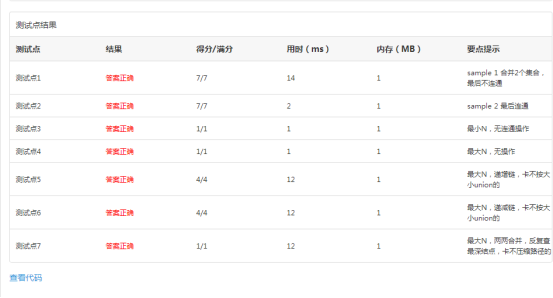
本博客的代码的思想和图片参考:好大学慕课浙江大学陈越老师、何钦铭老师的《数据结构》
代码的测试工具PTA
File Transfer
1 Question
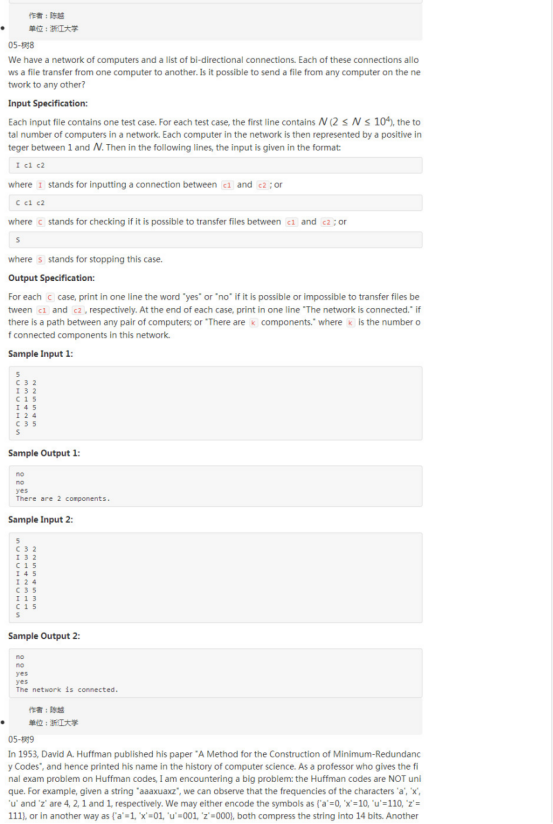
2 Explain
First, we will put N elements in a array,the elements is from 1 to N.The element in the array stand for the number of computer.
C1 stand for a computer and C2 stand for another computer.
“I C1 C2” will let C1 C2 to be a set,neither of C1 or C2 belong to any collection,we will make C1 point C2 or C2 point C1,let C1 and C2 to be one collection.If C1 belong to collection1 and C2 belong to collection, we will union collection and collection2.
“C C1 C2” means check C1 and C2 whether can transfer file. In another word C1 and C2 whether belong to one collection.If true indicating C1 can transfer file to C2,then program print “Yes”, otherwise indicating C1 C2 don’t transfer files each other,then program print “No”
“S” indicate the input finish,But we should print how many different
collection in this array.If the array only has one collection,indicating all all computer can transfer file each other program will output “The network is connected”.
Otherwise we will calculate how many different collection in this array. Then the program will input “The are X components”,X is the amount of different collections.
So the question become easy. ”I C1 C2” we only union the C1 C2.
and “C C1 C2” we just only to find whether the C1 and C2 is in same collection.
3 How to Operator to Set
3.1 build a Set in Old Way
In the class of He QinMing,we know can use the following data constructor to stand for a Set.
1 /*collection data constructor 2 3 we use the array of this to express collection. 4 5 The root element's parent is -1 6 7 the ordinary element parent is the index of parent. 8 9 */ 10 11 typedef struct node{ 12 13 elementType data; 14 15 int parent; 16 17 }coll,*pCollection; 18 19 20 21 pCollection s[MAXSIZE]
We can find element and union set by following method:
1 /* 2 3 find the collection's root element by the element needed to find. 4 5 @param s[] The arrar yto store collections elememts 6 7 @param element The element will be searched in the array 8 9 @return The index of root element of which the element be found,-1 will be return if the 10 11 element not be found in this collection 12 13 */ 14 15 int find(coll s[],elementType element){ 16 17 int i; 18 19 for(i=0;i<MAXSIZE&&s[i].data!=element;i++); 20 21 if(i>=MAXSIZE){/*在数组中没有找到该元素*/ 22 23 return -1; 24 25 } 26 27 for(;s[i].parent>=0;i=s[i].parent); 28 29 return i; 30 31 } 32 33 34 35 36 37 /* 38 39 unoin two collection by the two element in the two collection. 40 41 @param s[] the array to store collection element 42 43 @param x1 The element in collection one. 44 45 @param x2 The element in the collection two 46 47 */ 48 49 void unionCollection(coll s[],elementType x1,elementType x2){ 50 51 int root1 = find(s,x1); 52 53 int root2 = find(s,x2); 54 55 if(root1!=root2){ 56 57 s[root2].parent=root1; 58 59 } 60 61 }
3.2 Analyze the Old Way
for(i=0;i<MAXSIZE&&s[i].data!=element;i++);
we find the line code:the effective is a little low.The time is O(n).The key reason is the to find data take too long time.How to prompt it.
elementType data;
In the SET ARRAY, we know the element is from 1 to N. We can know the array index is from 0 to N-1,So Can we use index to stand for element?
The result is OK, we know “任何有限集合的( N个)元素都可
以被一一映射为整数 0 ~ N–1 ”. We change the data constructor only left
parent, and delete the data that be presented by the index of SET ARRAY.
So we can prompt the effective of <code>find<code> method and <code>unionCollection</code> method
3.3 The New Data Constructor and Algorithm
3.3.1 the data constructor
typedef elementType setType[MAXSIZE];
For example:
the index of SET ARRAY stand for element.
3.4 Code and Test

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 5 #define MAXSIZE 100000 6 7 #include<string.h> 8 9 10 11 typedef int elementType; 12 13 14 15 /* 16 17 define the data constructor of element of set. 18 19 we use SET ARRAY index to stand for the data to reduce the time at <code>find<code> method 20 21 the element of data is from 1 to N 22 23 the index of the SET ARRAY is from 0 to N-1. 24 25 This is good idea to use this method. 26 27 */ 28 29 /* 30 31 typedef struct node{ 32 33 //elementType data; 34 35 int parent; 36 37 }coll,pCollection; 38 39 40 41 Above equal following 42 43 */ 44 45 /*use the root node index to stand for set*/ 46 47 typedef int setName; 48 49 typedef elementType setType[MAXSIZE]; 50 51 52 53 54 55 /* 56 57 find the x's collection root element 58 59 @param s The SET ARRAY 60 61 @param x The element needed to be searched in this array. 62 63 */ 64 65 setName find(setType s,elementType x){ 66 67 /*init the array all elements to -1*/ 68 69 for(;s[x]>=0;x=s[x]); 70 71 return x; 72 73 74 75 } 76 77 78 79 80 81 /* 82 83 union two collection. 84 85 we think the root1 not equal root2 86 87 @param s The SET ARRAY 88 89 @param root1 The root element of the collection one 90 91 @param root2 The root element of the collection two 92 93 */ 94 95 void unionCollection(setType s,setName root1,setName root2){ 96 97 s[root2]=root1; 98 99 } 100 101 102 103 /*initialize the collection to -1 104 105 @param s The array stoteing set's element index 106 107 @param n The length of the set 108 109 */ 110 111 void initializeCollection(setType s,int n){ 112 113 int i; 114 115 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 116 117 s[i]=-1; 118 119 } 120 121 } 122 123 124 125 /* 126 127 "I C1 C2" 128 129 build connection about two set. 130 131 input two number,use <code>find<code> method to find the root element 132 133 of the set,if the collection is not equal,union them. 134 135 @param s The SET ARRAY to store the set's element parent index 136 137 */ 138 139 void input_connection(setType s){ 140 141 elementType u,v; 142 143 setName root1,root2; 144 145 scanf("%d %d ",&u,&v); 146 147 root1 = find(s,u-1); 148 149 root2 = find(s,v-1); 150 151 if(root1!=root2){ 152 153 unionCollection(s,root1,root2); 154 155 } 156 157 } 158 159 160 161 /* 162 163 "C C1 C2" 164 165 check the two conputer whether can transfer file each other. 166 167 First we will find the element C1 and C2 and get the root element root1 and root2 168 169 if the root1 equal root2 indicates the C1 and C2 in the same set,print "yse", otherwise 170 171 indicates the C1 and C2 not in the same set, print the "no" 172 173 @param s The SET ARRAY to store the set's element parent index 174 175 */ 176 177 void check_connection(setType s){ 178 179 elementType u,v; 180 181 setName root1,root2; 182 183 scanf("%d %d",&u,&v); 184 185 root1 = find(s,u-1); 186 187 root2 = find(s,v-1); 188 189 if(root1==root2){ 190 191 printf("yes "); 192 193 }else{ 194 195 printf("no "); 196 197 } 198 199 } 200 201 202 203 /* 204 205 check how many different set in this SET ARRAY 206 207 the algorithem is to calculate how many "-1" elements in the SET ARRAY. 208 209 if the count is equal one, indicate all computer can transfer file each other 210 211 then we will print "The network is connected. ". Otherwise we will print 212 213 "printf("There are %d components. ",count);" 214 215 */ 216 217 void check_network(setType s,int n){ 218 219 int i,count=0; 220 221 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 222 223 if(s[i]<0){ 224 225 count++; 226 227 } 228 229 } 230 231 if(count==1){ 232 233 printf("The network is connected. "); 234 235 }else{ 236 237 printf("There are %d components. ",count); 238 239 } 240 241 } 242 243 244 245 int main(){ 246 247 setType s; 248 249 int n; 250 251 char in; 252 253 scanf("%d",&n); 254 255 getchar(); 256 257 initializeCollection(s,n); 258 259 do{ 260 261 scanf("%c",&in); 262 263 //putchar(in); 264 265 switch(in){ 266 267 case 'I':input_connection(s);break; 268 269 case 'C':check_connection(s);break; 270 271 case 'S':check_network(s,n);break; 272 273 } 274 275 }while(in!='S'); 276 277 return 0; 278 279 }
The PAT result is
What result this?
1 void unionCollection(setType s,setName root1,setName root2){ 2 3 s[root2]=root1; 4 5 }
Then we update the code above to following:
1 void unionCollection(setType s,setName root1,setName root2){ 2 3 s[root1]=root2; 4 5 }
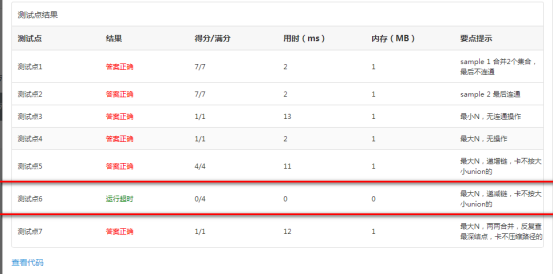
The PAT test result is
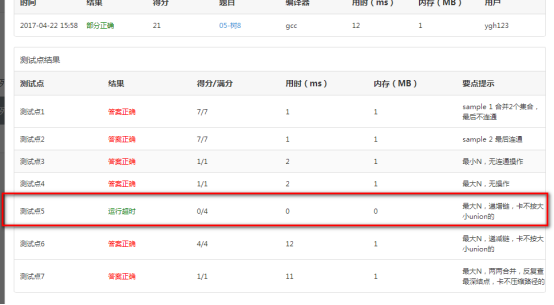
we find the test point five happens same error like last code.
What result it?
3.5 Think and Update
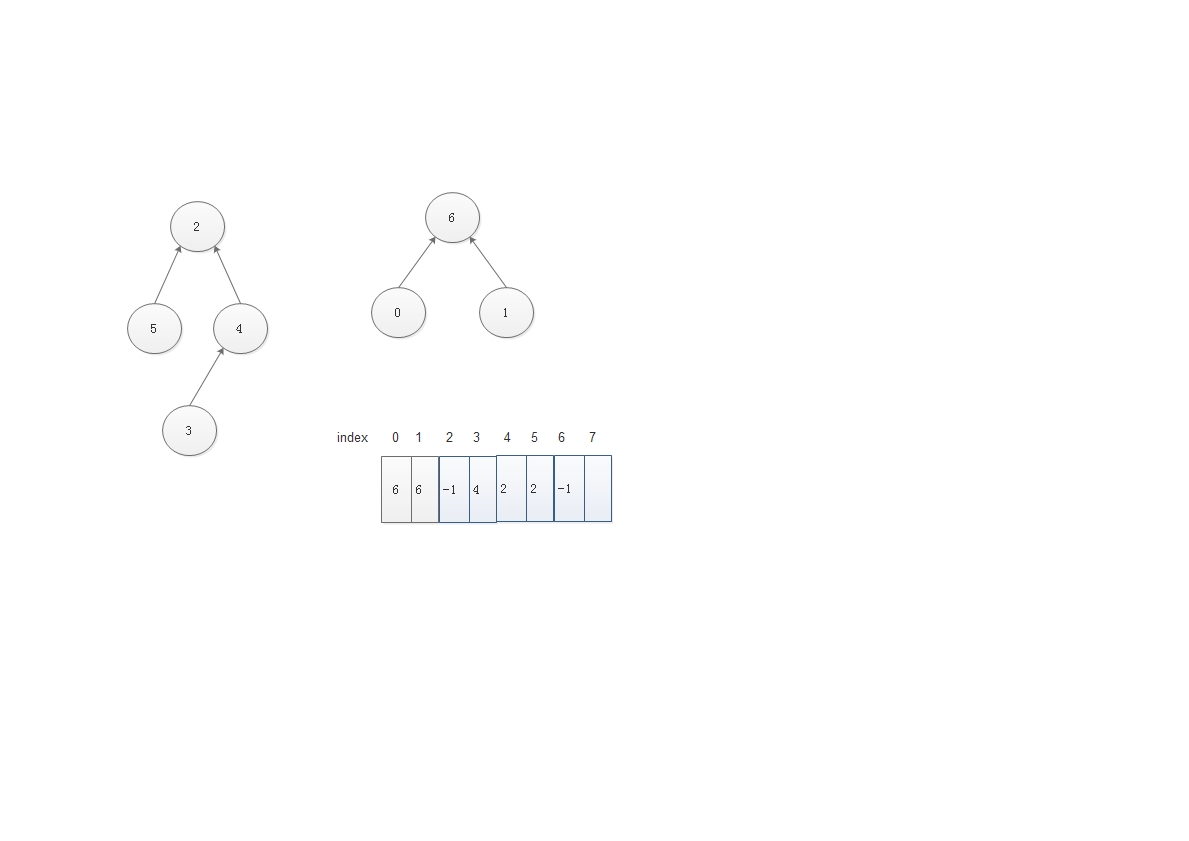
We find, If we only union root1 to root2 or union root2 to root1,a problem will happen.
If a lower tree add to a higher tree,the new tree height is equal with the higher tree’s height.But if a higher tree add to a lower tree, we will find the new tree height is (the higher tree’s height+1),
If we always do it,our tree’s height is terrible.
we can use following picture to explain it.
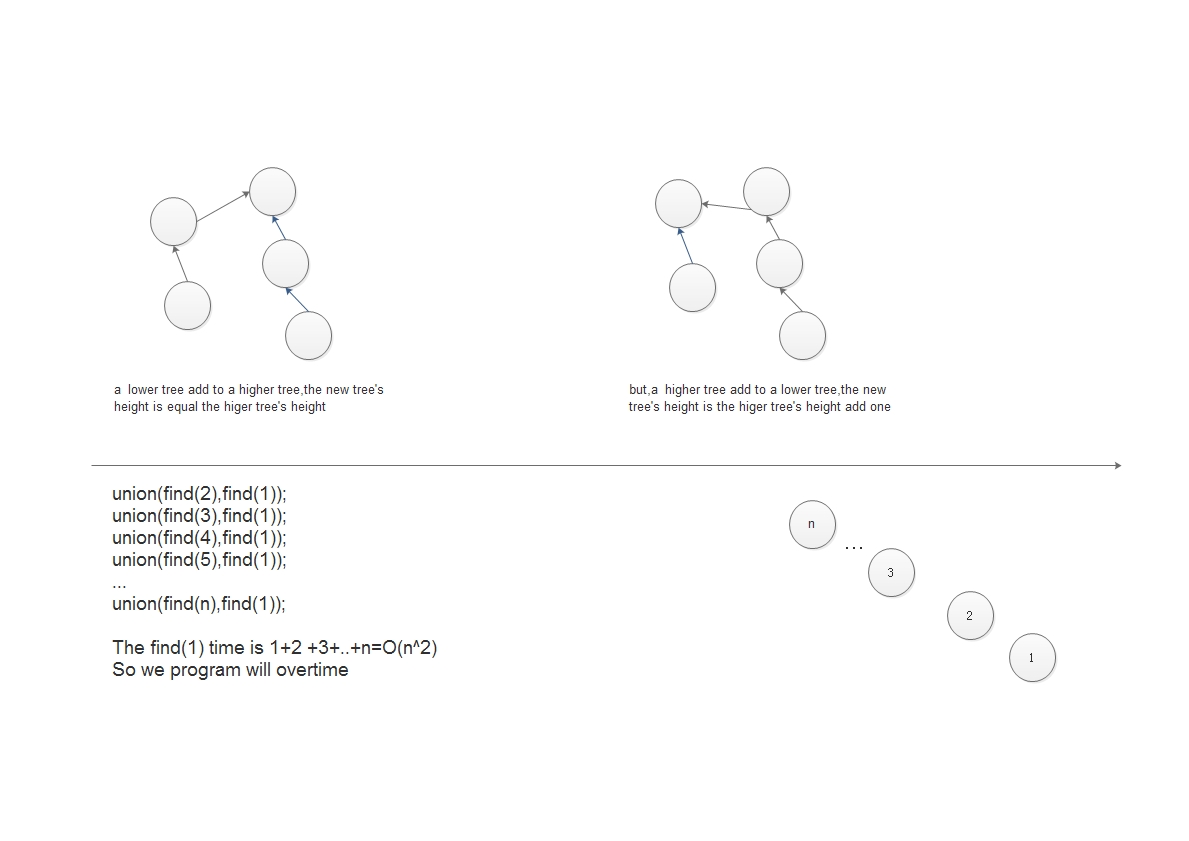
So we should let lower tree add to higher tree.
But how to calculate the tree’s height.
We can change root element -1 to -(tree’s height)
We can use two different method to implement it.But the total name is “按秩归并”
a) we can use tree’s height

b) we can use the tree’s mount

But the method b is better,because it can apply in following algorithm
3.6 New updated code
1 2 3 /* 4 5 union two collection. 6 7 we think the root1 not equal root2 8 9 We will add lower to higher tree.If the two tree height is equal,we let the tree's 10 11 height increase one 12 13 @param s The SET ARRAY 14 15 @param root1 The root element of the collection one 16 17 @param root2 The root element of the collection two 18 19 */ 20 21 void unionCollectionByTreeHeight(setType s,setName root1,setName root2){ 22 23 if(s[root2]<s[root1]){ 24 25 s[root1]=root2; 26 27 }else{ 28 29 if(s[root1]==s[root2]){ 30 31 s[root1]--;/*树高自增*/ 32 33 } 34 35 s[root2]=root1; 36 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 42 43 /* 44 45 union two collection. 46 47 we think the root1 not equal root2 48 49 We will add smaller scale tree to bigger scale tree. 50 51 @param s The SET ARRAY 52 53 @param root1 The root element of the collection one 54 55 @param root2 The root element of the collection two 56 57 */ 58 59 void unionCollectionMount(setType s,setName root1,setName root2){ 60 61 if(s[root2]<s[root1]){ 62 63 s[root2]+=s[root1]; 64 65 s[root1]=root2; 66 67 68 69 }else{ 70 71 s[root1]+=s[root2]; 72 73 s[root2]=root1; 74 75 } 76 77 }
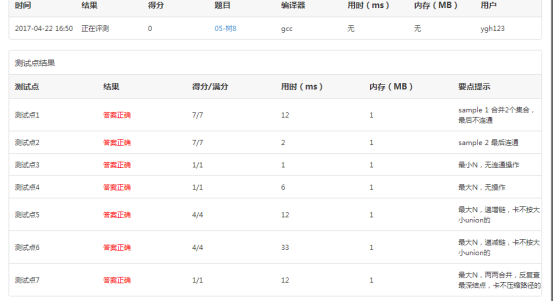
Then we call the unionCollectionMount method
1 void input_connection(setType s){ 2 elementType u,v; 3 setName root1,root2; 4 scanf("%d %d ",&u,&v); 5 root1 = find(s,u-1); 6 root2 = find(s,v-1); 7 if(root1!=root2){ 8 unionCollectionMount(s,root1,root2); 9 } 10 }
You find the test result all right:
3.7 Compress Path
We know the find algorithm.
1 /* 2 3 find the x's set root element 4 5 @param s The SET ARRAY 6 7 @param x The element needed to be searched in this array. 8 9 */ 10 11 setName find(setType s,elementType x){ 12 13 /*init the array all elements to -1*/ 14 15 for(;s[x]>=0;x=s[x]); 16 17 return x; 18 19 20 21 }
If a test data like following:

Although we make tree height add slower,but every time we need to find from 1 to N. If the N is enough big and tree height constant add,
the algorithm will take longer time. How to solve it problem.
The core cause is every time we need to find root element from 1 to N. We need to find many useless parent node to find the root element.
If we link the x(1) element and its parent to root node at the first time.
At second time we find from x(1), we find its root only need find one time.It reduce the much time.
We use a picture to explain this algorithm.
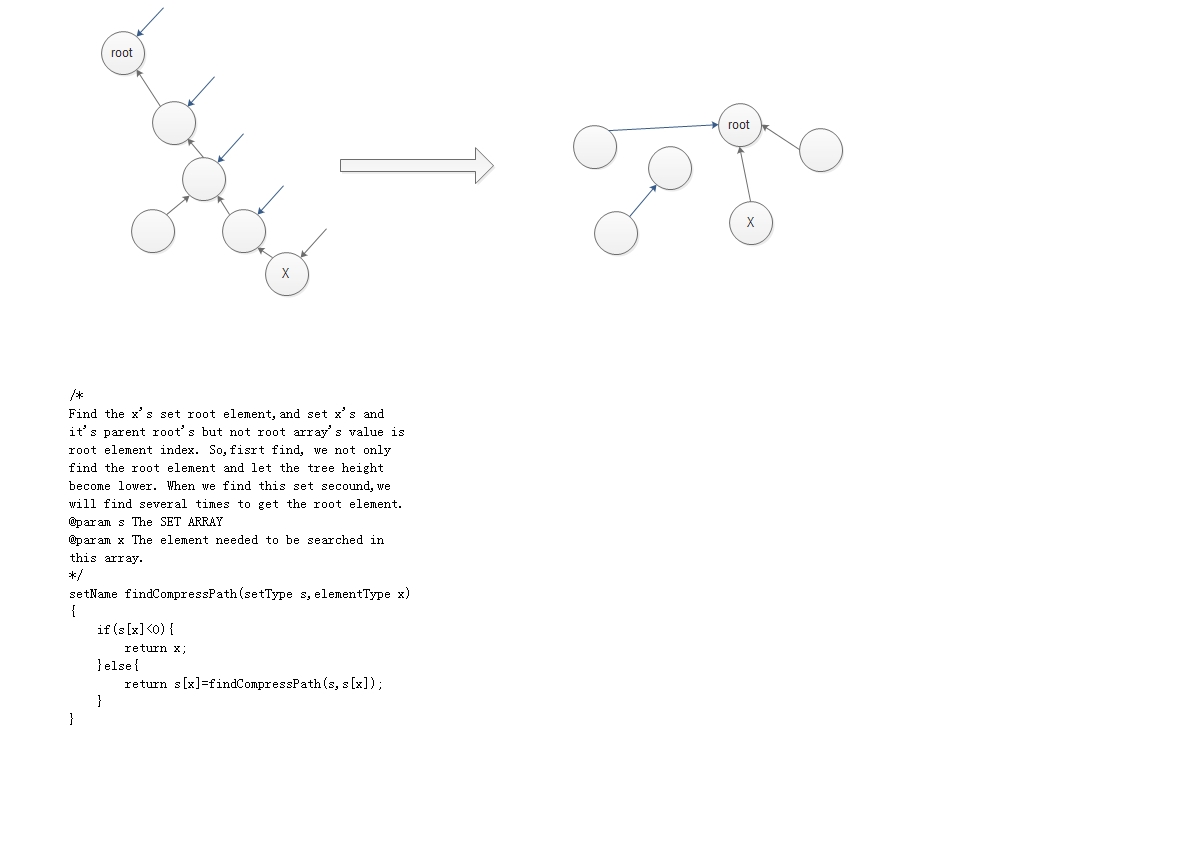
The code following:
1 /* 2 3 Find the x's set root element,and set x's and it's parent root's but not root array's value is 4 5 root element index. So,fisrt find, we not only find the root element and let the tree height 6 7 become lower. When we find this set secound,we will find several times to get the root element. 8 9 @param s The SET ARRAY 10 11 @param x The element needed to be searched in this array. 12 13 */ 14 15 setName findCompressPath(setType s,elementType x){ 16 17 if(s[x]<0){ 18 19 return x; 20 21 }else{ 22 23 return s[x]=findCompressPath(s,s[x]); 24 25 } 26 27 }
So the effective will prompt.
We change <code>find</code> method into <code>findCompressPath</code>
The test result is all right