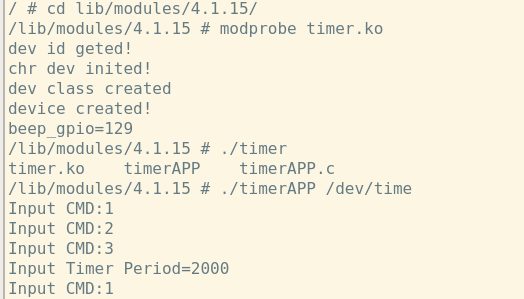
在上面一张我们在一个基础IO外设上加上了定时器功能,但是在设备驱动挂载完成后直接就运行定时器了,这样肯定是不行的。一定是需要一个APP程序和底层驱动进行交互。APP起码具备的功能有启动、停止定时器,修改定时器工作周期的功能。
在前面所有的APP中我们主要用了file_operations结构体中的open、read、write和realease。其实write就可以满足我们的需求,但是今天我们通过一个新的操作来实现数据的交互——ioctrl
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
ioctl和write用法有些区别,用man来打印一下看看

上面的是write的介绍,下面是ioctl的介绍

具体的区别我暂时还没搞太明白,但是很明显两个函数的参数是不一样的,write是通过指针指向要修改的地方,有个参数是指针类型。而ioctl是两个int类型的参数。
compat_ioctl 函数与 unlocked_ioctl 函数功能一样,区别在于在 64 位系统上,32 位的应用程序调用将会使用此函数。在 32 位的系统上运行 32 位的应用程序调用的是unlocked_ioctl。因为我们的I.MX6UL运行的是32位的程序,所以我们要使用的就是unlock_ioctl。
/** * @brief 文件操作集合 * */ static const struct file_operations key_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = new_dev_open, .unlocked_ioctl = new_dev_ioctl, };
unlock_ioctl函数
先看下函数的参数
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
我们可以查到ioctl的引用一直到include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctl.h这个文件中有下面的介绍
/* ioctl command encoding: 32 bits total, command in lower 16 bits, * size of the parameter structure in the lower 14 bits of the * upper 16 bits. * Encoding the size of the parameter structure in the ioctl request * is useful for catching programs compiled with old versions * and to avoid overwriting user space outside the user buffer area. * The highest 2 bits are reserved for indicating the ``access mode''. * NOTE: This limits the max parameter size to 16kB -1 ! */ /* * The following is for compatibility across the various Linux * platforms. The generic ioctl numbering scheme doesn't really enforce * a type field. De facto, however, the top 8 bits of the lower 16 * bits are indeed used as a type field, so we might just as well make * this explicit here. Please be sure to use the decoding macros * below from now on. */
第一个参数不用说了,就是文件句柄,第二个参数是命令,这个命令是有固定格式的,我们后面再讲。最后的参数可以用来传一个长整型的参数。既然第二个参数是命令,我们就可以使用switch语句来进行处理。内核中整个函数结果可以简化成这样的
static long new_dev_ioctl(struct file *file,unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg) { switch (cmd) { case cmd1: //do case1 break; case cmd2: //do case2 break; case cmd3: //do case3 break; } }
我们只需要根据不同的cmd对应的值去做相应的工作就行了。
cmd结构
虽然命令的数据类型是个int类型,但是这个数据时有形式要求的。这个在Documentation/ioctl/路径下的ioctl-number.txt里有详细的说明。我们可以在里面看一下内核里使用这个ioctl写的驱动样式.
随便在内核中搜索一下ioctl的驱动文件,可以发现下面的案例
1 #define CMD_COREB_START _IO('b', 0) 2 #define CMD_COREB_STOP _IO('b', 1) 3 #define CMD_COREB_RESET _IO('b', 2) 4 5 static long 6 coreb_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) 7 { 8 int ret = 0; 9 10 switch (cmd) { 11 case CMD_COREB_START: 12 bfin_write_SYSCR(bfin_read_SYSCR() & ~0x0020); 13 break; 14 case CMD_COREB_STOP: 15 bfin_write_SYSCR(bfin_read_SYSCR() | 0x0020); 16 bfin_write_SICB_SYSCR(bfin_read_SICB_SYSCR() | 0x0080); 17 break; 18 case CMD_COREB_RESET: 19 bfin_write_SICB_SYSCR(bfin_read_SICB_SYSCR() | 0x0080); 20 break; 21 default: 22 ret = -EINVAL; 23 break; 24 } 25 26 CSYNC(); 27 28 return ret; 29 }
在上面的驱动代码中,就是通过switch来实现cmd的处理的,注意cmd是开始定义的宏,这个宏是调用了一个_IO的函数。所以也就是说这个cmd的格式是有要求的。
cmd命令格式
Linux内核在使用ioctl函数来进行文件读写操作时,是对cmd参数有指定要求的。在内核文档ioctl/ioctl-decoding.txt里面有对其进行的详细说明
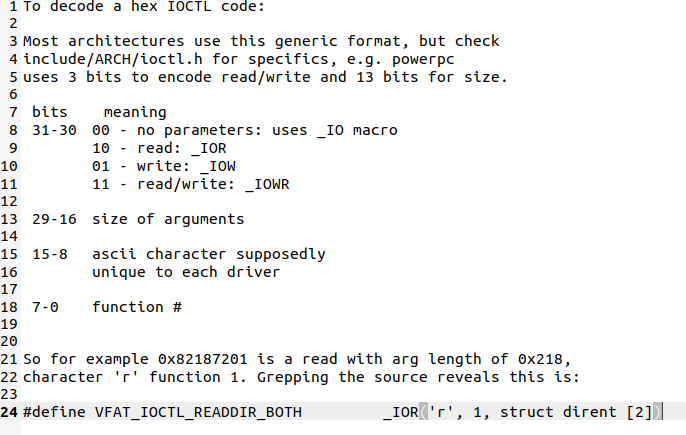
整个cmd包含了4个部分,包括了幻数、 序数、传输方向和数据大小,有些介绍在这里我们不再做详细的说明。总之我们要构造一个cmd是很麻烦的事情,还好,Linux在include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctl.h里为我们提供了一个API生成这个cmd,我们只需要传输相应的参数就可以了
1 #ifndef _UAPI_ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H 2 #define _UAPI_ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H 3 4 /* ioctl command encoding: 32 bits total, command in lower 16 bits, 5 * size of the parameter structure in the lower 14 bits of the 6 * upper 16 bits. 7 * Encoding the size of the parameter structure in the ioctl request 8 * is useful for catching programs compiled with old versions 9 * and to avoid overwriting user space outside the user buffer area. 10 * The highest 2 bits are reserved for indicating the ``access mode''. 11 * NOTE: This limits the max parameter size to 16kB -1 ! 12 */ 13 14 /* 15 * The following is for compatibility across the various Linux 16 * platforms. The generic ioctl numbering scheme doesn't really enforce 17 * a type field. De facto, however, the top 8 bits of the lower 16 18 * bits are indeed used as a type field, so we might just as well make 19 * this explicit here. Please be sure to use the decoding macros 20 * below from now on. 21 */ 22 #define _IOC_NRBITS 8 23 #define _IOC_TYPEBITS 8 24 25 /* 26 * Let any architecture override either of the following before 27 * including this file. 28 */ 29 30 #ifndef _IOC_SIZEBITS 31 # define _IOC_SIZEBITS 14 32 #endif 33 34 #ifndef _IOC_DIRBITS 35 # define _IOC_DIRBITS 2 36 #endif 37 38 #define _IOC_NRMASK ((1 << _IOC_NRBITS)-1) 39 #define _IOC_TYPEMASK ((1 << _IOC_TYPEBITS)-1) 40 #define _IOC_SIZEMASK ((1 << _IOC_SIZEBITS)-1) 41 #define _IOC_DIRMASK ((1 << _IOC_DIRBITS)-1) 42 43 #define _IOC_NRSHIFT 0 44 #define _IOC_TYPESHIFT (_IOC_NRSHIFT+_IOC_NRBITS) 45 #define _IOC_SIZESHIFT (_IOC_TYPESHIFT+_IOC_TYPEBITS) 46 #define _IOC_DIRSHIFT (_IOC_SIZESHIFT+_IOC_SIZEBITS) 47 48 /* 49 * Direction bits, which any architecture can choose to override 50 * before including this file. 51 */ 52 53 #ifndef _IOC_NONE 54 # define _IOC_NONE 0U 55 #endif 56 57 #ifndef _IOC_WRITE 58 # define _IOC_WRITE 1U 59 #endif 60 61 #ifndef _IOC_READ 62 # define _IOC_READ 2U 63 #endif 64 65 #define _IOC(dir,type,nr,size) \ 66 (((dir) << _IOC_DIRSHIFT) | \ 67 ((type) << _IOC_TYPESHIFT) | \ 68 ((nr) << _IOC_NRSHIFT) | \ 69 ((size) << _IOC_SIZESHIFT)) 70 71 #ifndef __KERNEL__ 72 #define _IOC_TYPECHECK(t) (sizeof(t)) 73 #endif 74 75 /* used to create numbers */ 76 #define _IO(type,nr) _IOC(_IOC_NONE,(type),(nr),0) 77 #define _IOR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size))) 78 #define _IOW(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size))) 79 #define _IOWR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size))) 80 #define _IOR_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),sizeof(size)) 81 #define _IOW_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size)) 82 #define _IOWR_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size)) 83 84 /* used to decode ioctl numbers.. */ 85 #define _IOC_DIR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_DIRSHIFT) & _IOC_DIRMASK) 86 #define _IOC_TYPE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_TYPESHIFT) & _IOC_TYPEMASK) 87 #define _IOC_NR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_NRSHIFT) & _IOC_NRMASK) 88 #define _IOC_SIZE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_SIZESHIFT) & _IOC_SIZEMASK) 89 90 /* ...and for the drivers/sound files... */ 91 92 #define IOC_IN (_IOC_WRITE << _IOC_DIRSHIFT) 93 #define IOC_OUT (_IOC_READ << _IOC_DIRSHIFT) 94 #define IOC_INOUT ((_IOC_WRITE|_IOC_READ) << _IOC_DIRSHIFT) 95 #define IOCSIZE_MASK (_IOC_SIZEMASK << _IOC_SIZESHIFT) 96 #define IOCSIZE_SHIFT (_IOC_SIZESHIFT) 97 98 #endif /* _UAPI_ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H */
我们主要使用的就是滴85~88行几组宏,说白了就是将0或1左右移动最后获取到指定的cmd。
#define _IO(type,nr) //没有参数的命令 #define _IOR(type,nr,size) //从驱动中读取数据 #define _IOW(type,nr,size) //向驱动中写入数据 #define _IOWR(type,nr,size) //双向数据传输
其中参数type就是幻数、nr是序号,size是大小,幻数也是个int点数据,可以在内核文档Documentation/ioctl/ioctl-number.txt里已经给出了参考值,可以根据需求从里面查询。
所以我们可以把我们需要对命令按照需求声明出来。我们的APP和驱动交互主要用来实现3个功能,启动、关闭定时器及修改定时器工作频率,打开和关闭是不用传递额外的参数的,而设置周期要写入个周期,就要用_IOW了。幻数使用的0xEF
#define CMD_CLOSE _IO(0xEF,1) //cmd值为1,关闭定时器 #define CMD_OPEN _IO(0xEF,2) //cmd值为2,启动定时器 #define CMD_PERIOD _IOW(0xEF,3,int) //cmd值为3,修改定时器工作频率
前两个不需要传参数,就用来_IO,不用指定count,设置频率涉及到应用程序向内核写数据,就用个_IOW,参数int意思是我们要传递个int类型的数据,所以长度就是int对应的长度值。可以看出来,使用Linux提供的方法来构建cmd就简单多了,我们只需要使用定义好的宏就可以了。
驱动修改
下面我们就可以根据ioctl的样式修改前面的驱动。主要就是unlocked_ioctl绑定的函数构建
static long new_dev_ioctl(struct file *file,unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg) { int ret = 0; int value = 0; struct new_dev *dev = file->private_data; switch (cmd) { case CMD_CLOSE: del_timer_sync(&dev->timer); gpio_set_value(dev->gpio,1); break; case CMD_OPEN: value = atomic_read(&dev->timer_per); mod_timer(&dev->timer,jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(value)); break; case CMD_PERIOD: ret = copy_from_user(&value,(int *)arg,sizeof(int)); //arg是应用传递给驱动的周期值数据首地址,长度为4个字节 if(ret<0){ return -EFAULT; } atomic_set(&dev->timer_per,value); mod_timer(&dev->timer,jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(value)); break; } }
驱动没什么可讲的,主要就是一个switch结构,根据APP通过ioctl操作传进来的cmd进行操作。要注意点就是第修改周期时使用了copy_from_user函数,注意传递函数时和APP里指针取值的对应。还有就是如果我们的定时器如果在运行中,是要不停读取timer_per这个变量值来设置定时器expires的,如果我们在没有停止定时器时去设置周期值,很有可能发生竞争,所以在一开始设计程序结构的时候,这个变量采用了原子变量,避免了竞争的发生。所以我前面说过,并发和竞争一定要在写代码前先想好,要不是改起来就很麻烦了!
下面吧整个驱动的代码放出来

/** * @file timer.c * @author your name (you@domain.com) * @brief 定时器测试驱动程序 * @version 0.1 * @date 2022-07-16 * * @copyright Copyright (c) 2022 * */ #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/uaccess.h> #include <linux/io.h> #include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/of.h> #include <linux/of_address.h> #include <linux/of_irq.h> #include <linux/gpio.h> #include <linux/of_gpio.h> #include <linux/ioctl.h> #define DEVICE_CNT 1 #define DEVICE_NAME "time" #define CMD_CLOSE _IO(0xEF,1) #define CMD_OPEN _IO(0xEF,2) #define CMD_PERIOD _IOW(0xEF,3,int) struct new_dev { dev_t dev_id; int major; int minor; struct class *class; struct device *device; struct cdev cdev; struct device_node *dev_nd; int gpio; struct timer_list timer; //定时器 atomic_t timer_per; //定时器周期 }; struct new_dev new_dev; static int new_dev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { filp->private_data = &new_dev; /* 设置私有数据 */ return 0; } /** * @brief 文件io操作 * * @param file * @param cmd * @param arg * @return long */ static long new_dev_ioctl(struct file *file,unsigned int cmd,unsigned long arg) { int ret = 0; int value = 0; struct new_dev *dev = file->private_data; switch (cmd) { case CMD_CLOSE: del_timer_sync(&dev->timer); gpio_set_value(dev->gpio,1); break; case CMD_OPEN: value = atomic_read(&dev->timer_per); mod_timer(&dev->timer,jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(value)); break; case CMD_PERIOD: ret = copy_from_user(&value,(int *)arg,sizeof(int)); //arg是应用传递给驱动的周期值数据首地址,长度为4个字节 if(ret<0){ return -EFAULT; } atomic_set(&dev->timer_per,value); mod_timer(&dev->timer,jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(value)); break; } } /** * @brief 文件操作集合 * */ static const struct file_operations key_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = new_dev_open, // .release = new_dev_release, .unlocked_ioctl = new_dev_ioctl, }; //gpio设备初始化 int beep_init(struct new_dev *dev) { int ret = 0 ; //从设备树搜索设备节点 dev->dev_nd = of_find_node_by_path("/beep"); if(dev->dev_nd == NULL){ printk("no device found\r\n"); ret = -EINVAL; goto fail_nd; } //获取beep对应GPIO dev->gpio = of_get_named_gpio(dev->dev_nd,"beep-gpios",0); printk("beep_gpio=%d\r\n",dev->gpio); if(dev->gpio < 0){ printk("no GPIO found!\r\n"); ret = -EINVAL; //errno-base.h中定义的异常数值到34,这里从100开始使用防止冲突 goto fail_gpio; } //请求GPIO ret = gpio_request(dev->gpio,"beep-gpio"); if(ret){ printk("gpio request err\r\n"); ret = -EBUSY; goto fail_request;} ret = gpio_direction_output(dev->gpio,1); if(ret < 0){ ret = -EINVAL; goto fail_gpioset; } return 0; fail_gpioset: gpio_free(dev->gpio); fail_request: fail_gpio: fail_nd: return ret; } timer_func(unsigned long arg){ static int stat = 1; int value = 0; struct new_dev *dev = (struct new_dev*)arg; stat = !stat; gpio_set_value(dev->gpio,stat); value = atomic_read(&dev->timer_per); mod_timer(&dev->timer,jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(value)); } static int __init timer_init(void){ int ret = 0; unsigned int value = 500; //申请设备号 new_dev.major = 0; if(new_dev.major){ //手动指定设备号,使用指定的设备号 new_dev.dev_id = MKDEV(new_dev.major,0); ret = register_chrdev_region(new_dev.dev_id,DEVICE_CNT,DEVICE_NAME); } else{ //设备号未指定,申请设备号 ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&new_dev.dev_id,0,DEVICE_CNT,DEVICE_NAME); new_dev.major = MAJOR(new_dev.dev_id); new_dev.minor = MINOR(new_dev.dev_id); } printk("dev id geted!\r\n"); if(ret<0){ //设备号申请异常,跳转至异常处理 goto faile_devid; } //字符设备cdev初始化 new_dev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE; cdev_init(&new_dev.cdev,&key_fops); //文件操作集合映射 ret = cdev_add(&new_dev.cdev,new_dev.dev_id,DEVICE_CNT); if(ret<0){ //cdev初始化异常,跳转至异常处理 goto fail_cdev; } printk("chr dev inited!\r\n"); //自动创建设备节点 new_dev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,DEVICE_NAME); if(IS_ERR(new_dev.class)){ //class创建异常处理 printk("class err!\r\n"); ret = PTR_ERR(new_dev.class); goto fail_class; } printk("dev class created\r\n"); new_dev.device = device_create(new_dev.class,NULL,new_dev.dev_id,NULL,DEVICE_NAME); if(IS_ERR(new_dev.device)){ //设备创建异常处理 printk("device err!\r\n"); ret = PTR_ERR(new_dev.device); goto fail_device; } printk("device created!\r\n"); //gpio外设初始化 ret = beep_init(&new_dev); if(ret<0){ printk("gpio init err\r\n"); goto fail_gpioinit; } //定时器初始化 init_timer(&new_dev.timer); atomic_set(&new_dev.timer_per,value); new_dev.timer.expires = jiffies + msecs_to_jiffies(value); new_dev.timer.function = timer_func; new_dev.timer.data = (unsigned long)&new_dev; add_timer(&new_dev.timer); return ret; fail_gpioinit: fail_device: //device创建失败,意味着class创建成功,应该将class销毁 printk("device create err,class destroyed\r\n"); class_destroy(new_dev.class); fail_class: //类创建失败,意味着设备应该已经创建成功,此刻应将其释放掉 printk("class create err,cdev del\r\n"); cdev_del(&new_dev.cdev); fail_cdev: //cdev初始化异常,意味着设备号已经申请完成,应将其释放 printk("cdev init err,chrdev register\r\n"); unregister_chrdev_region(new_dev.dev_id,DEVICE_CNT); faile_devid: //设备号申请异常,由于是第一步操作,不需要进行其他处理 printk("dev id err\r\n"); return ret; } static void __exit timer_exit(void) { gpio_set_value(new_dev.gpio,1); del_timer(&new_dev.timer); cdev_del(&new_dev.cdev); unregister_chrdev_region(new_dev.dev_id,DEVICE_CNT); device_destroy(new_dev.class,new_dev.dev_id); class_destroy(new_dev.class); gpio_free(new_dev.gpio); } module_init(timer_init); module_exit(timer_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); MODULE_AUTHOR("ZeqiZ");
应用APP
先把应用APP的代码放出来
/** * @file timerAPP.c * @author your name (you@domain.com) * @brief 定时器APP测试程序 * @version 0.1 * @date 2022-07-16 * * @copyright Copyright (c) 2022 * */ #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #define CMD_CLOSE _IO(0xEF,1) #define CMD_OPEN _IO(0xEF,2) #define CMD_PERIOD _IOW(0xEF,3,int) /** * @brief * * @param argc //参数个数 * @param argv //参数 * @return int */ int main(int argc,char *argv[]) { char *filename; //文件名 filename = argv[1]; //文件名为命令行后第二个参数(索引值为1) int value = 0; int ret = 0; //初始化操作返回值 int f = 0; //初始化文件句柄 unsigned int cmd; unsigned int arg; unsigned char str[100]; f = open(filename, O_RDWR); //打开文件 if(f < 0){ printf("file open error\r\n"); return -1; } while(1){ printf("Input CMD:"); ret = scanf("%d",&cmd); //cmd对应 if(ret !=1){ gets(str);//防止卡死 } if(cmd == 1){ //cmd值为1,关闭定时器 ioctl(f,CMD_CLOSE,&arg); } else if(cmd == 2){ //cmd值为2,启动定时器 ioctl(f,CMD_OPEN,&arg); } else if(cmd == 3){ //cmd值为3,设置定时器周期 printf("Input Timer Period="); ret = scanf("%d",&arg); if(ret !=1){ gets(str); } ioctl(f,CMD_PERIOD,&arg); } } close(f); //关闭文件 return 0; }
程序运行以后,先打开驱动文件,然后进入while循环等待键盘输入cmd的值。当输入1时,定时器关闭,输入2时定时器重新启动,输入3时从键盘获取新的周期值