题目:
为下面的Rectangle类实现构造函数,拷贝构造函数,赋值操作符,析构函数。
class Shape
{
int no;
};
class Point
{
int x;
int y;
};
class Rectangle: public Shape
{
int width;
int height;
Point * leftUp;
public:
Rectangle(int width, int height, int x, int y);
Rectangle(const Rectangle& other);
Rectangle& operator=(const Rectangle& other);
~Rectangle();
};
解析:
一 构造函数:
1.尽量使用初始化列表;
2.对leftUp指针的构造,leftUp指向一个Point对象,构造函数需要在堆内生成一个新的point对象,并用leftUp指向该对象
inline
Rectangle::Rectangle(int width,int heigt, int x,int y):width(width),height(height),leftUp(new Point(x,y)){}
//尽量使用初始化列表,包括对leftUp的初始化
二 拷贝构造函数:
1.尽量使用初始化列表
2.注意对父类继承而来的no的拷贝构造,方法是调用父类shape的拷贝构造函数 Shape(other)
3.对this->leftUp的拷贝构造,调用Point的拷贝构造函数,这样在Point内部有变化时,避免大量修改。
this->leftUp = new Point(*other.leftUp);
4.针对other.leftUp是否为空的讨论,空指针情况没必要在堆内生成对象,同时当other.leftUp为空时,this->leftUp初始默认是随机值,要对他进行赋值为空指针。
完整的拷贝构造函数:
inline
Rectangle::Rectangle(const Rectangle& other)
:Shape(other),width(other.width),height(other.height){ // 注意对继承而来对象no的拷贝构造,通过调用父类的拷贝构造函数
if(other.leftUp != NULL){ //针对other.leftUp是否为空的讨论,空指针情况没必要在堆内生成对象
this->leftUp = new Point(*other.leftUp); //调用Point的拷贝构造函数,这样在Point内部有变化时,避免大量修改。
}
else{
this->leftUp = NULL; //leftUp初始默认是随机值,要对他进行赋值为空指针。
}
}
三 赋值操作符
1.赋值操作符往往需要首先判定自己给自己赋值的情况,避免内存泄露
if(this == &other){
return *this;
}
2.调用父类的赋值操作符,完成对父类继承部分的赋值操作,方法如下:
Shape::operator=(other); //调用父类的赋值操作符,完成对父类继承部分的赋值操作
3.需要对leftUp,other.leftUp是否为空进行讨论
other.leftUp为空时,直接释放this->leftUp空间,并将其赋为空即可;
other.leftUp不为空时,
若this->leftUp也不为空,则直接将other->leftUp指向的内容赋值给this->leftUp指向的内容即可;
若this->leftUp为空,创建新的Point对象
Rectangle& Rectangle::operator= (const Rectangle& other){
if(this == &other){ //赋值操作符往往需要首先判定自己给自己赋值的情况,避免内存泄露
return *this;
}
Shape::operator=(other); //调用父类的赋值操作符,完成对父类继承部分的赋值操作
this->width = other.width;
this->height = other.height;
if(other.leftUp != NULL){
if(leftUp != NULL) {
*leftUp = *other.leftUp; //不必删除leftUp再重新构建,直接进行赋值即可(解指针,调用point类的赋值操作符即可)
}
else{
leftUp = new Point(*other.leftUp); //leftUp为空,不能解指针,需要创建一个新对象
}
}
else{
delete leftUp;
this->leftUp = NULL;
}
return *this;
}
四 析构函数
Rectangle:: ~Rectangle(){
delete leftUp;
}
五 整体代码和其他注意事项
1.Rectangle赋值构造函数,构造顺序:先父类,后按照子类中声明的顺序,与初始化列表中的顺序无关。
2.正确区分拷贝构造函数和赋值操作符。
拷贝构造函数是构造函数,也就是创建新对象时,所以一个对象存在,一个对象尚未存在;
赋值操作符使用时,两个对象必然都是存在的,所以需要讨论的问题是是否自我赋值等等。
3 面对此类问题方法:
先忘掉语法,画内存模型
本例即
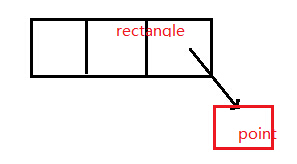
然后写的时候分析指针是否为空;
拷贝构造就是一边有,一边没有;赋值操作符就是两边都有;
结合指针是否为空,可以分析出上述的注意事项。
class Shape
{
int no;
};
class Point
{
private:
int x;
int y;
public:
Point(int x,int y):x(x),y(y){}
};
class Rectangle: public Shape
{
int width;
int height;
Point* leftUp;
public:
Rectangle(int width, int height, int x, int y);
Rectangle(const Rectangle& other);
Rectangle& operator=(const Rectangle& other);
~Rectangle();
};
inline
Rectangle::Rectangle(int width,int heigt, int x,int y):width(width),height(height),leftUp(new Point(x,y)){}
//尽量使用初始化列表,包括对leftUp的初始化
inline
Rectangle::Rectangle(const Rectangle& other)
:Shape(other),width(other.width),height(other.height){ // 注意对继承而来对象no的拷贝构造,通过调用父类的拷贝构造函数
if(other.leftUp != NULL){ //针对other.leftUp是否为空的讨论,空指针情况没必要在堆内生成对象
this->leftUp = new Point(*other.leftUp); //调用Point的拷贝构造函数,这样在Point内部有变化时,避免大量修改。
}
else{
this->leftUp = NULL; //leftUp初始默认是随机值,要对他进行赋值为空指针。
}
}
Rectangle& Rectangle::operator= (const Rectangle& other){
if(this == &other){ //赋值操作符往往需要首先判定自己给自己赋值的情况,避免内存泄露
return *this;
}
Shape::operator=(other); //调用父类的赋值操作符,完成对父类继承部分的赋值操作
this->width = other.width;
this->height = other.height;
if(other.leftUp != NULL){
if(leftUp != NULL) {
*leftUp = *other.leftUp; //不必删除leftUp再重新构建,直接进行赋值即可(解指针,调用point类的赋值操作符即可)
}
else{
leftUp = new Point(*other.leftUp); //leftUp为空,不能解指针,需要创建一个新对象
}
}
else{
delete leftUp;
this->leftUp = NULL;
}
return *this;
}
Rectangle:: ~Rectangle(){
delete leftUp;
}
