1.认识Spring
Spring是一个开源的控制反转(Inversion of Control ,IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架.它的主要目得是简化企业开发.
(1)IoC 控制反转:
public class PersonServiceBean { private PersonDao personDao = new PersonDaoBean(); public void save(Person person){ personDao.save(person); } }
PersonDaoBean 是在应用内部创建及维护的。所谓控制反转就是应用本身不负责依赖对象的创建及维护,依赖对象的创建及维护是由外部容器负责的。这样控制权就由应用转移到了外部容器,控制权的转移就是所谓反转。 [依赖对象:personDao ,应用可以看作是自己写的方法,而外部容器就是框架,Spring就是其中的一种,可以负责依赖对象的创建及维护]
(2)依赖注入:
当我们把依赖对象交给外部容器负责创建,那么PersonServiceBean 类可以改成如下:
public class PersonServiceBean { private PersonDao personDao ; //通过构造器参数,让容器把创建好的依赖对象注入进PersonServiceBean,当然也可以使用setter方法进行注入。 public PersonServiceBean(PersonDao personDao){ this.personDao=personDao; } public void save(Person person){ personDao.save(person); } }
所谓依赖注入就是指:在运行期,由外部容器动态地将依赖对象注入到组件中。
[这里是通过构造器中指定一个PersonDao 参数将依赖对象实例(实现该接口的类)注入到PersonServiceBean中,除此之外,还可以使用set方法注入]
(3)为何要使用Spring
在项目中引入spring立即可以带来下面的好处:
- 降低组件之间的耦合度,实现软件各层之间的解耦。 Controller –> Service –> DAO
- 可以使用容器提供的众多服务,如:事务管理服务、消息服务等等。当我们使用容器管理事务时,开发人员就不再需要手工控制事务.也不需处理复杂的事务传播。
- 容器提供单例模式支持,开发人员不再需要自己编写实现代码。
- 容器提供了AOP技术,利用它很容易实现如权限拦截、运行期监控等功能。
- 容器提供的众多辅作类,使用这些类能够加快应用的开发,如: JdbcTemplate、 HibernateTemplate。
- Spring对于主流的应用框架提供了集成支持,如:集成Hibernate、JPA、Struts等,这样更便于应用的开发。
- Spring提供的众多服务:
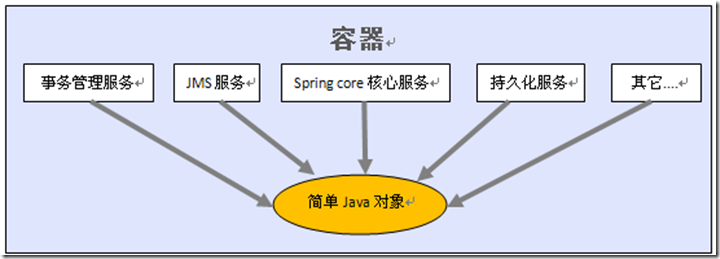
- 如果使用Spring,就不用手工的控制事务
Hibernate的事务操作: public void save(){ Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
session.beginTransaction();Info info = new Info("传智播客"); info.setContent("国内实力最强的java培训机构"); session.save(info );session.getTransaction().commit();} JDBC的事务操作: Connection conn = null; try { .......conn.setAutoCommit(false);Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); stmt.executeUpdate("update person where name='叶天'");conn.commit();.....} catch (Exception e) {conn.rollback(); } finally{conn.close();} - 如果使用spring, 也不需要处理复杂的事务传播行为
public void payment(){ Bean1.update();//更新金额 Bean2.save();//记录操作日志 } 如果我们不使用Spring,针对下面这两种业务需求,我们该如何做? 第1种可能的业务需求:要求Bean1.update()和Bean2.save()在同一个事务中执行。 第2种可能的业务需求:要求不管Bean1.update() 的事务是否成功,都需要记录操作日志。 public class Bean1 { public void update(){//注意:下面省略了一些代码 Connection conn = null; conn.setAutoCommit(false); Statement.executeUpdate(“update account set amount=? where id=?"); } } public class Bean2 { public void save(){//注意:下面省略了一些代码 Connection conn = null; conn.setAutoCommit(false); Statement.executeUpdate(“insert into Log (content) values (?)"); }
解决方案:
使用Spring,我们只需要通过声明式的事务属性配置就可以轻松地实现这两种业务需求 1.要求Bean1.update()和Bean2.save()的在同一个事务中执行 2.要求不管Bean1.update() 的事务是否成功,都需要记录日志。 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.Required) public void payment(){ Bean1.update();//更新金额 Bean2.save();//记录日志 } public class Bean1 { @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.Required) public void update(){ executeUpdate(“update account set amount=? where id=?"); } } public class Bean2 { @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.RequiresNew) public void save(){ executeUpdate(“insert into Log (content) values (?)"); } }
* 轻量级与重量级概念的划分
经常会有人问到spring属于轻量级框架,还是重量框架?其实划分一个应用是否属于轻量级还是重量级,主要看它使用了多少服务.使用的服务越多,容器要为普通java对象做的工作就越多,必然会影响到应用的发布时间或者是运行性能.
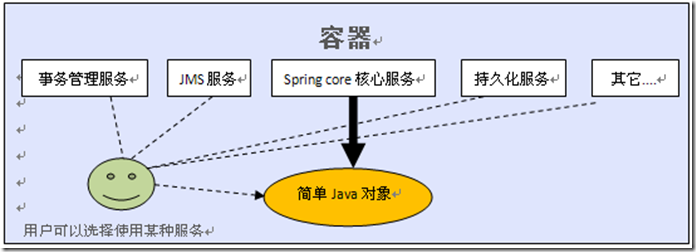
对于spring容器,它提供了很多服务,但这些服务并不是默认为应用打开的,应用需要某种服务,还需要指明使用该服务,如果应用使用的服务很少,如:只使用了spring核心服务,那么我们可以认为此时应用属于轻量级的,如果应用使用了spring提供的大部分服务,这时应用就属于重量级。目前EJB容器就因为它默认为应用提供了EJB规范中所有的功能,所以它属于重量级。
2.搭建环境
下载spring的地址: http://www.springsource.org/download
然后进行解压缩,在解压目录中找到下面jar文件,拷贝到类路径下
dist\spring.jar
lib\jakarta-commons\commons-logging.jar
如果使用了切面编程(AOP),还需要下列jar文件
lib/aspectj/aspectjweaver.jar和aspectjrt.jar
lib/cglib/cglib-nodep-2.1_3.jar
如果使用了JSR-250中的注解,如@Resource/@PostConstruct/@PreDestroy,还需要下列jar文件
lib\j2ee\common-annotations.jar
配置文件的模板:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> ..... </beans> 该配置模版可以从spring的参考手册或spring的例子中得到。配置文件的取名可以任意,文件可以存放在任何目录下,但考虑到通用性,一般放在类路径下。
3.”编写spring配置文件时,不能出现帮助信息”的问题的解决方法
由于spring的schema文件位于网络上,如果机器不能连接到网络,那么在编写配置信息时候就无法出现提示信息,解决方法有两种:
1。让机器上网,eclipse会自动从网络上下载schema文件并缓存在硬盘上。
2。手动添加schema文件,方法如下:
windwos->preferences->myeclipse->files and editors->xml->xmlcatalog
点"add",在出现的窗口中的Key Type中选择URI,在location中选"File system",然后在spring解压目录的dist/resources目录中选择spring-beans-2.5.xsd,
回到设置窗口的时候不要急着关闭窗口,应把窗口中的Key Type改为Schema location,
Key改为http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
4.Junit测试
单元测试这个功能很好,可以单独的测试某个方法
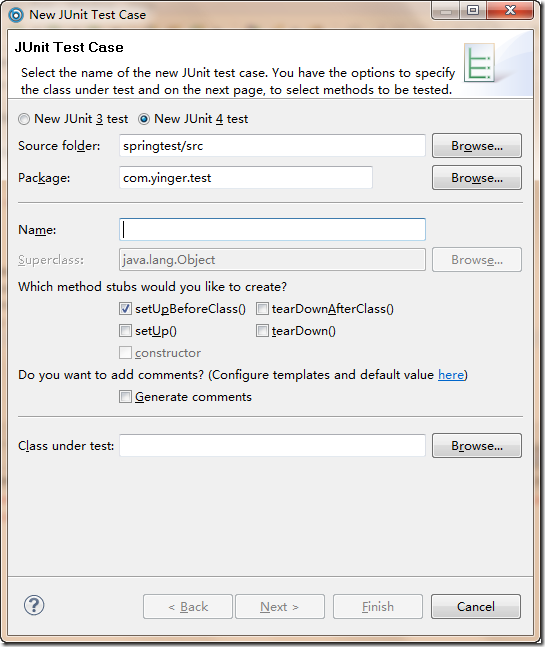
在Myeclipse中新建一个 “ JUnit Test Case ”,选择 new JUnit 4 test
然后填上Test的名称,以及所需要创建的方法
最后如果提示当前 build path 中没有 JUnit 4,那么就要 add,加入到path中的JUnit 4是Myeclipse Blue Edition安装时的存放的
如下图所示:
Class Under Test表示测试的类,可以不指定
5.第一个测试例子:
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd"> <bean id="personService" class="com.yinger.service.impl.PersonServiceBean"></bean> </beans>
接口: PersonService
package com.yinger.service; public interface PersonService { public void save(); }
实现类:PersonServiceBean
package com.yinger.service.impl; public class PersonServiceBean implements com.yinger.service.PersonService{ public void save() { System.out.println("save"); } }
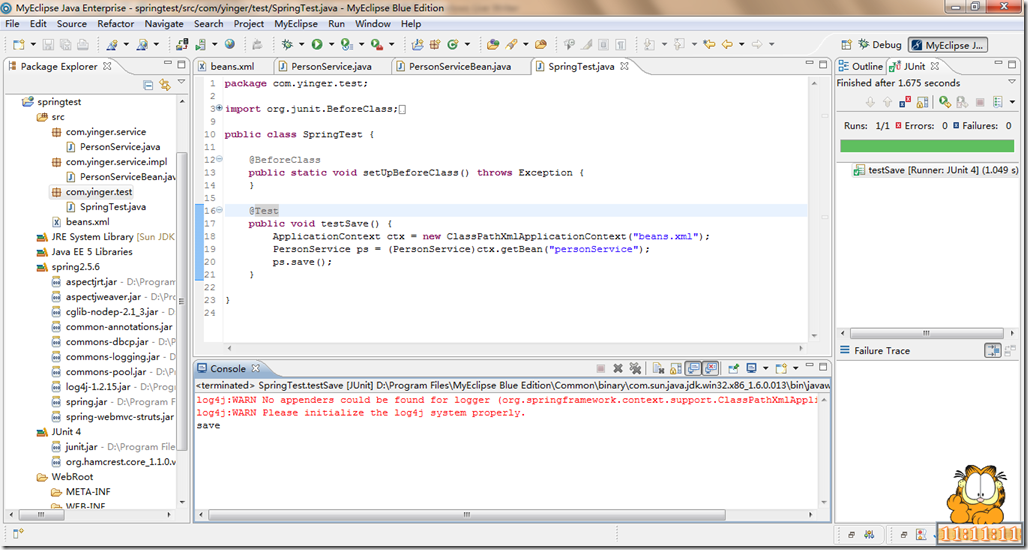
JUnit Test:
package com.yinger.test; import org.junit.BeforeClass; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.yinger.service.PersonService; public class SpringTest { @BeforeClass public static void setUpBeforeClass() throws Exception { } @Test public void testSave() { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); PersonService ps = (PersonService)ctx.getBean("personService"); ps.save(); } }
好了,然后 Run as –> JUnit Test
结果是: 最后一行输出了 save!呵呵,表示示例成功了!
log4j:WARN No appenders could be found for logger (org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext).
log4j:WARN Please initialize the log4j system properly.
save
文档结构目录:
仔细查看写过的代码,这不难理解IoC(控制反转)了!