Mybatis学习文档
更新于2021/09/01 22:32
Mybatis是持久层框架类似于Hibernate的orm持久层框架
一.自定义持久层框架
mybatis雏形
1.1 分析JDBC问题
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet =null;
try{
//加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//通过驱动管理类获取数据库连接
connection= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/vuetest?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai","root","manager");
//定义sql语句,?表示占位符
String sql = "select * from user where username =?";
//获取预处理statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数,第一个参数为sql语句中参数的序号,第二个参数设置为参数值
preparedStatement.setString(1,"张老师");
//发出sql执行请求,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username =resultSet.getString("username");
System.out.println("id:"+id+" username: "+username);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (resultSet != null){
try {
resultSet.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null){
try {
preparedStatement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 数据库配置信息存在硬编码问题,频繁创建和打开、关闭数据链接,太消耗资源
- Sql语句存在硬编码,不利于维护,实际使用中sql变化较大,sql变动需要更改java代码
- Sql参数设置硬编码(主要是使用prepareStatement向占有位符号传参数存在硬编码),因为sql语句的where条件不一定,所以修改sql还需要修改代码,不利于维护
- 结果集获取与遍历复杂,存在硬编码,sql变化导致解析代码发生变化,不利于维护,如果将数据库记录封装成一个pojo对象解析比较方便。
1.2 问题解决思路
- 使用数据库连接池初始化连接资源
- 使用配置文件解决硬编码问题
- 使用反射、内省等底层技术,自动将实体与表进行属性域字段的自动映射。
1.3 自定义框架设计
使用端:(项目)引入自定义持久层框架的jar包
- 提供两部分配置信息:数据库配置信息、sql配置信息:包括sql语句、参数类型、返回值类型
- 使用配置文件来提供这两部分配置信息
- sqlMapConfig.xml:存放数据库配置信息,存放mapper.xml的全路径
- mapper.xml:存放sql配置信息
框架端:(工程,自定义持久层框架本身)本质就是对JDBC代码进行封装
-
加载配置文件:根据配置文件路径,加载配置文件成字节输入流,存储在内存中
创建Resource类 方法:InputStream getResourceAsSteam(String path)
-
创建两个JavaBean:(容器对象):存放对配置文件解析出来的内容
Configuration:核心配置类,存放sqlMapConfig.xml解析出来的内容
MappedStatement:映射配置类,存放mapped.xml解析出来的内容
-
解析配置文件: dom4j
创建类:SqlSessionFactoryBuild 方法: build(InputStream in){
第一:使用dom4j解析配置文件,将解析出来的内容封装到容器对象中
第二:创建SqlSessionFactory对象:生产sqlSession会话对象(工厂模式)}
-
创建SqlSessionFactory接口以及实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory
第一:openSessioin():生产sqlSession
-
创建SqlSession接口以及实现类DefaultSession
定义对数据库的curd操作:selectList()、selectOne()、update()、delete()
-
创建Executor接口及实现类SimpleExecutor实现类
query(Configuration,MapperStatement,Object... params):执行JDBC代码
1.4 自定义框架实现
具体代码见我的GitHub
测试使用代码见README.md
1.5 自定义框架优化
在业务中使用代码如下:
public interface UserDao {
//查询所有用户
List<User> findAll() throws PropertyVetoException, DocumentException, SQLException, IntrospectionException, NoSuchFieldException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException;
//根据条件进行用户查询
User findByCondition(User user) throws PropertyVetoException, DocumentException, SQLException, IntrospectionException, NoSuchFieldException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException;
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public List<User> findAll() throws PropertyVetoException, DocumentException, SQLException, IntrospectionException, NoSuchFieldException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSqlSession();
List<User> selectList = sqlSession.selectList("user.selectList");
return selectList;
}
@Override
public User findByCondition(User user) throws PropertyVetoException, DocumentException, SQLException, IntrospectionException, NoSuchFieldException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSqlSession();
User userSelect = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectOne",user);
return userSelect;
}
}
以上代码的问题分析
- Dao层使用自定义持久层框架,存在代码重复,整个操作过程模板重复(加载配置文件、创建sqlSessionFactory生产sqlSession)
- statementId在Dao层存在硬编码问题
解决思路:使用代理模式生成Dao层代理实现类。
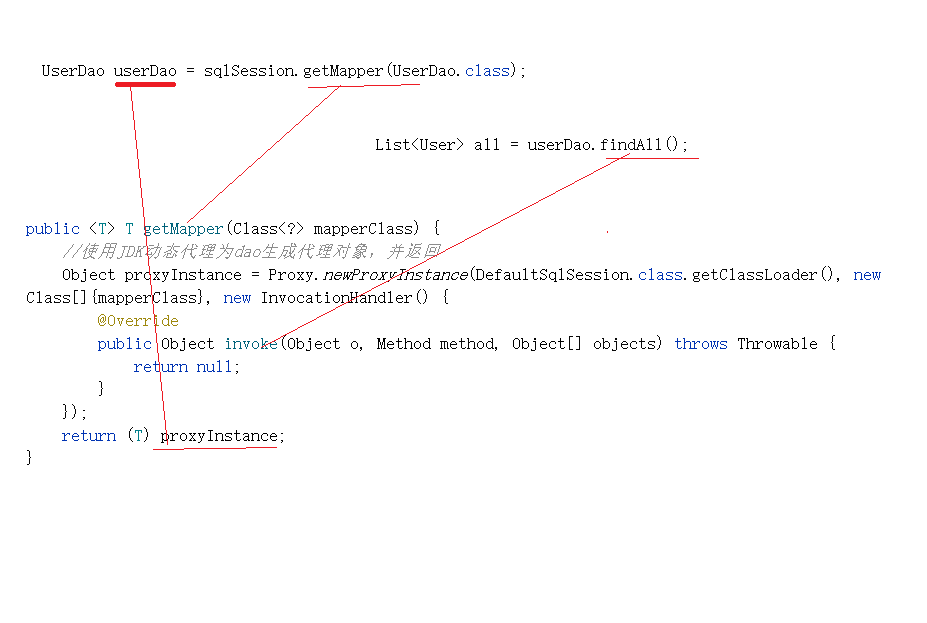
对invoke方法的编写:invoke方法:o:当前代理对象的引用,method:当前被调用方法的引用,objects:传递的参数
/**
* 为dao接口实现代理实现类
* @param mapperClass
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<?> mapperClass) {
//使用JDK动态代理为dao生成代理对象,并返回
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
//底层执行jdbc方法 根据不同情况来调用selectList后者selectOne
//准备参数 1.statementId:sql语句唯一标识
String methodName = method.getName();//方法名 eg:findAll
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();//接口全限定名
String statementId = className+"."+methodName;
//参数 2.params :objects
//获取被调用方法的返回值类型
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
//判断是否进行了泛型类型参数化 即返回值是否有泛型
if (genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
List<Object> objectList = selectList(statementId, objects);
return objectList;
}else {
Object objectOne = selectOne(statementId, objects);
return objectOne;
}
}
});
return (T) proxyInstance;
}
二.Mybatis介绍与入门
前身是apache下的开源项目,2010有aspache software foundation 迁移到了google code ,并且改名为Mybatis,2013年迁移到github。
mybatis是一款基于ORM的半自动轻量级持久层框架。可以自己优化核心sql,sql与java代码分开。
2.1Mybatis入门
工程搭建
导入jar包
配置SqlMapConfig.xml
配置log4j.properties
配置sql查询的映射文件
加载映射文件
完成需求
步骤
编写sql语句
配置user映射文件
编写测试程序
需求
根据用户ID查询用户信息
根据用户名模糊查询用户信息
插入用户(主键返回,UUID使用)
修改删除用户
SqlMapConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 加载属性文件 -->
<properties resource="log4j.properties">
<!--properties中还可以配置一些属性名和属性值 -->
<!-- <property name="jdbc.driver" value=""/> -->
</properties>
<!-- 和spring整合后 environments配置将废除-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事务管理,事务控制由mybatis-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 数据库连接池,由mybatis管理-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/pojo?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Hongkong&characterEncoding=utf-8&autoReconnect=true" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="manager" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加载 映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mybatis/user.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
user.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespqce:命名空间,用于隔离sql语句
#{}是占位符相当于jdbc的?
${}是字符串拼接指令,如果入参为普通数据类型括号内部只写value
-->
<mapper namespace="user">
<!-- id: sql id的唯一标识
parameterType:入参的数据类型
resultType:返回结果的数据类型
-->
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.yhr.mybatis.User">
SELECT ID,username,sex,address FROM usertable WHERE id= #{id2}
</select>
<!--returnType:如果返回结果为集合,只需设置为每一个的数据类型 -->
<select id="getUserByUserName" parameterType="string" resultType="com.yhr.mybatis.User">
SELECT ID,username,sex,address FROM usertable WHERE username like '%${value}%'
</select>
<!--插入用户 -->
<!-- useGeneratedKeys="true" 使用自增 keyProperty="id" 与之前的配套使用 这里只User的主键id -->
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.yhr.mybatis.User" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
<!-- selectKey:主键返回
keyProperty:user中的主键类型
resultType:主键数据类型
order:指定selectKey何时执行:AFTER|BEFORE
可以改变为useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"
-->
<!-- <selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey> -->
insert into usertable(username,sex,address) values(#{username},#{sex},#{address});
</insert>
<!-- -->
<insert id="insertUserUUID">
<selectKey keyProperty="uuid2" resultType="string" order="BEFORE">
select UUID()
</selectKey>
insert into usertable(username,sex,address,uuid2) values(#{username},#{sex},#{address},#{uuid2});
</insert>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.yhr.mybatis.User" >
update usertable set username=#{username} where id=#{id};
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="com.yhr.mybatis.User">
delete from usertable where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
MybatisTest.java
package com.yhr.mybatis.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import com.yhr.mybatis.User;
public class MybaitsTest {
//@Test
public void testGetUserById() throws IOException {
//创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssfd=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//创建核心配置文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//通过输入流创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssfd.build(inputStream);
//创建SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行查询
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("user.getUserById",1);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
//@Test
public void testGetUserByUserName() throws IOException {
//创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssfd=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//创建核心配置文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//通过输入流创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssfd.build(inputStream);
//创建SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行查询
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("user.getUserByUserName","张" );
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
//@Test
public void testInsertUser() throws IOException {
//创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssfd=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//创建核心配置文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//通过输入流创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssfd.build(inputStream);
//创建SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行查询
User user =new User();
user.setUsername("ll");
user.setSex("男");
user.setAddress("北京");
sqlSession.insert("user.insertUser", user);
System.out.println(user);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
//@Test
public void testInsertUserUUID() throws IOException {
//创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssfd=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//创建核心配置文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//通过输入流创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssfd.build(inputStream);
//创建SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行查询
User user =new User();
user.setUsername("ll");
user.setSex("男");
user.setAddress("北京");
sqlSession.insert("user.insertUserUUID", user);
System.out.println(user);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
//@Test
public void testUpdateUser() throws IOException {
//创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssfd=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//创建核心配置文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//通过输入流创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssfd.build(inputStream);
//创建SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行查询
User user =new User();
user.setId(0);
user.setUsername("adada");
sqlSession.update("user.updateUser", user);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testDeleteUser() throws IOException {
//创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder ssfd=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//创建核心配置文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//通过输入流创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = ssfd.build(inputStream);
//创建SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//执行查询
User user =new User();
user.setId(7);
sqlSession.delete("user.deleteUser", user);
System.out.println(user);
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}
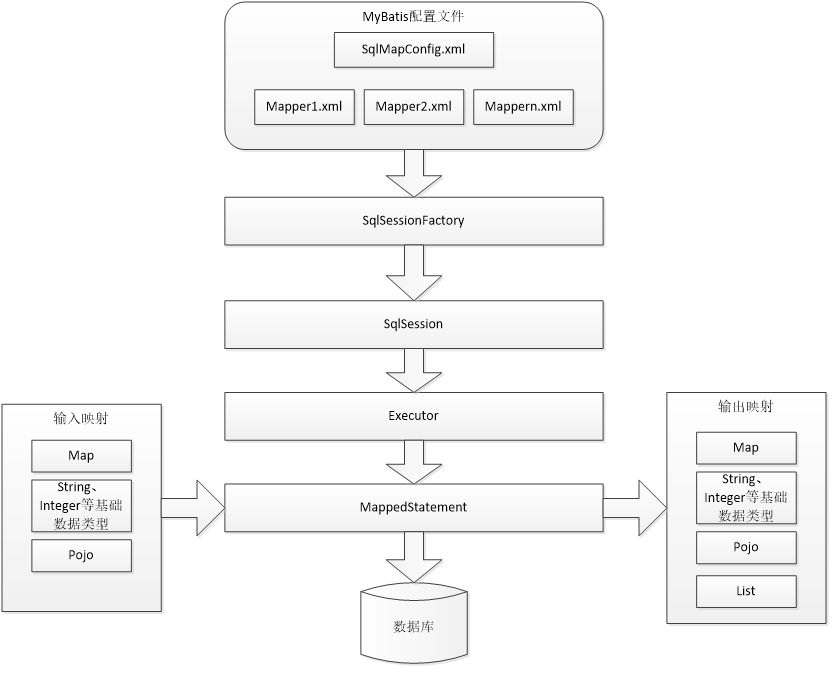
Mybatis架构图
三.Mybatis Dao 开发方式
Dao需求
根据用户ID查询用户信息
根据用户名查找用户列表
添加用户
3.1原始Dao开发方法
SqlSession的使用范围
SqlSession中封装了对数据库的操作如增删改查
SqlSession由SqlSessionFactory进行创建
SqlSessionFactory由SqlSessionFactoryBuilder进行创建
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder用于创建SqlSessionFactory,一旦创建完成就不需要SqlSessionFactoryBuilder了,因为SqlSession是由SqlSessionFactory创建的。所以可以将SqlSessionFactoryBuilder当作一个工具类使用,最佳的使用范围是方法范围即方法体内局部变量
SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory是一个接口,接口中定义了openSession的不同重载方法,SqlSessionFactory的最佳适用范围是整个应用运行期间,一旦创建后可以重复使用,通常以单例模式管理SqlSessionFactory
SqlSession
在 MyBatis 中,你可以使用
SqlSessionFactory来创建SqlSession。一旦你获得一个 session 之后,你可以使用它来执行映射了的语句,提交或回滚连接,最后,当不再需要它的时候,你可以关闭 session。使用 MyBatis-Spring 之后,你不再需要直接使用SqlSessionFactory了,因为你的 bean 可以被注入一个线程安全的SqlSession,它能基于 Spring 的事务配置来自动提交、回滚、关闭 session
1.使用原始user映射文件,不需修改
2.新建个UserDao接口
public interface UserDao{
User getUserById(Integer id);
List<User> getUserByUserName(String Username);
void insertUser(User user);
.....
}
3.新建个UserDaoImpl接口实现类
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public User getUserById(Integer id){
SqlSession sqlsession =SqlsessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession();
User user=sqlSession.selectOne("user.getUserById",id);
sqlsession.close();
return user;
}
}
4.使用Dao测试
public class UserDaoTest{
@Test
public void testGetUserById(){
UserDao userdao=new UserDaoImpl();
User user =userdao.getUserById(30);
System.out.pringln(user);
}
}
3.2接口动态代理开发方法
1.动态代理开发规则
动态代理开发规则:
1.namespace必须是接口的全路径名
2.接口的方法名必须与Sql id一致
3.接口的入参必须与parameterType类型一致
4.接口的返回值必须与resultType类型一致
2.动态代理开发步骤
UserMapper.xml
与上面user.xml一样
UserMapper
public interface UserMapper{
User getUserById(int id);
.........
}
UserMapperTest
public class UserMapperTest{
@Test
public void testGetUserById(){
SqlSession sqlsession =SqlsessionFactoryUtils.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession();
UserMapper usermapper=sqlsession.getMapper(UserMapper,class);
System.out.pringln(user);
sqlsession.close();
}
}
3.3注解开发
注解开发不易于维护一般适用于简单的项目
注解开发不需要映射文件.xml只需要sqlmapconfig.xml
常用注解
@Select 相当于映射文件中的select标签
@Insert 相当于映射文件中的insert标签
@SelectKey 相当于映射文件中的selectKey标签
@Update 相当于映射文件中的update标签
@Delete 相当于映射文件中的delete标签
@Result 相当于映射文件中的result标签
@One 相当于映射文件中的association标签,用于封装关联JavaBean对象
@Many 相当于映射文件中的collection标签,用于封装关联JavaBean对象集合
使用方法:
创建接口,在方法上添加注解
public interface UserDao{
@Select("select * from userwhere id=#{id}")
User queryId(Integer id);
@Delete("delete from user where id=#{id}")
void delete(Integer id)
}
在测试类中测试
@Test
public void query(){
User user=userDao.query(53);
System.out.pringln(user);
}
@Test
public void delete(){
userDao.delete(53);
session.commit();
}
PS:执行dml语句(CUD)一定到提交事务session.commit();
四.SqlMapConfig.xml
4.1 配置内容
SqlMapConfig.xml中配置的内容和顺序如下:
properties(属性)
settings(全局配置参数)
typeAliases(类型别名)
typeHandlers(类型处理器)
objectFactory(对象工场)
plugins(插件)
environments(环境集合属性对象)
environment(环境子属性对象)
transactionManager(事务管理)
dataSource(数据源)
mappers(映射器)
4.2 properties(属性)
<!-- 先加载内部标签,在加载外部文件,若外部文件与内部名称相同时,会将外部的值替换掉内部的值 -->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties">
<property name="jdbc.username" value="root1"/>
<property name="jdbc.password" value="root1"/>
</properties>
4.3 typeAliases
Mybatis支持的别名
别名 映射的类型
_byte byte
_long long
_short short
_int int
_integer int
_double double
_float float
_boolean boolean
string String
byte Byte
long Long
short Short
int Integer
integer Integer
double Double
float Float
boolean Boolean
date Date
decimal BigDecimal
bigdecmial BigDecimal
map Map
自定义别名
<typeAliases>
<!--单个别名扫描,别名的使用不区分大小写-->
<typeAlias type="com.yhr.mybatis.pojo.User" alias="user"/>
<!--别名包扫描器:别名是类的全称,不区分大小写-->
<package name="com.yhr.mybatis.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
4.4 mappers
<mapper>
<!--通过resource方法一次加载一个映射文件 -->
<!-- <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> -->
<mapper resource="mybatis/usermapper.xml"/>
<!--映射文件,class扫描器
遵循一些规范:需要将mapper接口类名和mapper.xml映射文件名称保持一致,且在一个目录中 上边规范的前提是:使用的是mapper代理方法
-->
<mapper class="com.yhr.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"/>
<!-- 批量加载mapper
指定mapper接口的包名,mybatis自动扫描包下边所有mapper接口进行加载
遵循一些规范:需要将mapper接口类名和mapper.xml映射文件名称保持一致,且在一个目录中 上边规范的前提是:使用的是mapper代理方法
-->
<package name="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mapper>
五.输入映射和输出映射
5.1 parameterType(输入类型)
传递简单类型
{}占位符 ${}进行sql拼接
eg:id= #{id2} username like '%${value}%'
传递pojo对象
Mybatis使用ognl表达式解析对象字段的值#{}或者${}括号中的值为pojo属性名称
eg:<...... parameterType="com.yhr.mybatis.User">
insert into usertable(username,sex,address) values(#{username},#{sex},#{address});
传递pojo包装对象
开发中通过可以使用pojo传递查询条件
查询条件可以是综合的查询条件,不仅包括用户查询条件还包括其他的查询条件(比如查询用户信息的时候,将用户购买商品信息也作为查询条件),这时可以使用包装对象传递输入参数。
包装对象:Pojo类中的一个属性是另外一个pojo
eg:<...... parameterType="com.yhr.mybatis.pojo.QueryVo">
SELECT ID,username,sex,address FROM usertable WHERE username like '%${user.username}%'
QueryVo.java:
public class QueryVo {
private User user;
public User getUser() {
return user;
}public void setUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}}
5.2 resultType(输出类型)
输出简单类型
需求:查询用户表数据条数
UserMapper.xml
<select id="queryUserCount" resultType="int"> Select count(*)from `user` </select>
输出pojo对象
输出pojo列表
5.3 resultMap
resulrType可以指定将查询结果映射为pojo,但需要pojo的属性名和sql查询的列名一致方可映射成功。
如果sql查询字段名和pojo的属性名不一致,可以通过resultMap将字段名和属性名做一个对应关系,resultMap实质上还需要将查询结果映射到pojo对象中。
resultMap可以实现将查询结果映射为复杂类型的pojo,比如在查询结果映射对象中包括pojo和list实现一对一和一对多查询。
需求:查询订单表order的所有数据
sql :Select id,user_id,number,createtime,note from
order<resultMap type="com.yhr.mybatis.pojo.Order" id="order_list_map"> <!--用于映射主键 --> <id property="id" column="id"/> <!-- 普通字段用result映射 --> <result property="userId" column="user_id"/> <result property="number" column="number"/> <result property="createtime" column="createtime"/> <result property="note" column="note"/> </resultMap> <!--使用resultMap --> <select id="getOrderListMap" resultMap="order_list_map"> select id,user_id,number,createtime,note from ordertable; </select>
六.动态sql
通过mybatis的各种标签方法实现动态拼接sql
需求:根据姓名和性别查询用户
select id ,username,sex,address from usertable where sex='男' and username like '%张%'
6.1 if标签
<select id="getUserByPojo" parameterType="User" resultType="User">
select id ,username,sex,address from usertable
where 1=1
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">and username like '%${username}%'</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">and sex=#{sex}</if>
</select>
6.2 Where标签
<select id="getUserByPojo" parameterType="User" resultType="User">
select id ,username,sex,address from usertable
<!-- where标签自动补上where关键字,同时处理多余的and,用了where标签就不能手动加上where关键字-->
<where>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">and username like '%${username}%'</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">and sex=#{sex}</if>
</where>
</select>
6.3 sql片段
<sql id="user_sql">
id ,username,sex,address
</sql>
<select id="getUserByPojo" parameterType="User" resultType="User">
select
<!-- sql片段使用:refid引用定义好的sql片段 -->
<include refid="user_sql"></include>
from usertable
<where>
<if test="username!=null and username!=''">and username like '%${username}%'</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">and sex=#{sex}</if>
</where>
</select>
6.4 foreach标签
<select id="getUserByIds" parameterType="QueryVo" resultType="User">
select <include refid="user_sql"></include>
from usertable
<where>
<!--foreach 集合标签
collection:要遍历的集合
open:循环开始之前输出的内容
close:循环借宿之后输出的内容
separator:分隔符
item:设置循环变量
-->
<!-- id in(0,1,8,9) -->
<foreach collection="ids" open="id in(" item="uid" separator="," close=")">
#{uid}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
七.关联查询
7.1 商品订单数据模型
订单表 用户表
一对一:一个订单只有一个用户创建
一对多:一个用户有多个订单
7.2 一对一查询
resultType(必须有数据库关系一样的pojo类)
1.建立OrderUser pojo类继承Order类
2.SQL语句:select o.id ,o.user_id,o.number,o.createtime,o.note,u.username,u.address
from ordertable o left join usertable u on o.user_id=u.id
3.编写OrderMapper.xml
4.编写测试类
resultMap
OrderMapper.xml
<resultMap type="Order" id="order_user_map">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<!-- 普通字段用result映射 -->
<result property="userId" column="user_id"/>
<result property="number" column="number"/>
<result property="createtime" column="createtime"/>
<result property="note" column="note"/>
<!--用于配置一对一关系
property:Order里的user属性
javaType:user的数据类型,支持别名
-->
<association property="user" javaType="User">
<id property="id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="username" column="username"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getOrderUserMap" resultMap="order_user_map">
select o.id ,o.user_id,o.number,o.createtime,o.note,u.username,u.address
from ordertable o left join usertable u on o.user_id=u.id
</select>
7.3 一对多查询
sql语句
select u.id ,u.username,u.sex,u.address,o.id,o.number,o.note from usertable u left join ordertable o on u.id=o.user_id
<resultMap type="User" id="user_order_map">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="username" column="username"/>
<result property="address" column="address"/>
<result property="sex" column="sex"/>
<!-- 一对多关联
property:User中的orders属性
ofType:orders的数据类型,支持别名
-->
<collection property="orders" ofType="Order">
<id property="id" column="oid"/>
<result property="number" column="number"/>
<result property="note" column="note"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserOrderMap" resultMap="user_order_map">
select u.id ,u.username,u.sex,u.address,o.id oid,o.number,o.note
from usertable u left join ordertable o on u.id=o.user_id
</select>
八、Mybatis缓存
缓存是内存中的数据,常常来自对数据库结果的保存,使用缓存,我们可以避免频繁的与数据库进行交互,提高响应速度。
mybatis提供了对缓存的支持,分为一级缓存和二级缓存:

一级缓存是sqlSession级别的缓存,在操作数据库时需要构造sqlSession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构HashMap用于存储缓存数据。不同的sqlSession之间的缓存数据区域(HashMap)是互不影响的。
一级缓存(HashMap):key:statementId,params,boundSql,rowBounds组成;value:查询出的对象
二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,多个sqlSession去操作同一个Mapper的SQL语句,多个sqlSessioin可以公用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨session的。
8.1 一级缓存
-
在一个sqlSession中,对Product表根据Id进行两次查询
@Test public void test1(){ //根据sqlSessionFactory产生session SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); ProductMapper productMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ProductMapper.class); //首先去一级缓存中查询:有:返回;没有:查询数据库,同时将查询出来的结果存到一级缓存中 Product product1 = productMapper.getProduct(1L); System.out.println(product1); //第二次查询,由于是同一个sqlSession,会在缓存中查询结果 //如果有,则直接从缓存中取出来,不和数据库交互 Product product2 = productMapper.getProduct(1L); System.out.println(product2); System.out.println(product1==product2);//两次地址值一样 sqlSession.close(); }
-
同样对user表进行两次查询,只不过两次查询之间进行了一次Update操作
@Test public void test2(){ //根据sqlSessionFactory产生session SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); ProductMapper productMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ProductMapper.class); //第一次查询,发出sql语句,将查询的结果放入缓存中 Product product1 = productMapper.getProduct(1L); System.out.println(product1); //更新库存数量 更新操作提交事务 //做增删改操作,并进行事务提交,就是刷新一级缓存 //也可以使用sqlSession.clearCache();手动刷新缓存 productMapper.decreaseProduct(1L,50); sqlSession.commit(); //第二次查询,由于同一个sqlSession.commit,会清空缓存信息 Product product2 = productMapper.getProduct(1L); System.out.println(product2); System.out.println(product1==product2);//两次地址值不一样 sqlSession.close(); }
-
总结
- 第一次发起查询用户id为1的用户信息,先去找缓存中是否有id为1的用户信息,如果没有,从数据库中查询用户信息,得到用户信息,将用户信息存储到一级缓存中。
- 如果中间sqlSession去执行commit操作,则会清空sqkSession中的一级缓存,目的是让缓存中的数据是最新的避免脏读。
- 第二此查询id为1的用户信息,去缓存中查询,有则直接提取数据,提高效率
8.2 一级缓存源码分析与原理探究
源码探究思路:探究源码请自己尝试,不要只看本文档的过程
提到一级缓存就离不开SqlSession,进入SqlSession接口的源码(如下),可以看到只有clearCache与缓存有关系,那么就从此方法入手
/**
* Clears local session cache.
*/
void clearCache();
分析源码时,要看此类是谁,父类和子类又是谁
进入SqlSession接口的DefaultSqlSession的实现类中的clearCache()方法:
@Override
public void clearCache() {
executor.clearLocalCache();
}
点击clearLocalCache()进入Executor接口,进入Executor接口下clearLocalCache()方法的实现类BaseExecutor的此方法
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
点击clear方法,进入到PerpetualCache类的clear()方法
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
分析了一圈,会发现流程会走到PerpetualCache类的clear()方法,点击cache,会发现cache就是一个HashMap,源码如下:
private Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
所以cache.clear()也就是map.clear();也就是说缓存其实就是本地的map对象,每一个SqlSession都会存放一个map对象的引用。
那么创建缓存的地方应该在哪里?由刚才的流程以及自定义持久层框架,可以大概推断缓存应该在sql的执行器也就是executor中创建,在BaseExecutor中会发现一个createCacheKey方法(源码如下):
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
//MappedStatement的id
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
//offset是0
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
//limit是Integer.MAXVALUE
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
//具体的sql语句
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
//更新了sql中的参数
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
由上面源码可见,创建缓存key会经历一些列的update方法,这个方法是由CacheKey(源码如下)执行的,由下面这个源码可知,update方法最终会存到updateList中。
/**
* Copyright 2009-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.cache;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ArrayUtil;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class CacheKey implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1146682552656046210L;
public static final CacheKey NULL_CACHE_KEY = new NullCacheKey();
private static final int DEFAULT_MULTIPLYER = 37;
private static final int DEFAULT_HASHCODE = 17;
private final int multiplier;
private int hashcode;
private long checksum;
private int count;
// 8/21/2017 - Sonarlint flags this as needing to be marked transient. While true if content is not serializable, this is not always true and thus should not be marked transient.
private List<Object> updateList;
public CacheKey() {
this.hashcode = DEFAULT_HASHCODE;
this.multiplier = DEFAULT_MULTIPLYER;
this.count = 0;
this.updateList = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void update(Object object) {
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : ArrayUtil.hashCode(object);
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
updateList.add(object);
}
//......略
}
那么创建缓存后应该用在哪里,第一个想法便是查询,因为缓存可以提高效率,所以我们查看query方法的部分源码如下:
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
我们可以看上面源码的这一部分:
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
如果查不到就从数据库中查,执行queryFromDatabase()方法(此方法源码请自行翻阅),并且执行localCache.putObject(key, list);语句存入缓存中。以上为一级缓存源码剖析。
8.3 二级缓存
⼆级缓存的原理和⼀级缓存原理⼀样,第⼀次查询,会将数据放⼊缓存中,然后第⼆次查询则会直接去缓存中取。但是⼀级缓存是基于sqlSession的,⽽⼆级缓存是基于mapper⽂件的namespace的,也就是说多个sqlSession可以共享⼀个mapper中的⼆级缓存区域,并且如果两个mapper的namespace 相同,即使是两个mapper,那么这两个mapper中执⾏sql查询到的数据也将存在相同的⼆级缓存区域中。
开启二级缓存
二级缓存需要手动开启,首先在sqlMapConfig加入
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
其次在UserMapper.xml中开启缓存
<cache></cache>
九.Mybatis逆向工程
下载逆向工程https://github.com/mybatis/generator/releases/tag/mybatis-generator-1.3.2
向Eclipse中导入此项目
9.1 使用步骤-代码方式
导入jar包:
log4j-xxx.jar
mybatis-xxx.jar
mybatis-generator-core-xxx.jar
mysql-connector-java-xxx.jar
创建generatorConfig.xml配置文件
使用执行java类
把生成的代码copy进项目中
- 配置文件:generatorConfig.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<context id="testTables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<commentGenerator>
<!-- 是否去除自动生成的注释 true:是 : false:否 -->
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="true" />
</commentGenerator>
<!--数据库连接的信息:驱动类、连接地址、用户名、密码 -->
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/taotaostore?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai"
userId="root"
password="manager">
</jdbcConnection>
<!-- 默认false,把JDBC DECIMAL 和 NUMERIC 类型解析为 Integer,为 true时把JDBC DECIMAL 和
NUMERIC 类型解析为java.math.BigDecimal -->
<javaTypeResolver>
<property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" />
</javaTypeResolver>
<!-- targetProject:生成PO类的位置 -->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.taotao.pojo"
targetProject=".src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
<!-- 从数据库返回的值被清理前后的空格 -->
<property name="trimStrings" value="true" />
</javaModelGenerator>
<!-- targetProject:mapper映射文件生成的位置 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.taotao.mapper"
targetProject=".src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!-- targetPackage:mapper接口生成的位置 -->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER"
targetPackage="com.taotao.mapper"
targetProject=".src">
<!-- enableSubPackages:是否让schema作为包的后缀 -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
</javaClientGenerator>
<!-- 指定数据库表 -->
<table schema="" tableName="tb_content"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_content_category"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_cat"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_desc"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_param"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_item_param_item"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_order"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_order_item"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_order_shipping"></table>
<table schema="" tableName="tb_user"></table>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>
- 运行java代码
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.mybatis.generator.api.MyBatisGenerator;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.Configuration;
import org.mybatis.generator.config.xml.ConfigurationParser;
import org.mybatis.generator.exception.XMLParserException;
import org.mybatis.generator.internal.DefaultShellCallback;
public class GeneratorSqlmap {
public void generator() throws Exception{
List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<String>();
boolean overwrite = true;
//指定 逆向工程配置文件
File configFile = new File("generatorConfig.xml");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config,
callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try {
GeneratorSqlmap generatorSqlmap = new GeneratorSqlmap();
generatorSqlmap.generator();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这样就生成了项目所需的pojo和mapper。copy进自己的项目即可
PS:Mapper.xml文件已经存在时,如果进行重新生成则mapper.xml文件时,内容不被覆盖而是进行内容追加,结果导致mybatis解析失败。
解决方法:删除原来已经生成的mapper xml文件再进行生成。
Mybatis自动生成的po及mapper.java文件不是内容而是直接覆盖没有此问题。
9.2 使用步骤-maven
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cjw</groupId>
<artifactId>myBatisGenerator</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<properties>
<mybatis.version>3.2.8</mybatis.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.36</mysql.version>
<mysql-connector-java.version>5.1.28</mysql-connector-java.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.17</log4j.version>
<!-- Encoding -->
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 数据库驱动包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql-connector-java.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis核心包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志文件管理包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.7</source>
<target>1.7</target>
</configuration>
<version>3.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
<configuration>
<!--配置文件的路径 -->
<configurationFile>src/main/resources/generatorConfig.xml</configurationFile>
<overwrite>true</overwrite>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
</project>
generatorConfig.xml配置文件
运行java代码