遇到的错误们
上述编译过程中常会出现下列问题:
1. LD_LIBRARY_PATH shouldn't contain the current directory
出现这个错误的原因是由于环境变量的LD_LIBRARY_PATH中出现了当前目录。找了好久不知道是啥原因,因为不可能把这目录放在环境变量啊。后来发现,通常我们写环境变量都喜欢写:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH = $LD_LIBRARY_PATH:foo/bar:hello/world:a/b
如果一开始LD_LIBRARY_PATH不存在的话,这个上面这串环境变量开头就是冒号,这就把当前文件夹包含进去了。一般来说我们挺需要这种效果,因为在编译的时候可以include某些东西,但是对于编译glibc来说这个是多余的。
最简单的解决方法就是unset LD_LIBRARY_PATH,这能把这个环境变量直接干掉。
2. 安装目录prefix没指定的错误:
*** On GNU/Linux systems the GNU C Library should not be installed into
*** /usr/local since this might make your system totally unusable.
*** We strongly advise to use a different prefix. For details read the FAQ.
*** If you really mean to do this, run configure again using the extra
*** parameter `--disable-sanity-checks'.
出现这个错误的原因在于,如果没指定prefix,则系统把这个程序装在/usr/local目录下。但是,c标准库要求必须安装在与根文件系统相同的分区中,否则不能用。但是/usr这个挂载点可能处在外部的分区。
--prefix=/usr --disable-profile --enable-add-ons --with-headers=/usr/include --with-binutils=/usr/bin
7.linux命令后台运行
有两种方式:
1. command & : 后台运行,你关掉终端会停止运行
2. nohup command & : 后台运行,你关掉终端也会继续运行 # nohup就是不挂起的意思( no hang up)如: nohup python unitl.py &