Description
Memory is now interested in the de-evolution of objects, specifically triangles. He starts with an equilateral triangle of side length x, and he wishes to perform operations to obtain an equilateral triangle of side length y.
In a single second, he can modify the length of a single side of the current triangle such that it remains a non-degenerate triangle (triangle of positive area). At any moment of time, the length of each side should be integer.
What is the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y?
The first and only line contains two integers x and y (3 ≤ y < x ≤ 100 000) — the starting and ending equilateral triangle side lengths respectively.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of seconds required for Memory to obtain the equilateral triangle of side length y if he starts with the equilateral triangle of side length x.
6 3
4
8 5
3
22 4
6
In the first sample test, Memory starts with an equilateral triangle of side length 6 and wants one of side length 3. Denote a triangle with sides a, b, and c as (a, b, c). Then, Memory can do 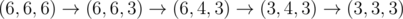 .
.
In the second sample test, Memory can do 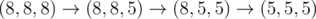 .
.
In the third sample test, Memory can do: 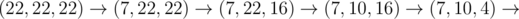
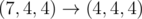 .
.
题意:将一个大的等边三角形变为小的等边三角形,最小需要几步
解法:我们倒过来考虑要方便很多,先增加其中一条边到最大,然后增加第二条边,依次循环到大的等边三角形
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,m;
int a,b,c;
int pos;
int cot=0;
cin>>n>>m;
a=m,b=m,c=m;
while(a!=n||b!=n||c!=n)
{
if(a!=n)
{
int pos1;
//cout<<"A"<<endl;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
// cout<<"B"<<endl;
// cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;
if((a+i)+b>c&&(b+c)>(a+i)&&(a+i)+c>b&&(a+i)<=n)
{
pos1=i;
// cot++;
}
}
a=a+pos1;
cot++;
// cout<<a<<endl;
// break;
// cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;
}
// cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;
// break;
if(b!=n)
{
int pos2;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
// cout<<"B"<<endl;
if((b+i)+a>c&&(a+c)>(b+i)&&(b+i)+c>a&&(b+i)<=n)
{
// b=b+i;
pos2=i;
//cot++;
}
}
b=b+pos2;
cot++;
// cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;
}
// cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;
// break;
if(c!=n)
{
int pos3;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if((c+i)+a>b&&b+(c+i)>a&&b+a>c+i&&(c+i)<=n)
{
// cout<<i<<endl;
pos3=i;
// c=c+i;
// cot++;
}
}
c=pos3+c;
cot++;
// cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;
}
// break;
// cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;*/
}
cout<<cot<<endl;
return 0;
}