创建线程
new MyThread().start();
new Thread(new MyRun()).start();
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("Hello Lambda!");
}).start();
常见方法
- sleep
- yield 让出线程,从running到ready状态
- join 线程A中调用B.join(),表示A让B先执行
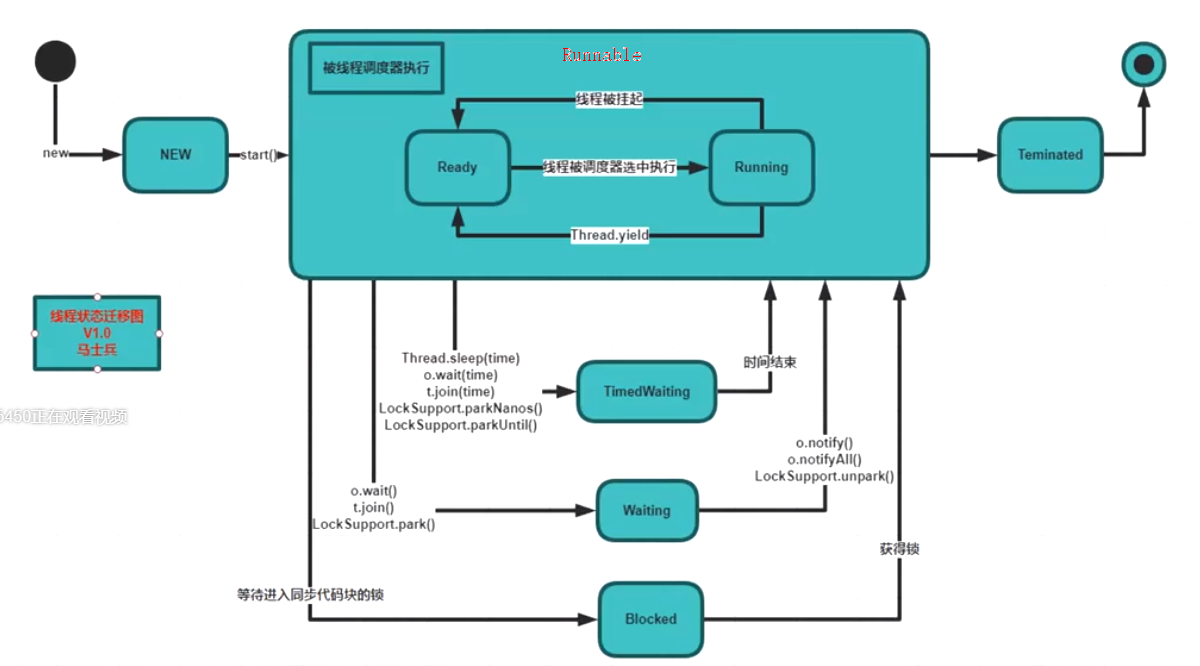
线程状态
总共6大块,分别是:new,runnable,timedwaiting,waiting,blocked,terminated
synchronize
原理:对象头(mark word)上有两位(00,01),表示不同类型的锁
同一个对象中的两个非静态synchronize方法,不能同时执行,由此可见,非静态的synchronize方法锁住的对象是当前对象,也就是和synchronize(this)等效
synchronize是可重入锁:两个synchronize方法A和B,A可以调用B,B也可以调用A
锁定的区域发生异常,默认情况下锁会被释放,写业务代码时要小心
synchronize的底层实现:
JDK早期,重量级锁
后来有锁升级的概念,第一次只在对象头记录线程的id,叫偏向锁;如果线程争用,升级为自旋锁;自旋10次之后,升级为重量级锁,也就是系统锁;
锁无法降级;
自旋锁是用户态,加锁和解锁快;重量级锁是内核态,效率低;
什么情况用自旋锁,什么情况用系统锁?运行时间长、线程多用重量级锁;反之用自旋锁
volatile
- 线程可见性
- 禁止指令重排
单例模式双重检查锁需要加volatile,答案是需要,原因就是指令重排(对象创建步骤可能重排序,如3和2交换:1、创建对象并赋初始值 2、赋值 3、变量指向堆内存)
其他并发控制类
- ReentrantLock
可以替换synchronize,功能比synchronize强大
lock&unlock 不能自动解锁,所以unlock一定要在finally中
trylock - CountDownLatch
功能和join一样
latch.countDown()
latch.await() - CyclicBarrier
满足一定数据量的线程后,一起启动 - ReentrantReadWriteLock
读锁=共享锁 readWriteLock.readLock();
写锁=排它锁=互斥锁 readWriteLock.writeLock();
读的时候,其他线程也可以读;写的时候,其他写线程都阻塞 - Semaphore
信号量,灯亮了可以执行,灭了不能执行
Semaphore s = new Semaphore(2);可以限流,最多2个线程执行
AQS
ReentrantLock、CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier都是AQS的实现,AQS的核心是含有一个volatile修饰的state,这个state由实现类维护,和一个包含Thread的双向链表(Node)
面试题:两个线程交替打印A1B2C3D4(可重入锁特性)
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
App app = new App();
Thread t1 = new Thread(app::printABC);
Thread t2 = new Thread(app::print123);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
public synchronized void printABC() {
String str = "ABCDEFG";
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(str.charAt(i));
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void print123() {
String str = "1234567";
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(str.charAt(i));
this.notify();
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
this.notify();
}
}
生产者消费者实现
public class MyContainer2<T> {
final private LinkedList<T> lists = new LinkedList<>();
final private int MAX = 10; //最多10个元素
private int count = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition producer = lock.newCondition();
private Condition consumer = lock.newCondition();
public void put(T t) {
try {
lock.lock();
while (lists.size() == MAX) { //想想为什么用while而不是用if?
producer.await();
}
lists.add(t);
++count;
consumer.signalAll(); //通知消费者线程进行消费
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public T get() {
T t = null;
try {
lock.lock();
while (lists.size() == 0) {
consumer.await();
}
t = lists.removeFirst();
count--;
producer.signalAll(); //通知生产者进行生产
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyContainer2<String> c = new MyContainer2<>();
//启动消费者线程
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println(c.get() + " OUT:" + new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()) + " left:" + c.count);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
//生产者延迟2秒启动
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//启动生产者线程
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
c.put(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " IN:" + new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "product" + i).start();
}
}
}
自定义线程池
public class App3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
App3 app3 = new App3();
app3.test();
}
public void test() {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
3, 3, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10000),
new MyThreadFactory("MyThreadGroup"),
new MyRejectedExecutionHandler());
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
pool.execute(new MyThread(i));
}
pool.shutdown();
}
class MyThread implements Runnable {
int id;
public MyThread(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " id=" + id);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "id=" + id;
}
}
class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
String threadGroup;
AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(1);
MyThreadFactory(String threadGroup) {
this.threadGroup = threadGroup;
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
String threadName = threadGroup + "-" + nextId.getAndIncrement();
Thread thread = new Thread(r, threadName);
return thread;
}
}
class MyRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
System.out.println("任务被拒绝 " + r);
}
}
}