一、String的定义
Java中的String在java.lang.String中定义。
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
private final char value[];
......
}
一旦创建了String对象(构造函数初始化),那它的值就无法改变了。如果需要对字符串做修改,只能通过StringBuffer和StringBulder类和方法。
二、String类常用的静态方法
1. 格式化字符串
public static String format(String format, Object... args)
样例1:
String tempString;
tempString = String.format(“整数是:%d,字符串是:%s”, 100, “hello”)
样例2:
String.format("Ni hao %s!",name);
样例3:
String.format("%04d", 22); //25为int型
//打印 0022
- 0 代表前面要补的字符
- 4 代表字符串长度
- d 表示参数为整数类型
样例4:
String name = “xiaoli”;
String.format("%8s!",name);
- 8 把字符串格式化为长度为8,补充空白字符。
format相关参数格式:


2. 把 对象/数组/基础类型 转换为字符串
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
public static String valueOf(char data[]) { return new String(data); }
public static String valueOf(char data[], int offset, int count)
public static String copyValueOf(char data[]) { return new String(data); }
public static String copyValueOf(char data[], int offset, int count)
public static String valueOf(boolean b) { return b ? "true" : "false"; }
public static String valueOf(char c)
public static String valueOf(int i)
//.....还支持long、float、double类型
样例:
char[] helloArray = {‘H’,’e’,’l’,’l’,’o’};
System.out.pringln(copyValueOf(hellArry, 2, 4)); //函数返回字符串是“llo”
三、String类常用的方法
1. String的构造方法
(1)创建内容为空的String对象
public String() { this.value = "".value; }
(2)根据字符串创建String对象
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
样例:
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
(3)根据 数组[] 创建 String对象
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}
public String(char value[], int offset, int count)
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count)
public String(byte bytes[])
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length)
public String(byte ascii[], int hibyte)
public String(byte ascii[], int hibyte, int offset, int count)
public String(byte bytes[], String charsetName)
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, Charset charset)
public String(byte bytes[], Charset charset)
样例:
char[] helloArray = {‘H’,’e’,’l’,’l’,’o’};
String tempString = new String(helloArray);
(4)根据StringBuilder创建String对象
public String(StringBuffer buffer)
(5)根据StringBuffer创建String对象
public String(StringBuilder builder)
2. 判断String长度方法
(1)获取长度
public int length()
样例:
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString.length());
(2)判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
3. 从String中返回字符串index位置的字符,返回值类型为char基础类型
public char charAt(int index)
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
char ch = tempString.charAT(6); //返回结果是W字符
4. 返回指定 字符/字符串 在字符串中首次/最后一次出现位置
int indexOf(int ch)
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) //fromIndex可以字符串开发搜索的位置索引
int indexOf(String str)
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
int lastIndexOf(int ch)
int lastIndexOf (int ch, int fromIndex)
int lastIndexOf (String str)
int lastIndexOf (String str, int fromIndex)
样例:
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString.indexOf (“or”, 5));
5. 判断String字符串以xxx开头/结尾
(1)判断String指定偏移开始是否以xxx为开头
boolean startsWith(String prefix)
boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) //其中toffset指定字符串中开始查找的位置
(2)判断String字符串以xxx结尾
public boolean endsWith(String suffix)
样例:
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString.endsWith(“ld”));
5. 字符串比较
(1)比较两个String字符串是否一致:
public boolean equals(Object anObject) //anObject不是String类型,则返回fase
public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer sb)
private boolean nonSyncContentEquals(AbstractStringBuilder sb)
(2)忽略大小写比较两个String字符串是否一致:
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
(3)按字典序比较两个字符串
//逐个按照字典序比较字符,此字符串大于参数的字符串,返回>0的数;相等返回0。
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
样例:
String tempString1 = “Hello”;
String tempString2 = “HeLLo!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString1.compareTo(tempSting2));
(4)忽略大小写按字典序比较两个字符串
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
6. 字符串拼接
(1) 使用+进行拼接
更常见的使用方式是String1 + Sting2
样例:
String tempString1 = “Hello”;
String tempString2 = “World!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString1 + “ ” + tempString2);
(2)使用concat()方法拼接
public String concat(String str)
样例:
String tempString1 = “Hello”;
String tempString2 = “World!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString1.concat(tempString2));
7. 字符串拆分
String类提供了split()方法,其作用是把String按照指定要求拆分成String[]数组。
split()方法定义如下:
public String[] split(String regex) //根据正则表达式拆分此字符串
public String[] split(String regex, int limit) //根据正则表达式拆分此字符串,limit指定分割的份数
(1)样例一:按照,号拆分字符串
String str = "1,2,3,4,5,6";
String[] strArr = str.split(",");
system.out.println(strArr)// ["1","2","3","4","5","6"]
注:如果用“.”或“|”作为分隔,必须使用转义写法:
String.split("\.")
String.split("\|")
(2)样例二:按照空白字符分割
String str = "java cpp php c# objective-c";
String[] strArr = str.split("\s");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strArr));// [java, cpp, php, c#, objective-c]
(3)样例三:按照按+、-、=符号拆分
String line = "100+200-150=150";
strArr = line.split("[\+\-=]");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strArr));//[100, 200, 150, 150]
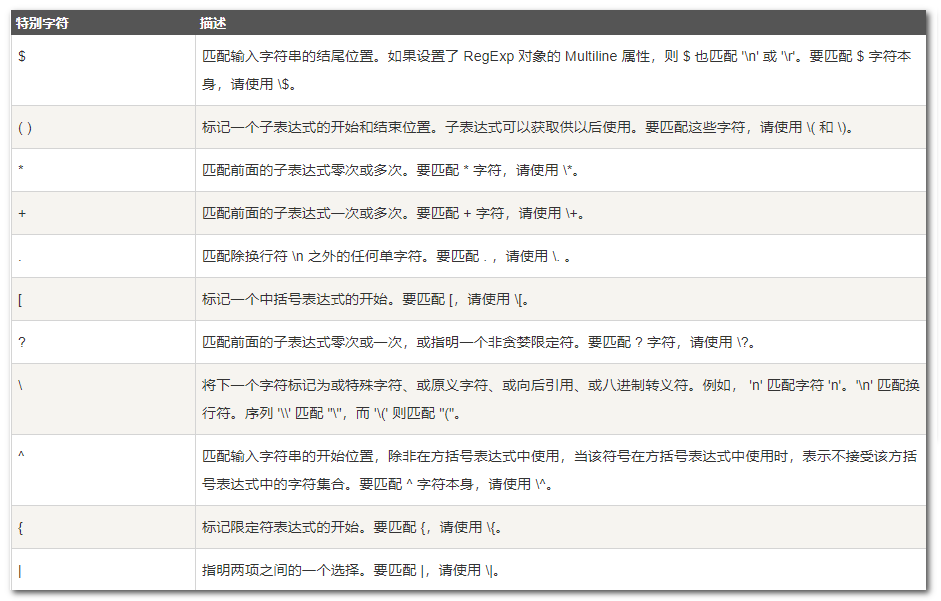
常用正则表达式字符参考:
(1)非打印字符
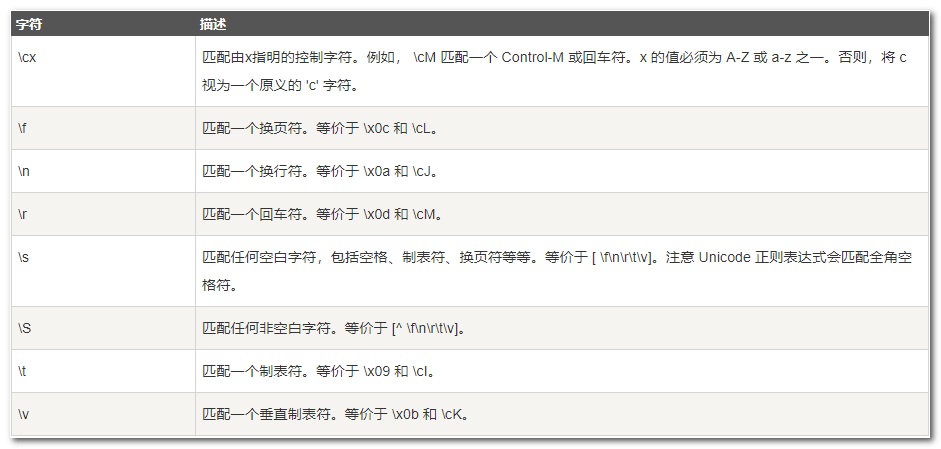
(2)特殊字符
8.指定索引返回子字符串
String substring(int beginIndex)
注:如下子字符串不包含endIndex对应内容,因为其实现原理是获取beginIndex开始(包含beginIndex)、len为endIndex-beginIndex的子字符串。
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
9. 字符串大小写转换
String toLowerCase()
String toLowerCase(Locale locale) //locale参数为指定的规则
String toUpperCase()
String toUpperCase(Locale locale)
10. 替换字符串中指定字符/字符串
(1)把字符串中所有oldChar字符替换成newChar字符:
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
样例:
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString.replace(‘o’, ‘T’));
11. 根据正则表达式替换字符串中指定内容
//替换字符串中所有匹配regex正则表达式的子串
public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceAll(replacement);
}
//替换字符串中所有匹配regex正则表达式的第一个子串
public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceFirst(replacement);
}
样例:
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
System.out.pringln(tempString.replaceFirst(“or(\.\*)”,“AA”)); //替换后的内容Hello WAA
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
String[] resultString = tempString.replaceFirst(“\.{1}o, "AA"); //表达式意思是o前1个任意字符
12. 字符串匹配是否匹配正则表达式
样例:
string str = "I have one box!";
Pattern regex = Pattern.compile(".*(One|Two|Three|Four|Five|Six|Seven|Eight|Nine|Zero)+.*");
if(regex.matcher(str).matches()) { //matches()方法返回boolean,判断是都匹配
System.out.println("matched");
}
13. 字符串反转
字符串反转需要用到StringBuffer封装类。
样例:
String str = "Hello World!";
String reverse = new StringBuffer(str).reverse().toString();
14. 字符串转换为数组
public char[] toCharArray()
void getChars(char dst[], int dstBegin)
public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin)
public void getBytes(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, byte dst[], int dstBegin)
public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName)
样例:
String tempString = “Hello World!”;
char[] strChar = tempString.toCharArray();
三、String和数字类型之间转换
1. 字符串与整数数字互相转换
(1)把字符串转换为整数:用的java.lang.Integer中的parseInt方法
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException //默认是10进制字符串
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException //redix表示字符串的进制数
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException //默认是10禁止字符串
public static int parseUnsignedInt(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException
Integer类的如下静态方法,本质上最终调用也是parseInt静态方法:
public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException
public static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException
如下构造方法,最终调用的也是parseInt静态方法:
public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException //调用的约束parseInt方法
parseInt()方法转换样例:
* parseInt("0", 10) returns 0
* parseInt("473", 10) returns 473
* parseInt("+42", 10) returns 42
* parseInt("-0", 10) returns 0
* parseInt("-FF", 16) returns -255
* parseInt("1100110", 2) returns 102
* parseInt("2147483647", 10) returns 2147483647
* parseInt("-2147483648", 10) returns -2147483648
* parseInt("2147483648", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("99", 8) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("Kona", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("Kona", 27) returns 411787
样例:
g s="123456";
int b=Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println(b);
(2)整数转换为字符串:Integer的toString方法
//把整数转换成 字符数组
static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf)
//最终调也调用到getChars
public static String toString(int i)
//转换成制定进制的字符串
public static String toString(int i, int radix)
//对象方法
public String toString()
//shift参数用于区分不同进制,比如二进制的shift=1;八进制的shift=3;十六进制的shift=4。
private static String toUnsignedString0(int val, int shift)
public static String toHexString(int i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 4);
}
public static String toOctalString(int i) {
return toUnsignedString0(i, 3);
}
(3)如果期望对转换后的字符串,进行前面加0补足长度,可以采用:
String.format("%06",intStr); //其中0表示补零而不是补空格,6表示至少6位
2. 字符串与浮点数字互相转换
类似,详见java.lang,Double中定义。
四、字符串与日期类型转换
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
项目过程中,经常遇到需要字符串格式的日期和Date类型的日期之间的相互转换。使用SimpleDateFormat类,可以方便完成想要的转换。
(1)Data类
public Date(String s) {
this(parse(s));
}
SimpleDateFormat能够实现本地化的时间格式化及转换。从选定一个自定义的模式(pattren)开始,模式由已经定义好的 'A' to 'Z' 及 'a' to 'z'字母组成,也可以在模式中引入文本,但要使用(单括号)括住。下图就是已经定义好的模式字母表:
| Letter | Date or Time Component | Presentation | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
G |
Era designator | Text | AD |
y |
Year | Year | 1996; 96 |
Y |
Week year | Year | 2009; 09 |
M |
Month in year | Month | July; Jul; 07 |
w |
Week in year | Number | 27 |
W |
Week in month | Number | 2 |
D |
Day in year | Number | 189 |
d |
Day in month | Number | 10 |
F |
Day of week in month | Number | 2 |
E |
Day name in week | Text | Tuesday; Tue |
u |
Day number of week (1 = Monday, ..., 7 = Sunday) | Number | 1 |
a |
Am/pm marker | Text | PM |
H |
Hour in day (0-23) | Number | 0 |
k |
Hour in day (1-24) | Number | 24 |
K |
Hour in am/pm (0-11) | Number | 0 |
h |
Hour in am/pm (1-12) | Number | 12 |
m |
Minute in hour | Number | 30 |
s |
Second in minute | Number | 55 |
S |
Millisecond | Number | 978 |
z |
Time zone | General time zone | Pacific Standard Time; PST; GMT-08:00 |
Z |
Time zone | RFC 822 time zone | -0800 |
X |
Time zone | ISO 8601 time zone | -08; -0800; -08:00 |
在一个模式中,模式字母可以重复,不同数量的字母代表不同的意思:
- text类型:格式化时,如果模式字母数量大于等于4,则使用完整格式表示(EEEE表示要将星期名字格式化为非缩写如Monday);转换时,结果不受字母数量的影响,都接受。
- number类型:格式化时,模式字母的重复次数就是格式化后最小位数,不够的用0填充(如"dddd"表示将日期格式化为4为数字,但日期最大为2为,所以导致高两位的数字被0填充,0011,表示11日);转换时:同格式化类似。
- Month类型:格式化时:如果模式字母重复次数大于或等于3,则被解释为text类型(July,Jul等),否则就解释为数字型。转换时:模式要和被转换的字符串对应,例如月份"12"对应的模式为"MM"或者"M",但是不能为"MMM",除非字符串为"OCT"或者"October";
样例:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Date date = new Date();
String strDateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(strDateFormat);
System.out.println(sdf.format(date));
}
}