今天继续来复习NIO三剑客的最后1个:selector
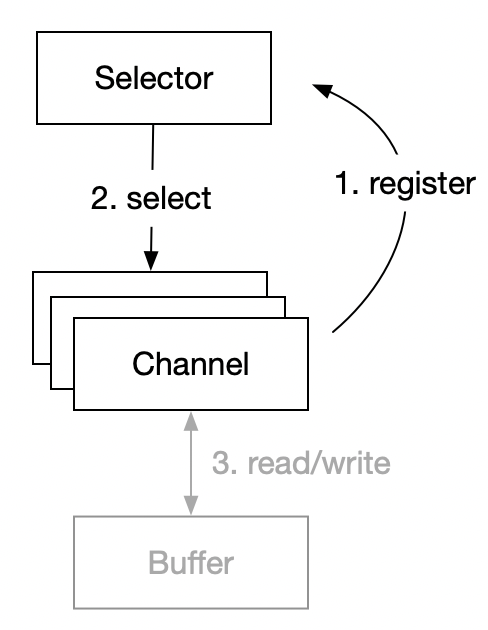
selector的工作原理,简单来看,就是上面这张图,Channel必须先向Selector注册(注:register的时候,可以选择关注哪些事件,比如:有新连接 或 有数据可读 等),注册成功后,Selector通过select方法来检查这些Channel上是否有事件发生,比如:有数据发过来,channel就可以把数据读到Buffer中。
这三者在类设计的层面是怎么串起来的?下面是Selector类的示意图:
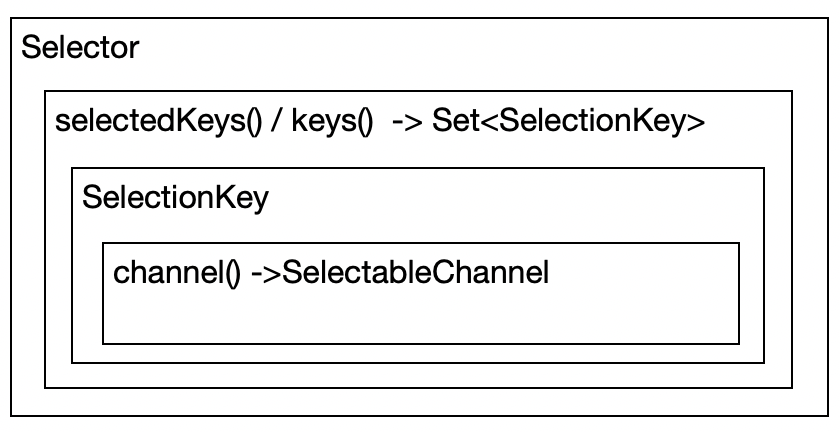
当Channel注册上来时,会被包装成一个SelectionKey放到Set中,通过keys()方法可以得到所有注册的SelectionKey。当Channel上有事件发生时,通过selectedKeys()方法,可以得到所有当前有事件发生的Set集合。很显然,selectedKeys是keys的子集。
SelectionKey类中,又通过channel()方法,持有Channel的引用,这样就能通过该引用来向Buffer读/写数据(注:记住NIO中,向Buffer中写入数据,在网络编程中其实就是向对方发数据)。
看起来并不复杂,但真正用NIO写一个基本的Server端Demo,还是要很多步骤的,正所谓知易行难,梳理了一张图,大家可以感受一下:
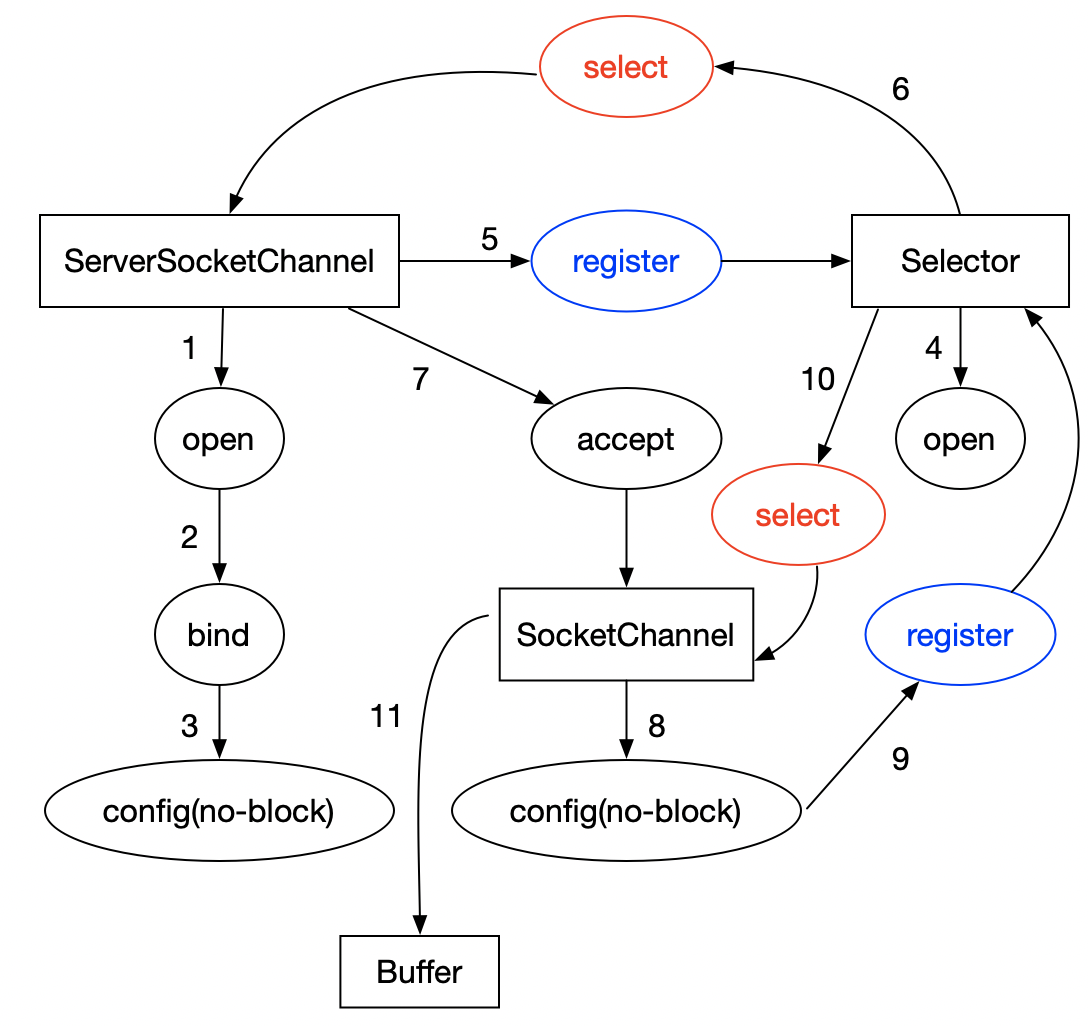
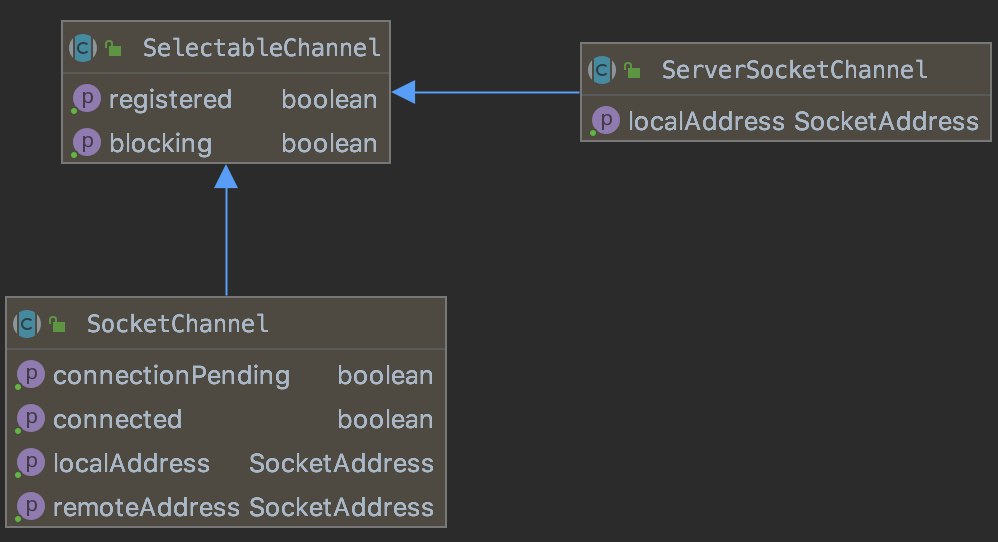
值得一提的是,这里用到二类Channel,它们都继承自SelectableChannel
下面来热热身,写一个最基本的ServerDemo:
package test.nio.study;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author 菩提树下的杨过(http://yjmyzz.cnblogs.com)
*/
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(8086);
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定ip:port
serverSocketChannel.bind(addr);
//配置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//获取Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//将channel注册到Selector(仅关注:新连接事件)
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//轮询事件
while (true) {
//每100ms轮一次
if (selector.select(100) == 0) {
continue;
}
//如果有事件发生,则拿到一个SelectionKey集合的迭代器
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
try {
//判断事件类型(当有新连接请求时)
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
//(接受)创建新连接,同时返回新连接的Channel(注:accept方法是阻塞的)
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " is connected");
//向client回显一句话
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(("hello:" + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + "
").getBytes()));
//新连接的Channel,也要注册到Selector,并关注读取事件(以响应客户端发过来的消息)
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
//有数据可读取时
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
try {
int count = channel.read(buffer);
if (count != -1) {
System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress() + " say:" + new String(Arrays.copyOf(buffer.array(), count)));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println(channel.getRemoteAddress() + " disconnected");
continue;
}
buffer.clear();
}
} finally {
//处理完后,一定要将自身移除,否则下一次select有事件触发时,无法正常处理
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
}
关键地方都加了详细注释,应该不难理解,把这个程序跑起来。
然后开2个终端(我是mac环境),都输入 telnet localhost 8160,相当于2个client端连接上来,然后每个终端里打几个字,向Server端发点数据。
接下来改造一下,写一个多人聊天室的原型,要实现的基本功能如下:
server端:
1、client连接成功时,server自动发问候语
2、新client上线时,通知其它client
3、有client说话时,转发给其它client(即:所有人,都能看到其它人发的最新消息)
4、有client下线(或断网时),通知其它人
client端:
1、连接到server端
2、能正常收发消息
先写client端代码,这个相对容易点:
package test.nio.study;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 菩提树下的杨过
*/
public class ChatRoomClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ChatRoomClient("localhost", 8086).start();
}
SocketChannel socketChannel;
Selector selector;
InetSocketAddress serverAddress;
boolean isConnected = false;
public ChatRoomClient(String host, int port) {
serverAddress = new InetSocketAddress(host, port);
}
/**
* 连接到server
*
* @param address
*/
private void connect(InetSocketAddress address) {
try {
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
boolean connect = socketChannel.connect(address);
if (!connect) {
//注:建立连接是需要时间的,调用完connect方法后,这里返回的connect大概率是false
int timeout = 5000;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//所以要通过finishConnect来轮询,才能知道最终是否连接成功,
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
Thread.sleep(50);
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - start > timeout) {
System.err.println("connect to " + address + " timeout");
return;
}
}
}
selector = Selector.open();
//注册,只关注读事件,同时关联一个buffer
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println(e);
}
isConnected = true;
System.err.println(address + " connect successfully");
}
/**
* 接收消息
*
* @param selector
*/
private void readMessage(Selector selector) {
if (!isConnected) {
return;
}
while (true) {
try {
//注:这里使用了阻塞版本的select方法(不想阻塞的话,可以用selectNow)
if (selector.select() > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
int count = channel.read(buffer);
if (count != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(Arrays.copyOf(buffer.array(), count)));
}
buffer.clear();
//千万要记得这个,不然下次事件触发,无法正常处理
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("read message error:" + e);
}
}
}
/**
* 发送消息
*
* @param channel
*/
private void sendMessage(SocketChannel channel) {
if (!isConnected) {
return;
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
try {
/**
* 等待键盘输入内容
*/
int count = System.in.read(buffer);
if (count > 0) {
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(Arrays.copyOf(buffer, count - 1)));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("send message error:" + e);
}
}
}
/**
* 启动
*/
private void start() {
connect(serverAddress);
new Thread(() -> {
sendMessage(socketChannel);
}, "send-thread").start();
new Thread(() -> {
readMessage(selector);
}, "read-thread").start();
}
}
服务端:
package test.nio.study;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 菩提树下的杨过
*/
public class ChatRoomServer {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
Selector selector;
public ChatRoomServer(int port) {
InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(port);
try {
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定ip:port
serverSocketChannel.bind(addr);
//配置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//获取Selector
selector = Selector.open();
//将channel注册到Selector(仅关注:新连接事件)
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("server init fail:" + e);
}
System.out.println("server started");
}
void connHandle(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
//(接受)创建新连接,同时返回新连接的Channel(注:accept方法是阻塞的)
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.err.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " connected");
//向client回显一句话
String message = "hello," + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + "
";
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes()));
sendMessageToOther(key, socketChannel, "hi, all");
//新连接的Channel,也要注册到Selector,并关注读取事件(以响应客户端发过来的消息)
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
void sendMessageToOther(SelectionKey key, SocketChannel channel, String message) throws IOException {
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.keys();
//转发到其它client
for (SelectionKey otherKey : keys) {
if (!otherKey.equals(key)) {
SelectableChannel otherChannel = otherKey.channel();
if (otherChannel instanceof SocketChannel) {
((SocketChannel) otherChannel).write(ByteBuffer.wrap((channel.getRemoteAddress() + " say:" + message).getBytes()));
}
}
}
}
boolean readHandle(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
try {
int count = channel.read(buffer);
if (count != -1) {
String message = new String(Arrays.copyOf(buffer.array(), count));
System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress() + " say:" + message);
//转发到其它人
sendMessageToOther(key, channel, message);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
String message = channel.getRemoteAddress() + " disconnected";
System.err.println(message);
sendMessageToOther(key, channel, "disconnected");
return false;
}
buffer.clear();
return true;
}
void start() {
//轮询事件
while (true) {
try {
//每100ms轮一次
if (selector.select(100) == 0) {
continue;
}
//如果有事件发生,则拿到一个SelectionKey集合的迭代器
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
try {
//判断事件类型(当有新连接请求时)
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
connHandle(key);
}
//有数据可读取时
if (key.isReadable()) {
if (!readHandle(key)) {
continue;
}
}
} finally {
//处理完后,一定要将自身移除,否则下一次select有事件触发时,无法正常处理
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println(e);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ChatRoomServer(8086).start();
}
}
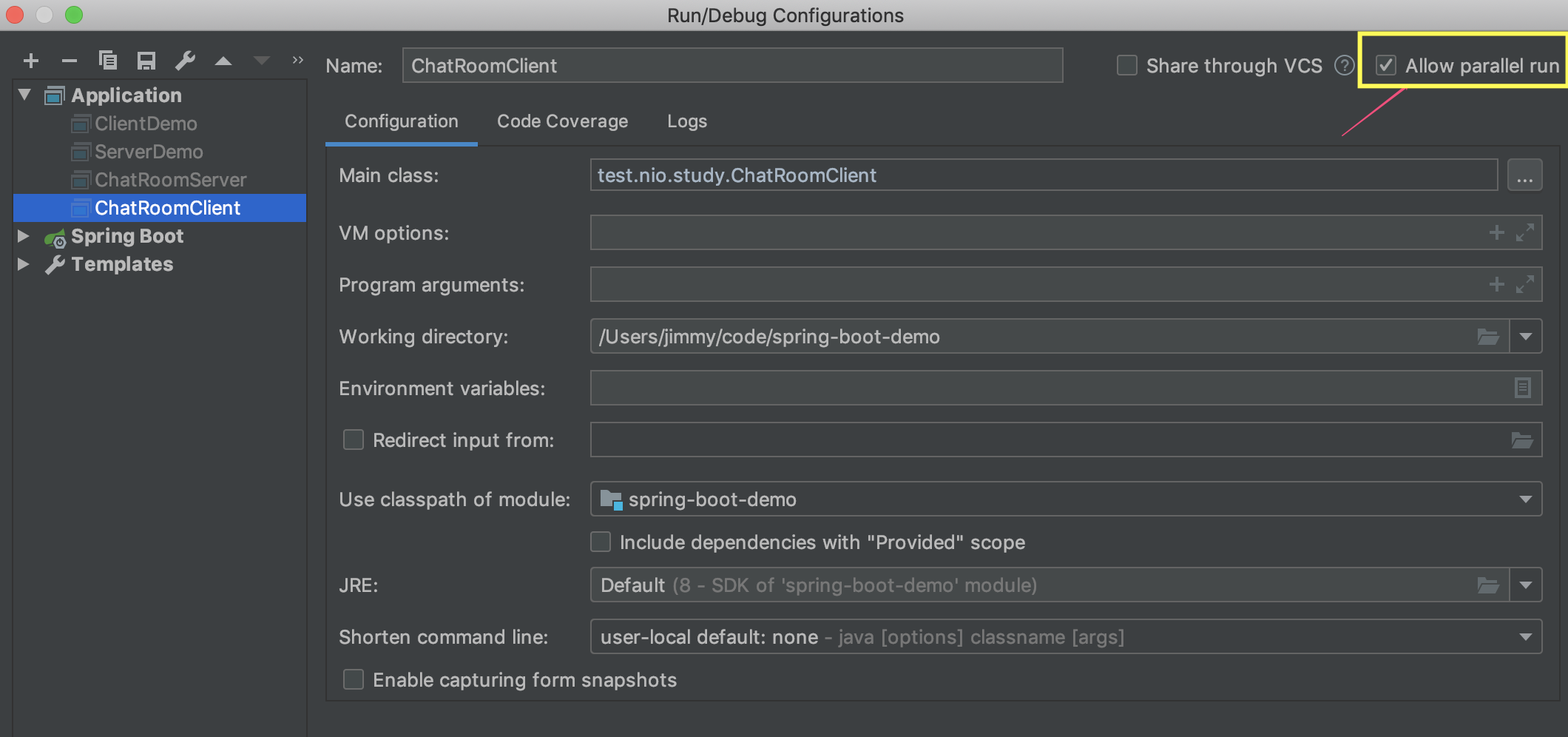
跑起来看看,不过这里有1个小技巧,使用idea的话,默认情况下,每个程序都是单实例运行,如果要同时启用多个client是不行,可参考下图设置:
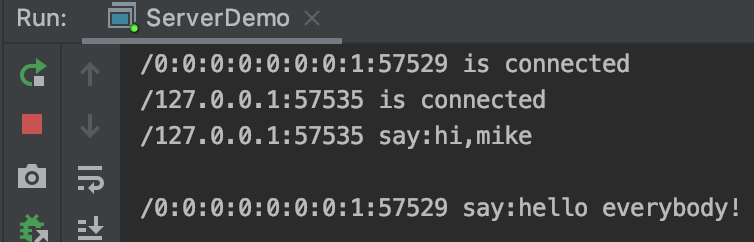
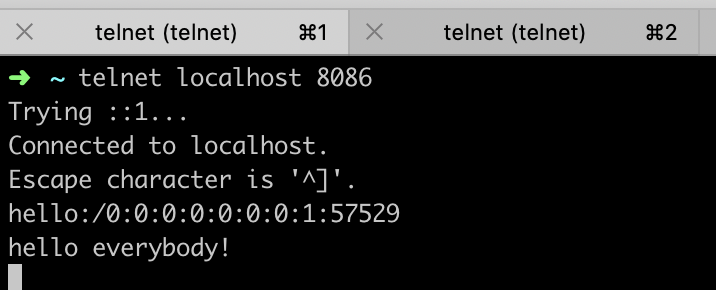
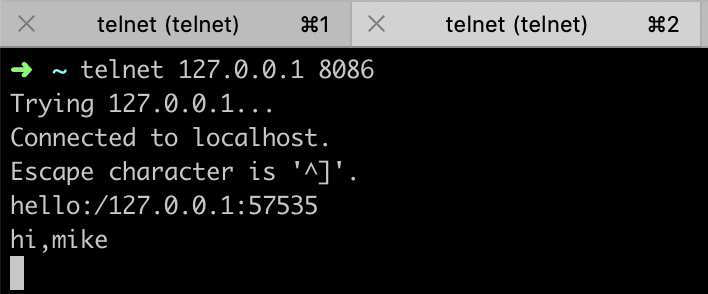
server端运行截图:
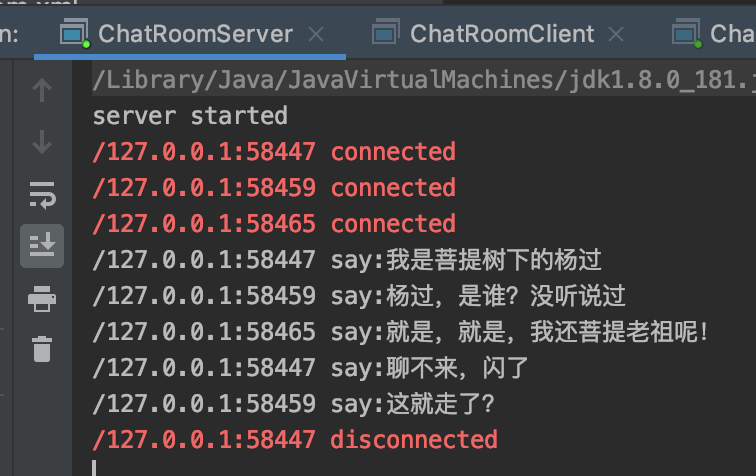
client-1运行截图:
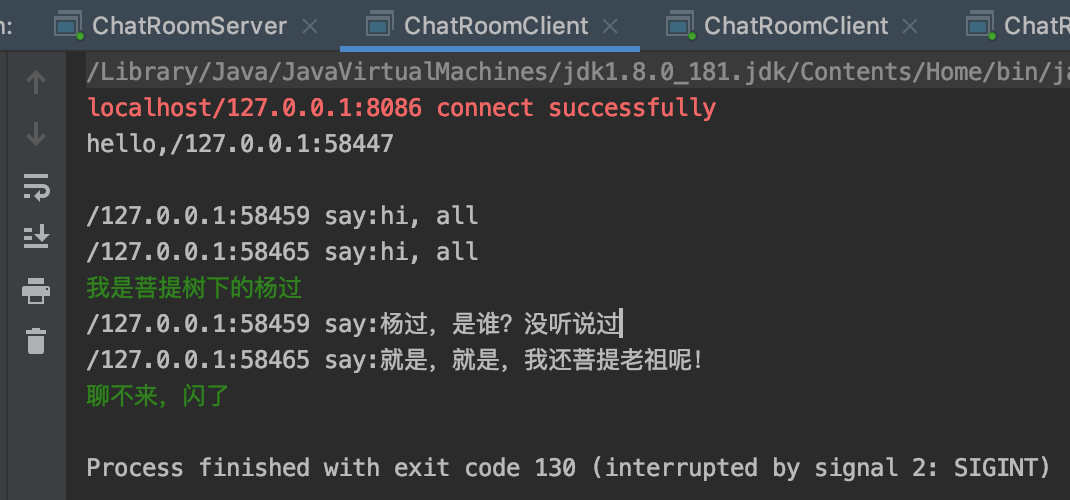
client-2截图:
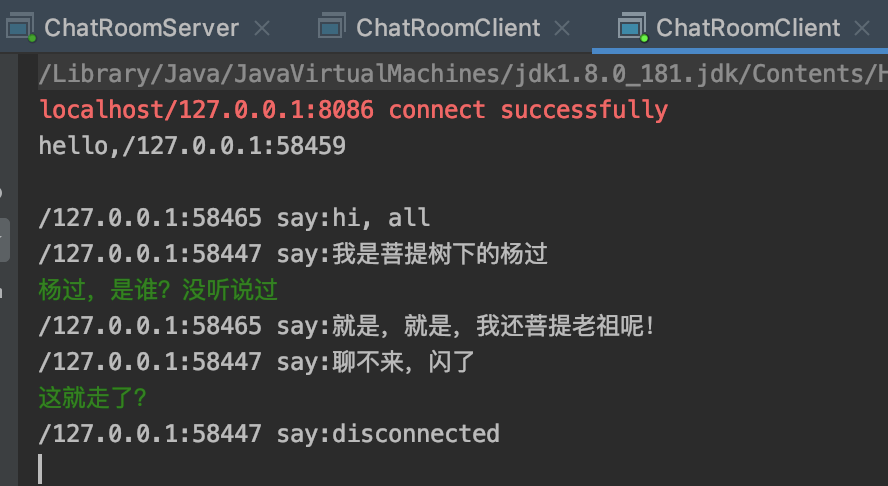
client-3运行截图:
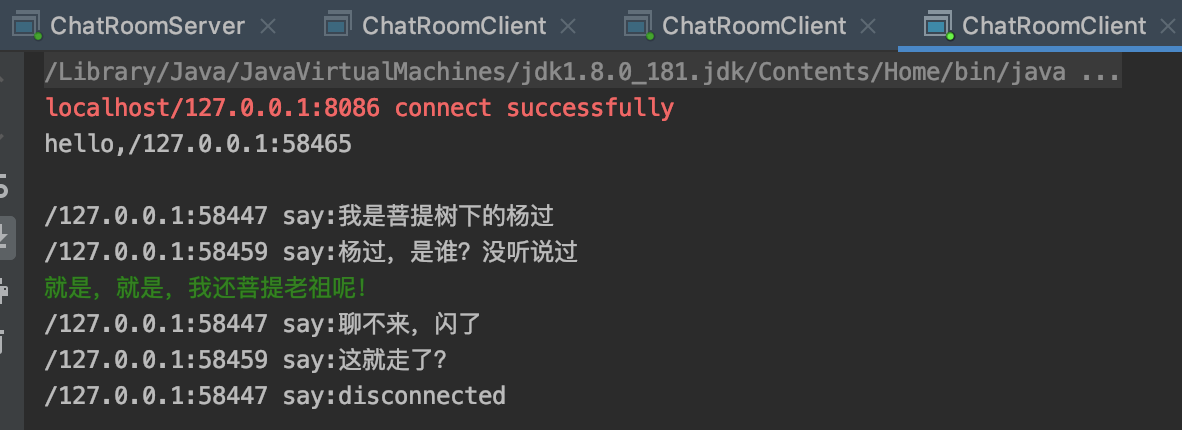
参考文章:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/13/docs/api/java.base/java/nio/channels/Selector.html