1. Class的属性
在JVM中,通常一个class会初始化成Klass(接口), InstanceKlass(实例), Method(方法), ConstantsPool(常量区)

在上图我们可以看到一个大概的Method,ConstantsPool,InstanceKlass之间的关系
InstanceKlass 里面保存着ConstantPool指针,Method指针的数组
Method对象里保存着ConstMethod指针
ConstMethod里保存着ConstantsPool的指针
ConstantsPool里保存着InstanceKlass的指针
我们可以通过Method -> ConstMethod -> ConstantsPool ->InstanceKlass构建Method 和InstanceKlass关系
2. Method
Method结构体如下,我们可以看到在Method的只是一个载体,保存着和方法区相关的指针
// |------------------------------------------------------| // | header | // | klass | // |------------------------------------------------------| // | ConstMethod* (oop) | // |------------------------------------------------------| // | methodData (oop) | // | methodCounters | // |------------------------------------------------------| // | access_flags | // | vtable_index | // |------------------------------------------------------| // | result_index (C++ interpreter only) | // |------------------------------------------------------| // | method_size | intrinsic_id| flags | // |------------------------------------------------------| // | code (pointer) | // | i2i (pointer) | // | adapter (pointer) | // | from_compiled_entry (pointer) | // | from_interpreted_entry (pointer) | // |------------------------------------------------------| // | native_function (present only if native) | // | signature_handler (present only if native) | // |------------------------------------------------------| class Method : public Metadata { friend class VMStructs; private: ConstMethod* _constMethod; // Method read-only data. MethodData* _method_data; MethodCounters* _method_counters; AccessFlags _access_flags; // Access flags int _vtable_index; // vtable index of this method (see VtableIndexFlag) ... nmethod* volatile _code; // Points to the corresponding piece of native code }
我们主要介绍Method结构体中的MethodData、ConstMethod、nmethod
2.1 MethodData
MethodData结构基础是ProfileData,记录函数运行状态下的数据,通常JIT编译的时候有多个Level,C2级别编译下需要进行编译优化的统计分析的数据,下表是几种JIT的编译级别
* The system supports 5 execution levels: * * level 0 - interpreter * * level 1 - C1 with full optimization (no profiling) * * level 2 - C1 with invocation and backedge counters * * level 3 - C1 with full profiling (level 2 + MDO) * * level 4 - C2
MethodData里面分为3个部分,一个是函数类型等运行相关统计数据,一个是参数类型运行相关统计数据,还有一个是extra扩展区保存着deoptimization的相关信息,整个内存情况请参考下图
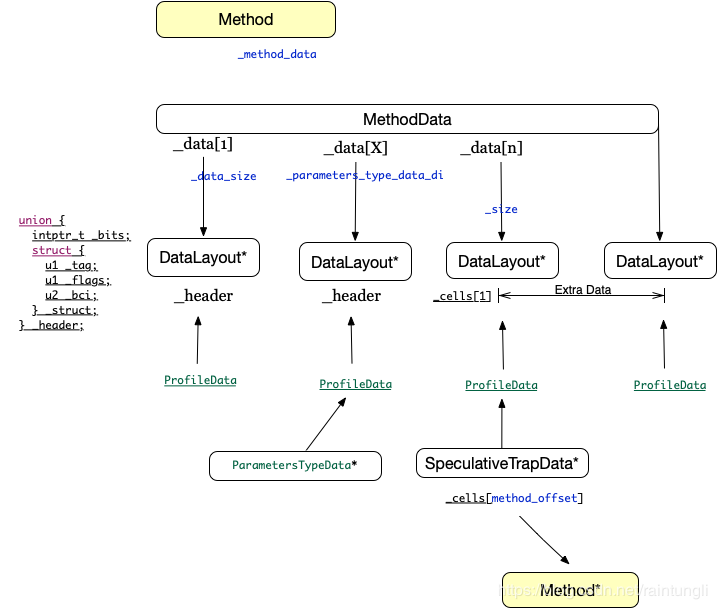
我们介绍一种extra扩展区的SpeculativeTrapData类型,这是在JVM在进行的deoptimization method A过程中会反向的将method A指针保存到method A调用的Method的Extra data中
2.2 ConstMethod
ConstMethod是Method的相关统计信息,如代码大小,代码名字的索引,方法的序列号,本地参数的数量等
1 enum { 2 _has_linenumber_table = 0x0001, 3 _has_checked_exceptions = 0x0002, 4 _has_localvariable_table = 0x0004, 5 _has_exception_table = 0x0008, 6 _has_generic_signature = 0x0010, 7 _has_method_parameters = 0x0020, 8 _is_overpass = 0x0040, 9 _has_method_annotations = 0x0080, 10 _has_parameter_annotations = 0x0100, 11 _has_type_annotations = 0x0200, 12 _has_default_annotations = 0x0400 13 }; 14 15 // Bit vector of signature 16 // Callers interpret 0=not initialized yet and 17 // -1=too many args to fix, must parse the slow way. 18 // The real initial value is special to account for nonatomicity of 64 bit 19 // loads and stores. This value may updated and read without a lock by 20 // multiple threads, so is volatile. 21 volatile uint64_t _fingerprint; 22 23 ConstantPool* _constants; // Constant pool 24 25 // Raw stackmap data for the method 26 Array<u1>* _stackmap_data; 27 28 int _constMethod_size; 29 u2 _flags; 30 u1 _result_type; // BasicType of result 31 32 // Size of Java bytecodes allocated immediately after Method*. 33 u2 _code_size; 34 u2 _name_index; // Method name (index in constant pool) 35 u2 _signature_index; // Method signature (index in constant pool) 36 u2 _method_idnum; // unique identification number for the method within the class 37 // initially corresponds to the index into the methods array. 38 // but this may change with redefinition 39 u2 _max_stack; // Maximum number of entries on the expression stack 40 u2 _max_locals; // Number of local variables used by this method 41 u2 _size_of_parameters; // size of the parameter block (receiver + arguments) in words 42 u2 _orig_method_idnum; // Original unique identification number for the method
其中_constants,_method_idnum这两个是链接method的参数,因为method有constMethod指针,但constMethod没有method的指针,如何通过constMethod来获取Method,需要通过ConstantPool -> InstanceKlass -> Method数组->第_method_idnum个来获取Method指针
2.3 nmethod
nmethod全名native method,指向的是Java method编译的一个版本。当一个方法被JNI编译后会生成一个nmethod,指向的是编译的代码,整个 nmethod结构包含如下:
1 // - header (the nmethod structure) 2 // [Relocation] 3 // - relocation information 4 // - constant part (doubles, longs and floats used in nmethod) 5 // - oop table 6 // [Code] 7 // - code body 8 // - exception handler 9 // - stub code 10 // [Debugging information] 11 // - oop array 12 // - data array 13 // - pcs 14 // [Exception handler table] 15 // - handler entry point array 16 // [Implicit Null Pointer exception table] 17 // - implicit null table array
里面包含的代码段,异常处理等,有一个指向method的指针,和指向method*的指针jmethodID
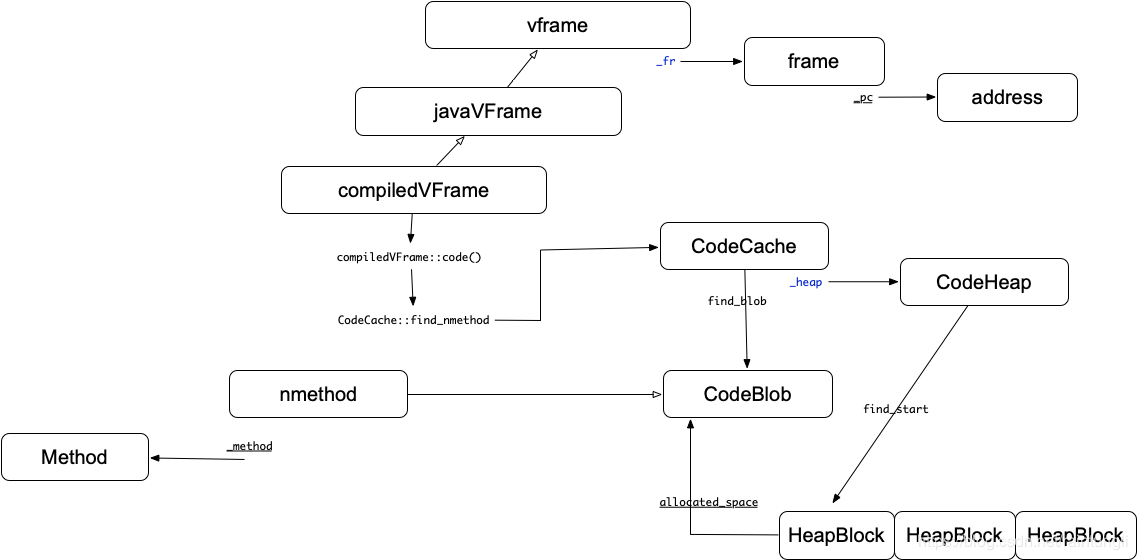
nmethod本质是一个codeblob,被保存在codecache中的CodeHeap堆区的HeapBlock块中。Method保存着最新的nmethod的指针,同时nmethod也有指向被编译的Method的指针。在上图的表示中,我们可以通过轮训整个codecache的codeheap区获取到所有已经编译的nmethod
2.3.1 nmethod的状态
1 enum { in_use = 0, // executable nmethod 2 not_entrant = 1, // marked for deoptimization but activations may still exist, 3 // will be transformed to zombie when all activations are gone 4 zombie = 2, // no activations exist, nmethod is ready for purge 5 unloaded = 3 }; // there should be no activations, should not be called, 6 // will be transformed to zombie immediately
nmethod有4种状态:
0代表这还在使用
1表示可以被转化成zombie的状态,但依然存活
2是zombie状态代表nmethod可被回收
3是not_entrant和zombie的中间状态,表示可以立刻转化成zombie状态
nmethod的状态的改变是通过sweeper来改变,比如在deoptimization场景下原来已经编译的nmethod设置成not_entrant的状态,通过sweeper最后转化成了zombie的状态后被回收,而当nmethod在0,1的状态下还是代表存活的状态
2.3.2 nmethod编译
nmethod是通过CompilerThread线程(JavaThread)进行独立编译的,对不同的C1,C2 级别会构建不同数量的线程,默认是C1是1个线程,C2是2个线程,该线程数量无法通过参数设置改变线程数量
线程会去轮训CompileQueue的队列,CompileQueue里会保存着每个要执行的CompileTask,当CompileQueue的任务执行完后线程会堵塞
1 void CompileBroker::compiler_thread_loop() { 2 CompilerThread* thread = CompilerThread::current(); 3 CompileQueue* queue = thread->queue(); 4 ... 5 // Poll for new compilation tasks as long as the JVM runs. Compilation 6 // should only be disabled if something went wrong while initializing the 7 // compiler runtimes. This, in turn, should not happen. The only known case 8 // when compiler runtime initialization fails is if there is not enough free 9 // space in the code cache to generate the necessary stubs, etc. 10 while (!is_compilation_disabled_forever()) { 11 // We need this HandleMark to avoid leaking VM handles. 12 HandleMark hm(thread); 13 14 if (CodeCache::unallocated_capacity() < CodeCacheMinimumFreeSpace) { 15 // the code cache is really full 16 handle_full_code_cache(); 17 } 18 19 CompileTask* task = queue->get(); 20 if (task == NULL) { 21 continue; 22 } 23 24 // Give compiler threads an extra quanta. They tend to be bursty and 25 // this helps the compiler to finish up the job. 26 if( CompilerThreadHintNoPreempt ) 27 os::hint_no_preempt(); 28 29 // trace per thread time and compile statistics 30 CompilerCounters* counters = ((CompilerThread*)thread)->counters(); 31 PerfTraceTimedEvent(counters->time_counter(), counters->compile_counter()); 32 33 // Assign the task to the current thread. Mark this compilation 34 // thread as active for the profiler. 35 CompileTaskWrapper ctw(task); 36 nmethodLocker result_handle; // (handle for the nmethod produced by this task) 37 task->set_code_handle(&result_handle); 38 methodHandle method(thread, task->method()); 39 40 // Never compile a method if breakpoints are present in it 41 if (method()->number_of_breakpoints() == 0) { 42 // Compile the method. 43 if ((UseCompiler || AlwaysCompileLoopMethods) && CompileBroker::should_compile_new_jobs()) { 44 invoke_compiler_on_method(task); 45 } else { 46 // After compilation is disabled, remove remaining methods from queue 47 method->clear_queued_for_compilation(); 48 task->set_failure_reason("compilation is disabled"); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 53 // Shut down compiler runtime 54 shutdown_compiler_runtime(thread->compiler(), thread); 55 }
当该方法有断点的时候并不进行编译,当参数-XX:-BackgroundCompilation设置成不是后台编译的时候,并不代表是在用户线程编译,而是提交任务CompileTask到CompileQueue,唯一的区别是堵塞当前线程等待CompileThread直到Task编译成功
1 void CompileBroker::compile_method_base(methodHandle method, 2 int osr_bci, 3 int comp_level, 4 methodHandle hot_method, 5 int hot_count, 6 const char* comment, 7 Thread* thread) { 8 ...... 9 10 if (blocking) { 11 wait_for_completion(task); 12 } 13 }
2.3.3 nmethod的回收(sweep)
在2.3.2中描述过,nmethod进入zombie状态,代表着该nmethod会回收,nmethod是在GC的时候被回收的么?并不是而是在接收CompileTask的时候由CompileThread来触发,但是并不代表着GC无关,这里有个比较复杂的算法,在GC的时候会更改一些统计数据。
CompileThread 满足下列条件会触发nmethod 进行sweep函数NMethodSweeper::possibly_sweep();
一轮sweep :代表从nmethod从头到尾一次回收
当从CompileQueue里获取到ComileTask的时候触发
当从CompileQueue里没有获取到ComileTask的时候,在等待一定的时间NmethodSweepCheckInterval(default=5) * 1000后触发
当从CodeCache已经满的情况下(-XX:ReservedCodeCacheSize=100M)
当然触发possibly_sweep并不代表一定会触发一定去回收nmethod 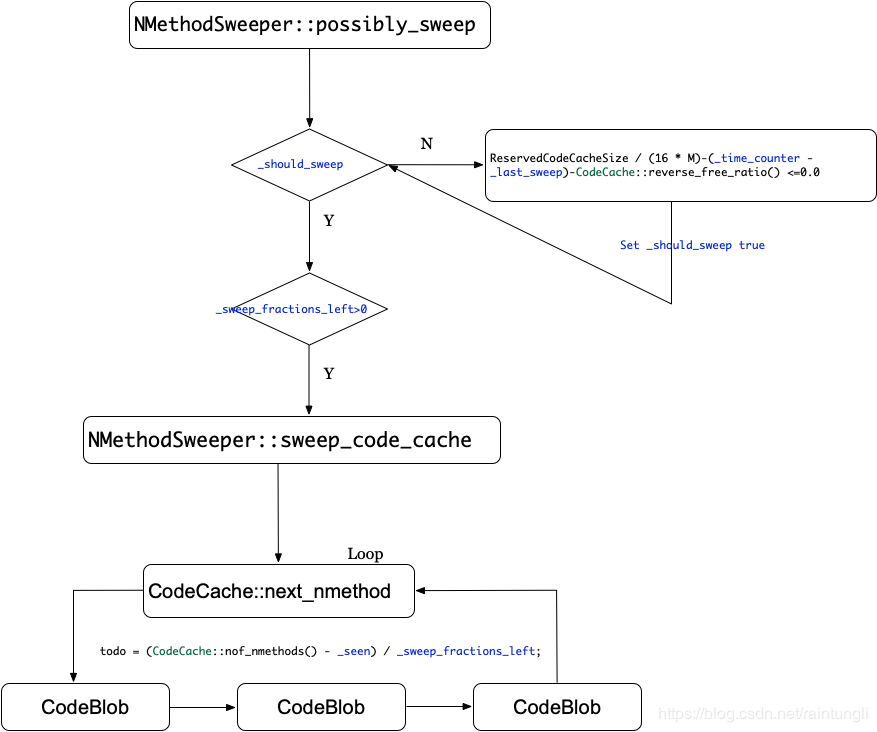
在上图我们可以看到整一个nmethod的回收是个复杂的算法
首先取决于你的-XX:ReservedCodeCacheSize参数,JVM会以16M为一次,所允许的最大次数为ReservedCodeCacheSize/16M
_time_counter代表已经进入Softpoint的次数(也就是前面提到的GC)
_last_sweep代表着已经sweep完成的次数
CodeCache::reverse_free_ratio()=最大的容量/空闲的内存
_sweep_fractions_left 默认值ReservedCodeCacheSize/16M当调用possibly_sweep的时候会减去1,当等于0的时候代表sweep 结束(设置_should_sweep =false),需要等到进入softpoint才能重置会ReservedCodeCacheSize/16M
我们可以看到当进入Softpoint次数越多,空闲的内存越少越会促发sweep code cache, 而调用函数NMethodSweeper::sweep_code_cache并不代表一定会回收所有的nmethod,在函数里还有一个 int todo = (CodeCache::nof_nmethods() - _seen) / _sweep_fractions_left;来控制这次轮训多少个nmethod,_seen代表这一轮sweep 已经轮训的个数,CodeCache::nof_nmethods()代表nmethods的总数,_sweep_fractions_left就是前面定义的,我们可以看到在sweep_code_cache并不是一次全部轮询所有的nmethods,而是将剩余的总数/_sweep_fractions_left的数量,越到一轮的sweep后期清除的数量越多,是一个渐进式的回收方式。
函数NMethodSweeper::mark_active_nmethods()会被进入softpoint的时候触发
1 void NMethodSweeper::mark_active_nmethods() { 2 assert(SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "must be executed at a safepoint"); 3 // If we do not want to reclaim not-entrant or zombie methods there is no need 4 // to scan stacks 5 if (!MethodFlushing) { 6 return; 7 } 8 9 // Increase time so that we can estimate when to invoke the sweeper again. 10 _time_counter++; 11 12 // Check for restart 13 assert(CodeCache::find_blob_unsafe(_current) == _current, "Sweeper nmethod cached state invalid"); 14 if (!sweep_in_progress()) { 15 _seen = 0; 16 _sweep_fractions_left = NmethodSweepFraction; 17 _current = CodeCache::first_nmethod(); 18 _traversals += 1; 19 _total_time_this_sweep = Tickspan(); 20 Threads::nmethods_do(&mark_activation_closure); 21 22 } else { 23 // Only set hotness counter 24 tty->print_cr("### Sweep mark_active_nmethods not in progress %d /" PTR_FORMAT " ", _traversals, _current); 25 Threads::nmethods_do(&set_hotness_closure); 26 } 27 28 OrderAccess::storestore(); 29 }
在函数里我们看到重置了_seen 和 _sweep_fractions_left,而并不是每个nmethod进入not_entrant都能进入zombie状态,同时要不能被VM调用或者ServiceThread
1 bool nmethod::can_convert_to_zombie() { 2 assert(is_not_entrant(), "must be a non-entrant method"); 3 4 // Since the nmethod sweeper only does partial sweep the sweeper's traversal 5 // count can be greater than the stack traversal count before it hits the 6 // nmethod for the second time. 7 tty->print_cr("### nmethod stack_traversal_mark %d %d",stack_traversal_mark(),NMethodSweeper::traversal_count()); 8 return stack_traversal_mark()+1 < NMethodSweeper::traversal_count() && 9 !is_locked_by_vm(); 10 }