mybatis源码(十一) mybatis插件原理及其应用
mybatis插件:MyBatis提供了扩展机制,能够在执行Mapper时改变SQL的执行行为。这种扩展机制是通过拦截器来实现的,用户自定义的拦截器也被称为MyBatis 插件。MyBatis框架支持对Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、 StatementHandler四种组件的方法进行拦截。
Executor 的创建是在SqlSession创建的时候创建的

private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) { Transaction tx = null; try { // 获取Mybatis主配置文件配置的环境信息 final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment(); // 创建事务管理器工厂 final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment); // 创建事务管理器 tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit); // 根据Mybatis主配置文件中指定的Executor类型创建对应的Executor实例 final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); // 创建DefaultSqlSession实例 return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit); } catch (Exception e) { closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close() throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } }
StatementHandler 的创建是在执行sql语句前创建的,例如:

public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor { public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } @Override public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.update(stmt); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler是在SimpleStatementHandler、PreparedStatementHandler、CallableStatementHandler的构造方法中,调用父类的构造方法实现的

protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); this.executor = executor; this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement; this.rowBounds = rowBounds; this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory(); if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement generateKeys(parameterObject); boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject); } this.boundSql = boundSql; this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql); this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql); }
总之,都是在执行sql前,就创建的对象
1.为什么只能拦截这四种插件呢?
1.mybatis可以根据用户配置的参数创建不同的实例,根据Configuration对象。(这4个组件)
2.mybatis通过工厂方式创建4种组件,在工厂方法中,可以执行拦截逻辑
Configuration类部分代码如下:
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 执行拦截器链的拦截逻辑
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
// 执行拦截器链的拦截逻辑
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 执行拦截器链的拦截逻辑
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
// 根据executor类型创建对象的Executor对象
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 如果cacheEnabled属性为ture,这使用CachingExecutor对上面创建的Executor进行装饰
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 执行拦截器链的拦截逻辑
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
可以看到这四个方法里面,都有一个interceptorChain.pluginAll 的调用过程
pluginAll 返回ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler、Executor的代理对象
可以看下InterceptorChain 的源代码
public class InterceptorChain {
// 通过List对象维护所有拦截器实例
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
// 调用所有拦截器对象的plugin()方法执行拦截逻辑
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
由上代码可以看到,mybatis的拦截器执行链中维护了一个所有拦截器的List集合。拦截器链执行的方法调用是interceptor.plugin(targer),
看下Interceptor接口,里面只有三个方法
public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
Object plugin(Object target);
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
Interceptor接口中定义了3个方法:
intercept()方法用于定义拦截逻辑,该方法会在目标方法调用时执行。
plugin()方法用于创建Executor、ParameterHandler、 ResultSetHandler 或Statementh Handler的代理对象,该方法的参数即为Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler或StatementHandler组件的实例。
setProperties()方法用于设置插件的属性值。
需要注意的是,intercept()接 收一一个Invocation对象作为参数,Invocation对象中封装了目标对象的方法及参数信息。
Invocation类的源代码如下:
Invocation类中提供了一个proceed()方法,该方法用于执行目标方法的逻辑。所以在自定义插件类中,拦截逻辑执行完毕后一般都需要调用proceed()方法执行目标方法的原有逻辑。

public class Invocation { // 目标对象,即ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler或者Executor实例 private final Object target; // 目标方法,即拦截的方法 private final Method method; // 目标方法参数 private final Object[] args; public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) { this.target = target; this.method = method; this.args = args; } public Object getTarget() { return target; } public Method getMethod() { return method; } public Object[] getArgs() { return args; } /** * 执行目标方法 * @return 目标方法执行结果 * @throws InvocationTargetException * @throws IllegalAccessException */ public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException { return method.invoke(target, args); } }
当我们自定义拦截器的时候,需要实现该接口。mybatis中提供了ExamplePlugin类,供我们参考,可以看一下源代码
@Intercepts({})
public class ExamplePlugin implements Interceptor {
private Properties properties;
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// TODO:自定义拦截逻辑
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
// 调用Plugin类的wrap()方法返回一个动态代理对象
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// 设置插件的属性信息
this.properties = properties;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
}
我们深入interceptor.plugin(target);的方法,发现他调用的是Plugin.wrap(target, this); 继续深入,查看PluginPlugin的源代码如下:
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
//目标对象,即Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler对象
private final Object target;
// 用户自定义拦截器实例
private final Interceptor interceptor;
// Intercepts注解指定的方法
private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
/**
* wrap()方法的第一个参数为目标对象,即Executor、ParameterHandler、 ResultSetHandler、 StatementHandler类的实例;
* 第二个参数为拦截器实例。在wrap()方法中首先调用getSignatureMap()方法获取Intercepts注解指定的要拦截的组件及方法,
* 然后调用getAllInterfaces()方法获取当前Intercepts注解指定要拦截的组件的接口信息,接着调用Proxy类的静态方法
* newProxyInstance()创建一个动态代理对象。
* 该方法用于创建Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler的代理对象
*
* @param target
* @param interceptor
* @return
*/
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 调用getSignatureMap()方法获取自定义插件中,通过Intercepts注解指定的方法
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
/**
* Plugin类的invoke()方法会在调用目标对象的方法时执行,在invoke()方法中首先判断该方法是否被Intercepts注解指定为被拦截的方法,如果是,则调用用户自定义
* 拦截器的intercept()方法,并把目标方法信息封装成Invocation对象作为intercept()方法的参数。
*
* @param proxy
* @param method
* @param args
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 如果该方法是Intercepts注解指定的方法,则调用拦截器实例的intercept()方法执行拦截逻辑
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
/**
* Plugin类的getSignatureMap()方法中,首先获取Intercepts注解,然后获取Intercepts注解中配置的所有Signature注解,接着对所有的Signature注解信息进行遍历,
* 将Signature注解中指定要拦截的组件及方法添加到Map对象中,其中
* Key为Executor、 ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler或StatementHandler对应的Class对象,Value为拦截的所有方法对应的Method对象数组。
*
* @param interceptor
* @return
*/
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取Intercepts注解信息
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
// 获取所有Signature注解信息
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, Set<Method>>();
// 对所有Signature注解进行遍历,把Signature注解指定拦截的组件及方法添加到Map中
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type());
if (methods == null) {
methods = new HashSet<Method>();
signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods);
}
try {
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
/**
* 获取目标类型的接口信息
*
* @param type
* @param signatureMap
* @return
*/
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
}
由上述代码,发现Plugin,实现了InvocationHandler 即JDK内置的动态代理方式创建代理对象,同时使用Proxy.newProxyInstance返回了代理对象。
如上面的代码所示,wrap()方法的第一个参数为目标对象,即Executor、ParameterHandler、 ResultSetHandler、 StatementHandler类的实例;第二个参数为拦截器实例。在wrap()方法中首先调用
getSignatureMap()方法获取Intercepts注解指定的要拦截的组件及方法,然后调用getAllInterfaces()方法获取当前Intercepts注解指定要拦截的组件的接口信息,接着调用Proxy类的静态方法
newProxyInstance()创建一个动态代理对象。
2.自定义mybatis插件
2.1mybatis自定义插件,都必须实现Interceptor接口,并在intercept()中编写拦截逻辑
2.2 拦截器上面要添加@Intercepts注解,标注拦截器的类型和拦截的方法
例如:
@Intercepts({
@Signature(method = "prepare", type = StatementHandler.class, args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})
})
public class PageInterceptor implements Interceptor {
2.3 通过plugin()方法返回一个动态代理对象
例如:
/**
* 拦截器对应的封装原始对象的方法
*/
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
2.4通过setProperties方法设置Plugin标签中配置的属性值
例如:
/**
* 设置注册拦截器时设定的属性
*/
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.databaseType = properties.getProperty("databaseType");
}
2.5 mybaits提供了ExamplePlugin的例子供参考

@Intercepts({}) public class ExamplePlugin implements Interceptor { private Properties properties; @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { // TODO:自定义拦截逻辑 return invocation.proceed(); } @Override public Object plugin(Object target) { // 调用Plugin类的wrap()方法返回一个动态代理对象 return Plugin.wrap(target, this); } @Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) { // 设置插件的属性信息 this.properties = properties; } public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } }
3.mybatis插件加载的地方
3.1 在mybatis的plugins标签下面,配置要加载的插件

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> 2 <!DOCTYPE configuration 3 PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" 4 "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> 5 6 <configuration> 7 <settings> 8 <setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="true"/> 9 </settings> 10 11 // 配置插件 12 <plugins> 13 <plugin interceptor="com.blog4java.plugin.pager.PageInterceptor"> 14 <property name="databaseType" value="hsqldb"/> 15 </plugin> 16 17 <plugin interceptor="com.blog4java.plugin.slowsql.SlowSqlInterceptor"> 18 <property name="limitSecond" value="0"/> 19 </plugin> 20 </plugins> 21 22 <environments default="dev" > 23 <environment id="dev"> 24 <transactionManager type="JDBC"> 25 <property name="" value="" /> 26 </transactionManager> 27 <dataSource type="UNPOOLED"> 28 <property name="driver" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver" /> 29 <property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:mybatis" /> 30 <property name="username" value="sa" /> 31 <property name="password" value="" /> 32 </dataSource> 33 </environment> 34 <environment id="qa"> 35 <transactionManager type="JDBC"> 36 <property name="" value="" /> 37 </transactionManager> 38 <dataSource type="UNPOOLED"> 39 <property name="driver" value="org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver" /> 40 <property name="url" value="jdbc:hsqldb:mem:mybatis_qa" /> 41 <property name="username" value="admin" /> 42 <property name="password" value="admin" /> 43 </dataSource> 44 </environment> 45 </environments> 46 47 <mappers> 48 <mapper resource="com/blog4java/mybatis/example/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> 49 </mappers> 50 </configuration>
3.2 从XmlConfigBuilder类开始解析mybaits-config的主配置文件
首先调用XmlConfigBuilder.parse()方法
public Configuration parse() {
// 防止parse()方法被同一个实例多次调用
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// 调用XPathParser.evalNode()方法,创建表示configuration节点的XNode对象。
// 调用parseConfiguration()方法对XNode进行处理
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
然后调用parseConfiguration 解析<configuration>标签
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
然后调用pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); 解析mybatis主配置文件下面的plugins标签
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 获取<plugin>标签的interceptor属性
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
// 获取拦截器属性,转换为Properties对象
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 创建拦截器实例
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
// 设置拦截器实例属性信息
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
// 將拦截器实例添加到拦截器链中
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
由上代码可以看出,循环解析<plugins>标签下面的每一个<plugin> ,然后创建拦截器添加到集合中
Configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance) 的源码如下:
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
刚才说过,interceptorChain内部维护了一个List集合,用来存储拦截器
4.Mybatis插件创建动态代理对象的工作原理
以执行一个查询操作为例,SqlSession是MyBatis中提供的面向用户的操作数据库的接口,而真正执行SQL操作的是Executor组件。MyBatis通过工厂模式创建Executor实例,
Configuration类中提供了一个newExecutor()工厂 方法,该方法返回的实际上是一个Executor的动态代理对象。
SqlSession获取Executor实例的过程如下:
(1) SqlSession中会调用Configuration类提供的newExecutor()工厂方法创建Executor对象。
(2) Configuration类中通过一个InterceptorChain对象维护了用户自定义的拦截器链。newExecutor()工厂方法中调用InterceptorChain对象的pluginAll()方法。
(3) InterceptorChain对象 的pluginAll()方法中会调用自定义拦截器的plugin()方法。
(4)自定义拦截器的plugin()方法是由我们来编写的,通常会调用Plugin类的wrap()静态方法创建一个代理对象。
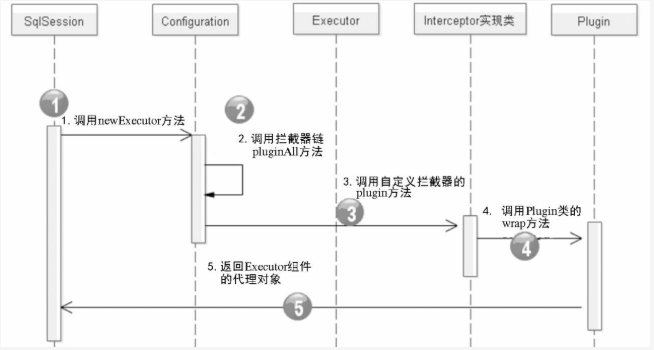
mybatis动态代理对象创建过程
Sq|Session获取到的Executor实例实际上已经是一个动态代理对象了。当我们调用SqlSession对象的selectOne()方法执行查询操作时,大致会经历下面几个过程:
(1)SqlSession操作数据库需要依赖于Executor组件,SqlSession会调用Configuration对象的newExecutor()方法获取Executor的实例。
(2) SqlSession获取到的是Executor组件的代理对象,执行查询操作时会调用代理对象的query()方法。
(3)按照JDK动态代理机制,调用Executor代理对象的query()方法时,会调用Plugin类的invoke()方法。
(4) Plugin类的invoke()方法中会调用自定义拦截器对象的intercept()方法执行拦截逻辑。
(5)自定义拦截器对象的intercept()方法调用完毕后,调用目标Executor对象的query()方法。
(6)所有操作执行完毕后,会将查询结果返回给SqlSession对象。

mybatis插件拦截逻辑执行过程
