1 手机和电脑用数据线连接
使用通过数据线连接手机,将开发者模式打开并授权
通过adb_tools工具,在目录下输入adb命令
|
adb devices |
可以查看连接的Android设备的信息
2 获取手机相关的信息
通过如下命令可以查看连接电脑的Android手机相关的信息
|
adb shell dumpsys window displays |
获取屏幕密度
|
adb shell wm density |

获取手机型号
|
adb shell getprop ro.product.device |

获取Android系统的版本
|
adb shell getprop ro.build.version.release |

3 截屏
输入如下命令:
|
adb shell screencap -p /sdcard/auto.png |
此时,截屏的图片就保存到 /sdcard/auto.png文件中。
注意:/sdcard/和/data/目录是可以写入的。
可以通过命令
|
adb shell ls /sdcard/ -l |
查看sdcard目录下所有的文件。
通过如下命令把手机上的文件拷贝到电脑上
|
adb pull /sdcard/auto.png d: |
此时,图片就会被拷贝到D盘根目录下了。打开即可看到当前手机的屏幕信息。
4 屏幕点击事件
通过如下命令模拟手机的滑动事件
|
adb shell input swipe x1 y1 x2 y2 duration |
通过adb shell input swipe命令进行滑动
l x1、y1:滑动开始的点。
l x2、y2:滑动结束的点。
l duration:持续的时间(单位ms)。
特殊情况下:如果不写duration参数,就理解为点击事件。如果写duration,然后x1y1和x2y2是相同的点,就表示长按。
跳一跳关键是:duration的值的计算。
尝试:
|
adb shell input swipe 100 100 100 100 700 |
尝试修改duration的值,看看跳的效果。
求得可以拿到加分的中间值。比如555~871都可以拿到加分(555以下和871以上就不能拿到加分),此时则取中间值为(555+871)/2=713 作为后面计算的参考值。
5 duration值的计算
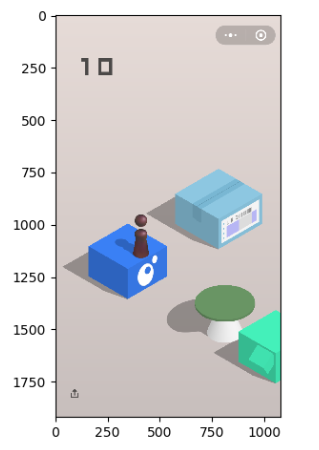
假设我们截屏的效果是如下:

从图中可以看到,时间的值跟开始位置到结束位置的距离有关。
假设时间是t,距离是s。公式应该是s = at
基本思路:两点之间的距离乘以一个时间系数。
所以要从截图上识别出起跳位置的坐标(x1,y1)和目标位置的坐标(x2,y2)。
起跳位置的坐标:小人的底座中心点
目标位置的坐标:目标菱形的中心点
然后计算这两点之间的距离(欧氏距离):sqrt((x1-x2)2+(y1-y2)2)
6 截屏的代码
创建img目录,后面把所有截屏的图片都放到该目录下(原则上每跳一步都需要截屏一次)
operation.py
|
import os import datetime from PIL
import Image # 实现控制Android设备等相关的操作 class Operation: # 构造方法 def __init__(self): pass # 截屏 def screen_cap(self): filename =
time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%H%M%S") + ".png" # 截屏并保存到手机的目录上 cmd = "adb shell screencap -p
/sdcard/auto.png" os.system(cmd) # 把手机目录上的文件拷贝到PC上 cmd = "adb pull /sdcard/auto.png" + "
img/" + filename
os.system(cmd) # 打开图像文件 # return Image.open(filename)
|
main.py
|
from .operation import * |
|
# 测试截屏 def test_screen_cap(): op = Operation() op.screen_cap()
|
7 显示图片的代码
需要安装matplotlib库
|
pip install matplotlib |
需要安装opencv的库
|
pip install opencv-python |
draw.py
|
import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt # 绘图 import cv2 # 读取图片文件 # 实现显示图片 绘制图片等功能 class Draw: # 构造器 def __init__(self): # 初始化图像plt对象 self.fig = plt.figure() # 显示图片 def show_pic(self,
filename,scale=1): # 读取图像 img = cv2.imread(filename) # 调整显示的比例 img = cv2.resize(img, (0,0), fx=scale, fy=scale) # 显示图像 plt.imshow(img) plt.show()
|
main.py
|
# 测试显示图片 def test_show_pic(): draw = Draw() draw.show_pic("img/auto.png")
|
8 计算两点之间的欧氏距离
创建文件algorithm.py文件,添加计算欧氏距离的方法
algorithm.py
|
# 算法类 class Algorithm: # 构造器 def __init__(self): pass # 计算两点之间的欧氏距离 # p1和p2表示两个点 用元组来表示 def euclidean_distance(self,p1,p2): return ((p1[0] - p2[0])**2 + (p1[1] - p2[1])**2) ** 0.5
|
main.py
|
# 测试计算欧氏距离 def test_euclidean_distance(): algorithm = Algorithm() p1 = (3,4) p2 = (6,8) d =
algorithm.euclidean_distance(p1,p2) print(d)
|
9 寻找关键坐标——框架
关键是查找起跳点的坐标和目标点的坐标。
在algorithm.py中添加方法find_point()
|
# 寻找关键坐标 # 返回值1,2 start_x, start_y 起跳点的坐标 170,555 # 返回值3,4 end_x, end_y 目标点的坐标 395,425 def find_point(self): start_x = start_y = 0 end_x = end_y = 0 return start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y
|
main.py
|
# 测试寻找关键坐标 def test_find_point(): algorithm = Algorithm() start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y =
algorithm.find_point() print("start_point:",
start_x, start_y) print("end_point:", end_x, end_y)
|