Map 是非常常用的一种数据接口。在 Java 中,提供了成熟的 Map 实现。
Map 主要用于存储键(key)值(value)对,根据键得到值,因此键不允许键重复,但允许值重复。
在散列中有几个名词需要解释下:
Capacity: 容量,hash表里bucket(桶)的数量,也就是散列数组的大小
Initial capacity: 初始容量,常见hash表时,初始bucket的数量,默认构建容量是16,也可以使用特定的容量
Size: 大小,当散列表中存储数据的数量
Load factor: 加载因子,默认值0.75(75%),向散列表增加数据时如果size/capacity的值大于Load factor则会发生扩容并且重新散列(refresh/ resize)
Map的主要实现类有HashMap、HashTable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、IdentityHashMap、ConcurrentHashMap、WeakHashMap、ConcurrentSkipListMap、EnumMap在HashTable的子类中还有Properties类的实现。
AbstractHashMap接口
AbstractMap实现了Map的接口,实现了基础的Map的方法。
例如
public int size() //当前Map的大小
public boolean isEmpty()
public boolean containsValue(Object value)
public boolean containsKey(Object key)
public V get(Object key)
public V put(K key, V value)
public V remove(Object key)
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)
public void clear()
public Set<K> keySet()
public Collection<V> values()
public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
HashMap
hashMap是一种经常使用的Map实现方式,它根据键的hashCode值来存储数据,根据键可以直接获取它的值,具有很快的访问速度。HashMap最多允许一条记录为null,不允许多条记录为null(HashMap的null值总是存在table[0]中的位置).HashMap不支持线程的同步,即任意时刻如果存在多条线程同时操作hashMap会导致数据的不统一。
HashMap实现基本的Map几口,扩展AbstractMap类
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
HashMap的实现原理:HashMap内部维护一个数组,并将Key做Hash算法,然后将Hash值映射到内存地址上,即数组的下标索引,这样就可以通过Key直接获取所对应的数据。而对于发生碰撞的位置,则会维护一个链表,所有在同一位置发生碰撞的元素都会存放在同一位置的链表中,hashf算法的实现参照http://blog.csdn.net/zq602316498/article/details/39351363
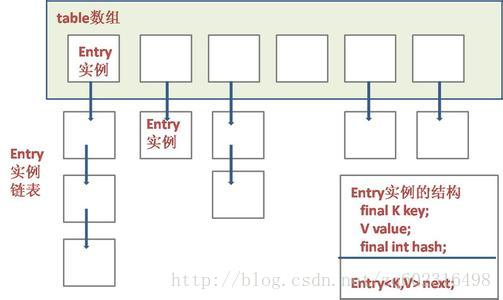
HashMap的resize性能:
当hashmap中的元素越来越多的时候,碰撞的几率也就越来越高(因为数组的长度是固定的),所以为了提高查询的效率,就要对hashmap的数组进行扩容,数组扩容这个操作也会出现在ArrayList中,所以这是一个通用的操作,很多人对它的性能表示过怀疑。在hashmap数组扩容之后,最消耗性能的点就出现了:原数组中的数据必须重新计算其在新数组中的位置,并放进去,这就是resize。
那么hashmap什么时候进行扩容呢?当hashmap中的元素个数超过数组大小*loadFactor时,就会进行数组扩容,loadFactor的默认值为0.75,也就是说,默认情况下,数组大小为16,那么当hashmap中元素个数超过16*0.75=12的时候,就把数组的大小扩展为2*16=32,即扩大一倍,然后重新计算每个元素在数组中的位置,而这是一个非常消耗性能的操作,所以如果我们已经预知hashmap中元素的个数,那么预设元素的个数能够有效的提高hashmap的性能。比如说,我们有1000个元素new HashMap(1000), 但是理论上来讲new HashMap(1024)更合适,不过上面annegu已经说过,即使是1000,hashmap也自动会将其设置为1024。 但是new HashMap(1024)还不是更合适的,因为0.75*1000 < 1000, 也就是说为了让0.75 * size > 1000, 我们必须这样new HashMap(2048)才最合适,既考虑了&的问题,也避免了resize的问题。
LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap 继承与HashMap 实现Map接口,里面的数据是有序的,能保证输出的顺序和输入的顺序(应用场景:购物车等需要顺序的)
在使用Iterator遍历LinkedHashMap时,先得到的记录肯定是先插入的(也可以在构造时用参数,按照应用次数排序)。在遍历的时候肯定会比HashMap慢。有HashMap的全部特性。
LinkedHasmp同样是非线程安全的。
源码构造LinkedHashMap时有一个 accessOrder标志位,当它false时,表示双向链表中的元素按照Entry插入LinkedHashMap到中的先后顺序排序,即每次put到LinkedHashMap中的Entry都放在双向链表的尾部,这样遍历双向链表时,Entry的输出顺序便和输入的顺序一致,这也是默认的双向链表的存储顺序;当它为true时,表示双向链表中的元素按照访问的先后顺序排列(类似于LRU算法),可以看到,虽然Entry插入链表的顺序依然是按照其put到LinkedHashMap中的顺序,但put和get方法均有调用recordAccess方法(put方法在key相同,覆盖原有的Entry的情况下调用recordAccess方法),该方法判断accessOrder是否为true,如果是,则将当前访问的Entry(put进来的Entry或get出来的Entry)移到双向链表的尾部(key不相同时,put新Entry时,会调用addEntry,它会调用creatEntry,该方法同样将新插入的元素放入到双向链表的尾部,既符合插入的先后顺序,又符合访问的先后顺序,因为这时该Entry也被访问了),否则,什么也不做。
LinkedHahsMap源码分析:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/37867985
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>
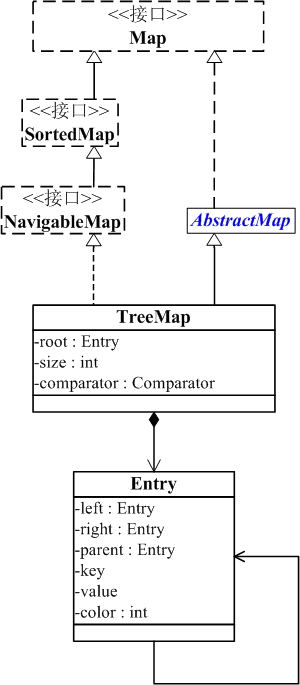
TreeMap
在介绍TreeMap前首先需要介绍两个接口 sortedMap、NavigableMap
sortedMap继承与Map接口,增加了基本的Map排序功能接口,最重要的是Map需要实现一个comparator方法来实现key 或者value的排序

public interface SortedMap<K,V> extends Map<K,V> { /** * Returns the comparator used to order the keys in this map, or * {@code null} if this map uses the {@linkplain Comparable * natural ordering} of its keys. * * @return the comparator used to order the keys in this map, * or {@code null} if this map uses the natural ordering * of its keys */ Comparator<? super K> comparator(); /** * Returns a view of the portion of this map whose keys range from * {@code fromKey}, inclusive, to {@code toKey}, exclusive. (If * {@code fromKey} and {@code toKey} are equal, the returned map * is empty.) The returned map is backed by this map, so changes * in the returned map are reflected in this map, and vice-versa. * The returned map supports all optional map operations that this * map supports. * * <p>The returned map will throw an {@code IllegalArgumentException} * on an attempt to insert a key outside its range. * * @param fromKey low endpoint (inclusive) of the keys in the returned map * @param toKey high endpoint (exclusive) of the keys in the returned map * @return a view of the portion of this map whose keys range from * {@code fromKey}, inclusive, to {@code toKey}, exclusive * @throws ClassCastException if {@code fromKey} and {@code toKey} * cannot be compared to one another using this map's comparator * (or, if the map has no comparator, using natural ordering). * Implementations may, but are not required to, throw this * exception if {@code fromKey} or {@code toKey} * cannot be compared to keys currently in the map. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromKey} or {@code toKey} * is null and this map does not permit null keys * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code fromKey} is greater than * {@code toKey}; or if this map itself has a restricted * range, and {@code fromKey} or {@code toKey} lies * outside the bounds of the range */ SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey); /** * Returns a view of the portion of this map whose keys are * strictly less than {@code toKey}. The returned map is backed * by this map, so changes in the returned map are reflected in * this map, and vice-versa. The returned map supports all * optional map operations that this map supports. * * <p>The returned map will throw an {@code IllegalArgumentException} * on an attempt to insert a key outside its range. * * @param toKey high endpoint (exclusive) of the keys in the returned map * @return a view of the portion of this map whose keys are strictly * less than {@code toKey} * @throws ClassCastException if {@code toKey} is not compatible * with this map's comparator (or, if the map has no comparator, * if {@code toKey} does not implement {@link Comparable}). * Implementations may, but are not required to, throw this * exception if {@code toKey} cannot be compared to keys * currently in the map. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code toKey} is null and * this map does not permit null keys * @throws IllegalArgumentException if this map itself has a * restricted range, and {@code toKey} lies outside the * bounds of the range */ SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey); /** * Returns a view of the portion of this map whose keys are * greater than or equal to {@code fromKey}. The returned map is * backed by this map, so changes in the returned map are * reflected in this map, and vice-versa. The returned map * supports all optional map operations that this map supports. * * <p>The returned map will throw an {@code IllegalArgumentException} * on an attempt to insert a key outside its range. * * @param fromKey low endpoint (inclusive) of the keys in the returned map * @return a view of the portion of this map whose keys are greater * than or equal to {@code fromKey} * @throws ClassCastException if {@code fromKey} is not compatible * with this map's comparator (or, if the map has no comparator, * if {@code fromKey} does not implement {@link Comparable}). * Implementations may, but are not required to, throw this * exception if {@code fromKey} cannot be compared to keys * currently in the map. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromKey} is null and * this map does not permit null keys * @throws IllegalArgumentException if this map itself has a * restricted range, and {@code fromKey} lies outside the * bounds of the range */ SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey); /** * Returns the first (lowest) key currently in this map. * * @return the first (lowest) key currently in this map * @throws NoSuchElementException if this map is empty */ K firstKey(); /** * Returns the last (highest) key currently in this map. * * @return the last (highest) key currently in this map * @throws NoSuchElementException if this map is empty */ K lastKey(); /** * Returns a {@link Set} view of the keys contained in this map. * The set's iterator returns the keys in ascending order. * The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are * reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified * while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through * the iterator's own {@code remove} operation), the results of * the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal, * which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via the * {@code Iterator.remove}, {@code Set.remove}, * {@code removeAll}, {@code retainAll}, and {@code clear} * operations. It does not support the {@code add} or {@code addAll} * operations. * * @return a set view of the keys contained in this map, sorted in * ascending order */ Set<K> keySet(); /** * Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map. * The collection's iterator returns the values in ascending order * of the corresponding keys. * The collection is backed by the map, so changes to the map are * reflected in the collection, and vice-versa. If the map is * modified while an iteration over the collection is in progress * (except through the iterator's own {@code remove} operation), * the results of the iteration are undefined. The collection * supports element removal, which removes the corresponding * mapping from the map, via the {@code Iterator.remove}, * {@code Collection.remove}, {@code removeAll}, * {@code retainAll} and {@code clear} operations. It does not * support the {@code add} or {@code addAll} operations. * * @return a collection view of the values contained in this map, * sorted in ascending key order */ Collection<V> values(); /** * Returns a {@link Set} view of the mappings contained in this map. * The set's iterator returns the entries in ascending key order. * The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are * reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified * while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through * the iterator's own {@code remove} operation, or through the * {@code setValue} operation on a map entry returned by the * iterator) the results of the iteration are undefined. The set * supports element removal, which removes the corresponding * mapping from the map, via the {@code Iterator.remove}, * {@code Set.remove}, {@code removeAll}, {@code retainAll} and * {@code clear} operations. It does not support the * {@code add} or {@code addAll} operations. * * @return a set view of the mappings contained in this map, * sorted in ascending key order */ Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet(); }
Navgable继承与sortedMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法,比如返回有序的key集合
TreeMap是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的,继承与AbstractMap,实现NavigableMap接口
TreeMap源码继承方式
public class TreeMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
另外,TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fastl的。
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeMap中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。 TreeMap() // 创建的TreeMap包含Map TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> copyFrom) // 指定Tree的比较器 TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) // 创建的TreeSet包含copyFrom TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> copyFrom)
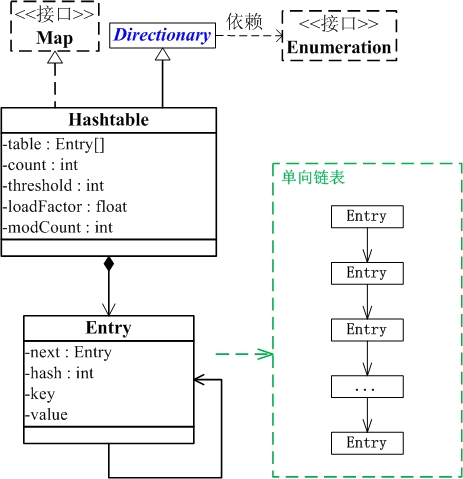
HashTable
HashTable实现了Map的接口继承与Dictionary类
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
HashMap与HashTable有很多地方相同,所以总是拿来一起比较
Hashtable 的实例有两个参数影响其性能:初始容量 和 加载因子。容量 是哈希表中桶 的数量,初始容量 就是哈希表创建时的容量。注意,哈希表的状态为 open:在发生“哈希冲突”的情况下,单个桶会存储多个条目,这些条目必须按顺序搜索。加载因子 是对哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一个尺度。初始容量和加载因子这两个参数只是对该实现的提示。关于何时以及是否调用 rehash 方法的具体细节则依赖于该实现。
通常,默认加载因子是 0.75, 这是在时间和空间成本上寻求一种折衷。加载因子过高虽然减少了空间开销,但同时也增加了查找某个条目的时间(在大多数 Hashtable 操作中,包括 get 和 put 操作,都反映了这一点)。
HashTable源码解析:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310887.html
IdentityHashMap
public class IdentityHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, java.io.Serializable, Cloneable
IdentityHashMap继承与AbstractMap实现了Map接口
1、IdentityHashMap允许key值重复,虽然其实现了Map的接口,但是重写了equal方法,但是--key必须是两个对象,即对于k1和k2,当k1==k2 时,IdentityHashMap认为两个key相等,而HashMap只有在k1.equals(k2) ==true 时才会认为两个key相等
简单来说IdentityHashMap与常用的HashMap的区别是:前者比较key时是“引用相等”而后者是“对象相等”,IdentityHashMap允许使用null作为Key和value,不保证任何key-value对之间的顺序,更不能保证他们的顺序随时间的推移不发生变化。
2、IdentityHashMap有其特殊用途,比如序列化或者深度复制。或者记录对象代理。
3、HashMap使用的是equals(),HashMap使用的是hashCode()查找位置,IdentityHashMap使用的是System.identityHashCode(object),IdentityHashMap理论上来说速度要比HashMap快一点
4、举个例子,jvm中的所有对象都是独一无二的,哪怕两个对象是同一个class的对象,而且两个对象的数据完全相同,对于jvm来说,他们也是完全不同的,如果要用一个map来记录这样jvm中的对象,你就需要用IdentityHashMap,而不能使用其他Map实现。
public static void main(String[] args) { Map map = new IdentityHashMap(); map.put("a", 1); map.put(new String("a"), 2); map.put(new String("a"), 4); map.put(new String("a"), 5); map.put("a", 3); //输出为4 System.out.println("Identity Map KeySet Size :: " + map.keySet().size()); }
WeakHashMap
在介绍WeakHahsMap的时候需要先介绍4个java对象引用的概念
1)强引用:任何时候都不会被垃圾回收器回收,如果内存不足,宁愿抛出OutOfMemoryError
2) 软引用:只有内存将满的时候才会被垃圾回收器回收,如果还有可用的内存,垃圾回收器就不会回收
3)弱引用:只要垃圾回收器运行,就肯定会被回收,不管还有没有可用内存
4)虚引用:徐引用就等于没有引用,任何时候都可能被GC回收
WeakHashMap实现了Map接口,是HashMap的一种实现,它比HashMap多了一个引用队列,对比HashMap和WeakHashMap,注意“基本”两个字,除了没有实现Cloneable和Serializable这两个标记接口,最大的区别在于在于expungeStaleEntries()这个方法
它使用弱引用作为内部数据的存储方案。WeakHashMap是弱引用的一种典型应用,它可以作为简单的缓存表解决方案
/** * Reference queue for cleared WeakEntries */ private final ReferenceQueue<Object> queue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
在WeakHashMap中可以看到每调用一次expungeStaleEntries()方法,就会在引用队列中寻找是否有被清楚的key对象,如果有则在table中找到其值,并将value设置为null,next指针也设置为null,让GC去回收这些资源。
将一对key, value放入到 WeakHashMap 里并不能避免该key值被GC回收,除非在 WeakHashMap 之外还有对该key的强引用
首先测试以下代码
public static void main(String[] args) { /**会导致报内存溢出错误 * xception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at collections.WeakHashMapTest.main(WeakHashMapTest.java:39) */ Map<Integer,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) { Integer ii = new Integer(i); map.put(ii, new byte[i]); } //正常运行 Map<Integer,Object> map1 = new WeakHashMap<>(); for(int i=0;i<1000000;i++) { Integer ii = new Integer(i); map1.put(ii, new byte[i]); } }

public static void main(String[] args) { // 初始化3个“弱键” String w1 = new String("one"); String w2 = new String("two"); String w3 = new String("three"); // 新建WeakHashMap Map wmap = new WeakHashMap(); // 添加键值对 wmap.put(w1, "w1"); wmap.put(w2, "w2"); wmap.put(w3, "w3"); // 打印出wmap System.out.printf(" wmap:%s ",wmap ); // containsKey(Object key) :是否包含键key System.out.printf("contains key two : %s ",wmap.containsKey("two")); System.out.printf("contains key five : %s ",wmap.containsKey("five")); // containsValue(Object value) :是否包含值value System.out.printf("contains value 0 : %s ",wmap.containsValue(new Integer(0))); // remove(Object key) : 删除键key对应的键值对 wmap.remove("three"); System.out.printf("wmap: %s ",wmap ); // ---- 测试 WeakHashMap 的自动回收特性 ---- // 将w1设置null。 // 这意味着“弱键”w1再没有被其它对象引用,调用gc时会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对 w1 = null; // 内存回收。这里,会回收WeakHashMap中与“w1”对应的键值对 System.gc(); // 遍历WeakHashMap Iterator iter = wmap.entrySet().iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { Map.Entry en = (Map.Entry)iter.next(); System.out.printf("next : %s - %s ",en.getKey(),en.getValue()); } // 打印WeakHashMap的实际大小 System.out.printf(" after gc WeakHashMap size:%s ", wmap.size()); }
ConcurrentHashMap
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable
ConcurrentHashMap在线程安全的基础上提供了更好的写并发能力,但同时降低了对读一致性的要求(这点好像CAP理论啊 O(∩_∩)O)。ConcurrentHashMap的设计与实现非常精巧,大量的利用了volatile,final,CAS等lock-free技术来减少锁竞争对于性能的影响
以后会放到多线程编程里面详细解释,暂时不做详谈。
EnumMap
EnumMap的key不允许为null,value可以为null,按照key在enum中的顺序进行保存,非线程安全。
EnumMap是专门为枚举类型量身定做的Map实现。虽然使用其它的Map实现(如HashMap)也能完成枚举类型实例到值得映射,但是使用EnumMap会更加高效:它只能接收同一枚举类型的实例作为键值,并且由于枚举类型实例的数量相对固定并且有限,所以EnumMap使用数组来存放与枚举类型对应的值。这使得EnumMap的效率非常高。EnumMap在内部使用枚举类型的ordinal()得到当前实例的声明次序,并使用这个次序维护枚举类型实例对应值在数组的位置。
import java.util.Map.Entry; import sun.misc.SharedSecrets; public class EnumMap<K extends Enum<K>, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements java.io.Serializable, Cloneable{ private final Class<K> keyType; private transient K[] keyUniverse; private transient Object[] vals; private transient int size = 0; }
具体的使用方式如下:
public enum Color { RED,BLUE,BLACK,YELLOW,GREEN; } public static void main(String[] args) { EnumMap<Color,String> map = new EnumMap<>(Color.class); map.put(Color.YELLOW, "黄色"); map.put(Color.RED, "红色"); map.put(Color.BLUE, null); // map.put(null, "无"); //会报NullPonitException的错误 map.put(Color.BLACK, "黑色"); map.put(Color.GREEN, "绿色"); for(Map.Entry<Color,String> entry:map.entrySet()) { System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue()); } System.out.println(map); }
基本常用的Map就介绍到这里,下一篇文章会详细介绍下每个map之间的不同,在不同场景下该如何选择。
