二叉排序树
什么是二叉排序树、
二叉排序树要么是空二叉树,要么具有如下性质:
二叉排序树中,如果其根结点有左子树,那么左子树上所有结点的值都小于根结点的值;
二叉排序树中,如果其根结点有右子树,那么右子树上所有结点的值都大于根结点的值;
二叉排序树的左右子树也要求都是二叉排序树.
例子
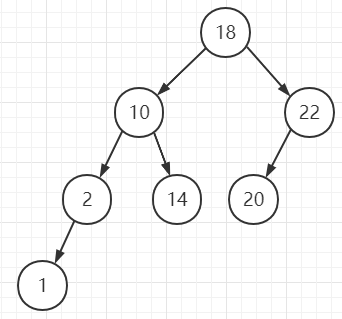
根据以上性质,我们得知二叉排序树的中序遍历是一个有序序列(升序),如上图中序遍历得到的序列为:1 2 10 14 18 20 22
结构定义
struct Node {
int key;
Node *lchild, *rchild;
};
节点初始化
我们定义一个函数Node* getNewNode(int key),其传入参数是一个key,返回值为一个节点地址,表示初始化一个具体key值的节点,这里是为了给插入节点函数服务所实现的。
Node *getNewNode(int key) {
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->key = key;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NIL;
}
插入操作
根据上面二叉排序树的性质1和性质2,当我们往一个二叉排序树种插入一个节点时,当要插入的节点的key值小于根节点的key值,则递归插入到根节点的左子树;若要插入的节点的key值大于根节点的key值,则递归插入到根节点的右子树;若二叉排序树中存在与要插入节点一样key值得节点,则不插入并返回该节点的地址。由于性质决定,插入的新节点,一定会是二叉排序树的叶子节点。
代码
Node *insert(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,可以在这里插入新节点,且插入后该节点为叶子节点
if (root == NULL) {
return getNewNode(key);
}
if (key == root->key) {//这里不重复插入相同key值得节点
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//若插入key比当前节点的key小,则递归到当前节点的左子树中去插入
root->lchild = insert(root->lchild, key);
} else (key > root->key) {//若插入key比当前节点的key大,则递归到当前节点的右子树中去插入
root->rchild = insert(root->rchild, key);
}
return root;
}
删除操作
根据删除节点的度来区分,我们可以把删除操作主要分为三个部分,:
删除度为0的节点 -> 直接删除
删除度为1的节点 -> 把删除节点的孤儿节点挂到自己的位置上
删除度为2的节点 -> 转化为删除要删除节点的前驱或者后继
对于度为2的节点:
前驱 -> 左子树的最大值
后继 -> 右子树的最小值
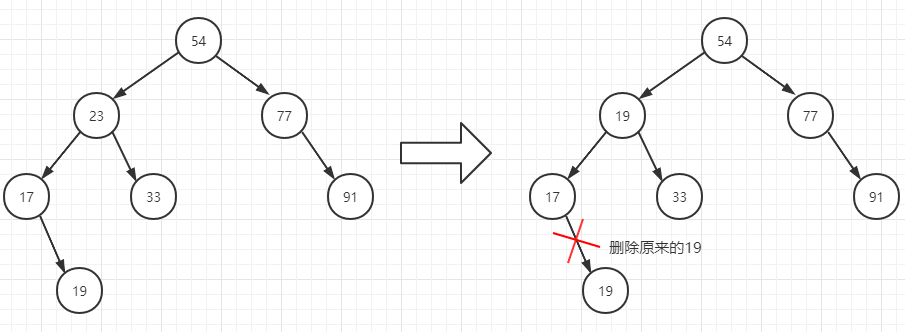
删除度为2的例子
比如我们想删除节点23,节点23度为2,这时候我们找到它的前驱节点19,把前驱节点的key值填到23节点的位置,再删除23的前驱节点19。
代码
求出某个节点前驱的代码
//传入某个节点的地址root,然后求出root节点的前驱节点的地址,并返回
Node *prodecessor(Node *root) {
Node *p = root->lchild;
while (p != NIL) {
p = p->rchild;
}
return p;
}
删除节点代码
Node *erase(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,直接返回
if (root == NULL) {
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//key值小于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, key);
} else if (key > root->key) {//key值大于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->rchild = erase(root->rchild, key);
} else {//key值与当前节点的key一样,则以度的数量开始区分删除情况。
if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL) {//度为1:直接删除
free(root);;
return NULL;
} else if (root->lchild == NULL || root->rchild == NULL) {//度为2:直接返回孤儿节点的地址给自身
Node *temp = root->lchild == NULL ? root->rchild : root->lchild;
free(root);
return temp;
} else {//度为2:直接转化为删除该节点的前驱节点
Node *temp = predecessor(root);
root->key = temp->key;
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, temp->key);
}
}
return root;
}
遍历二叉排序树
这里我们采用中序遍历的方式遍历二叉排序树。
void in_order(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return ;
}
in_order(root->lchild);
printf("%d ", root->key);
in_order(root->rchild);
return ;
}
完整代码
这里我们给出完整代码,该代码带有测试程序,首先根据提示,有选择操作的选项,输入1表示插入操作;输入2表示删除操作,选择完操作后,需要输入一个key,然后每次操作完毕,都会中序遍历输出该二叉排序树的所有节点。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define KEY(n) (n ? n->key : -1)
typedef struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *lchild, *rchild;
} Node;
Node *getNewNode(int key) {
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->key = key;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
}
void clear(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return ;
}
clear(root->lchild);
clear(root->rchild);
free(root);
return ;
}
Node *insert(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,可以在这里插入新节点,且插入后该节点为叶子节点
if (root == NULL) {
return getNewNode(key);
}
if (root->key == key) {//这里不重复插入相同key值得节点
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//若插入key比当前节点的key小,则递归到当前节点的左子树中去插入
root->lchild = insert(root->lchild, key);
} else {//若插入key比当前节点的key大,则递归到当前节点的右子树中去插入
root->rchild = insert(root->rchild, key);
}
return root;
}
Node *prodecessor(Node *root) {
Node *p = root->lchild;
while (p->rchild != NULL) {
p = p->rchild;
}
return p;
}
Node *erase(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,直接返回
if (root == NULL) {
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//key值小于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, key);
} else if (key > root->key){//key值大于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->rchild = erase(root->rchild, key);
} else {//key值与当前节点的key一样,则以度的数量开始区分删除情况。
if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL) {//度为0:直接删除
free(root);
return NULL;
} else if (root->lchild == NULL || root->rchild == NULL) {//度为1:直接返回孤儿节点的地址给自身
Node *p = root->lchild == NULL ? root->rchild : root->lchild;
free(root);
return p;
} else {//度为2:直接转化为删除该节点的前驱节点
Node *p = prodecessor(root);
root->key = p->key;
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, p->key);
}
}
return root;
}
void print_node(Node *root) {
printf("(%d: %d, %d)
", KEY(root), KEY(root->lchild), KEY(root->rchild));
}
void _in_order(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return ;
}
_in_order(root->lchild);
print_node(root);
_in_order(root->rchild);
return ;
}
void in_order(Node *root) {
printf("binary tree:
");
_in_order(root);
printf("
");
}
void menu(void) {
printf("Please enter the operation:
");
printf("Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
");
printf("Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
");
printf("Press TRL + D to quit!
");
}
int main() {
Node *root = NULL;
int op, key;
menu();
while (~scanf("%d", &op)) {
if (op != 1 && op != 2) {
printf("please enter the right operation!
");
continue;
}
switch (op) {
case 1:
printf("Enter the key you want to insert: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
root = insert(root, key);
break;
case 2:
printf("Enter the key you want to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
root = erase(root, key);
break;
}
in_order(root);
menu();
}
clear(root);
return 0;
}
测试结果
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 12
binary tree:
(12: -1, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 8
binary tree:
(8: -1, -1)
(12: 8, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 34
binary tree:
(8: -1, -1)
(12: 8, 34)
(34: -1, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 56
binary tree:
(8: -1, -1)
(12: 8, 34)
(34: -1, 56)
(56: -1, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
2 12
Enter the key you want to delete: binary tree:
(8: -1, 34)
(34: -1, 56)
(56: -1, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1 12
Enter the key you want to insert: binary tree:
(8: -1, 34)
(12: -1, -1)
(34: 12, 56)
(56: -1, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
思考
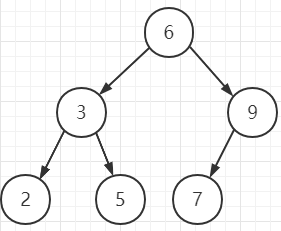
如果我们分别进行两棵二叉排序树的插入构建。其中插入到这两棵树的节点的key和节点数量完全相同,唯一不同的是插入顺序不同,例如:
第一棵树按一下顺序插入6个元素: 6 9 3 2 7 5
第二棵树按以下顺序插入6个元素: 2 3 5 6 7 9
查找一个元素的时间复杂度一样吗?
这里,我们先直接画出这两棵树
第一棵
第二棵
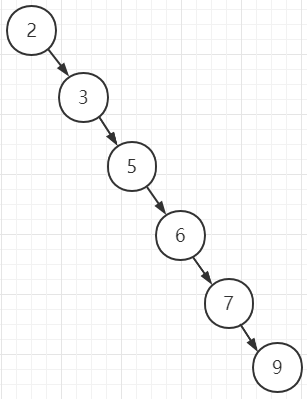
这里的时候,第一棵二叉排序树的元素平均查找期望是(1+2*2+3*3)/6 = 5/2,大致是O(logN)级别的时间复杂度;而第二棵树的凭据查找期望是(1+2+3+4+5+6)/6 = 7/3,且这很明显,这里第二颗树已经退化成链表,这时候它的查找效率是O(N),而对比第一棵树,由于是一棵完全二叉树,其查找效率在O(logN)。由此,我们可以下定结论:
- 插入顺序会影响最终的树形结构
- 不同的树形结构,查找效率不同
为了解决以上二叉排序树会退化成链表,导致查找效率变低的情况,在二叉排序树的基础上,二叉平衡树诞生了。
拓展
二叉排序树的删除代码优化
删除掉处理度为0的代码逻辑,不影响代码整体功能
Node *erase(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,直接返回
if (root == NULL) {
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//key值小于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, key);
} else if (key > root->key) {//key值大于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->rchild = erase(root->rchild, key);
} else {//key值与当前节点的key一样,则以度的数量开始区分删除情况。
if (root->lchild == NULL || root->rchild == NULL) {//删除度为0或者1都可以这个分支。
Node *temp = root->lchild == NULL ? root->rchild : root->lchild;
delete root;
return temp;
} else {//度为2:直接转化为删除该节点的前驱节点
Node *temp = predecessor(root);
root->key = temp->key;
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, temp->key);
}
}
return root;
}
如何解决排名相关的检索需求
- 修改二叉排序树的结构定义,增加 size 字段,记录每棵树的节点数量
- 若K = LS + 1,则根节点就是排名第 k 位的元素
- 若K <= LS,则排名第 K 位的元素在左子树中
- 若K > LS + 1,则排名第 k 位的元素在右子树中
PS:LS指某个节点的左子树节点数量
带排名版本的二叉排序树
结构定义
typedef struct Node {
int key, size;
struct Node *lchild, *rchild;
} Node;
在结构定义中,增加了size字段名,用来记录每个子树的节点数量。
节点初始化
Node *getNewNode(int key) {
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->key = key;
p->size = 1;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
}
节点初始化,由于增加了size字段,同样的,节点初始化的时候,size字段也要初始化为1.
子树节点数量更新函数
void update_size(Node *root) {
root->size = SIZE(root->lchild) + SIZE(root->rchild) + 1;
}
每一个根节点的节点数量为其左右子树节点数的和加1。
插入
Node *insert(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,可以在这里插入新节点,且插入后该节点为叶子节点
if (root == NULL) {
return getNewNode(key);
}
if (root->key == key) {//这里不重复插入相同key值得节点
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//若插入key比当前节点的key小,则递归到当前节点的左子树中去插入
root->lchild = insert(root->lchild, key);
} else {//若插入key比当前节点的key大,则递归到当前节点的右子树中去插入
root->rchild = insert(root->rchild, key);
}
update_size(root);//更新节点数量
return root;
}
在插入操作返回前,必须先更新节点数量。
删除
Node *erase(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,直接返回
if (root == NULL) {
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//key值小于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, key);
} else if (key > root->key){//key值大于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->rchild = erase(root->rchild, key);
} else {//key值与当前节点的key一样,则以度的数量开始区分删除情况。
if (root->lchild == NULL || root->rchild == NULL) {//删除度为0或者1都可以这个分支。
Node *p = root->lchild == NULL ? root->rchild : root->lchild;
free(root);
return p;
} else {////度为2:直接转化为删除该节点的前驱节点
Node *p = prodecessor(root);
root->key = p->key;
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, p->key);
}
}
update_size(root);//更新节点数量
return root;
}
同样的,在删除操作返回前,也要更新节点数量。
注意:
无论是插入还是删除,之所以在返回root节点前更新节点数量,这是因为插入和删除只会影响到回溯时经过的节点(也就是插入节点的祖先节点)对应的子树的节点数量。
查找第K位元素
int find_k(Node *root, int k) {
if (root == NULL || k == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (k == SIZE(root->lchild) + 1) {//若root节点的左子树节点数量 + 1等于 k,则root节点就是第K个节点
return root->key;
}
if (k <= SIZE(root->lchild)) {//若root节点的左子树节点数量大于等于k,则递归到左子树中去找第K个节点
return find_k(root->lchild, k);
}
//若root左子树节点数量 + 1小于K,则递归到右子树中去找右子树中第K - size(L(root)) - 1个节点。
if (k > SIZE(root->lchild) + 1) {
return find_k(root->rchild, k - SIZE(root->lchild) - 1);
}
}
宏定义
#define KEY(n) (n ? n->key : -1)//返回某个节点的key值
#define SIZE(n) (n ? n->size : 0)//返回某个节点对应的树的节点数量
解决 Top-K 问题(找到小于第 k 位的所有元素)
- 根节点就是第 k 位元素的话,就把左子树中的值全部输出出来
- 第 k 位在左子树中,前 k 位元素全都在左子树中
- 第 k 位在右子树中,说明根节点和左子树中的元素,都是前 k 位元素里面的值
void output_k(Node *root, int k) {
if (root == NULL || k <= 0) {
return ;
}
if (k == SIZE(root->lchild)) {
_in_order(root->lchild);
} else if (k < SIZE(root->lchild)) {
output_k(root->lchild, k);
} else {
_in_order(root->lchild);
print_node(root);
output_k(root->rchild, k - SIZE(root->lchild) - 1);
}
}
加上拓展后的完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define KEY(n) (n ? n->key : -1)
#define SIZE(n) (n ? n->size : 0)
typedef struct Node {
int key, size;
struct Node *lchild, *rchild;
} Node;
Node *getNewNode(int key) {
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->key = key;
p->size = 1;
p->lchild = p->rchild = NULL;
}
void clear(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return ;
}
clear(root->lchild);
clear(root->rchild);
free(root);
return ;
}
void update_size(Node *root) {
root->size = SIZE(root->lchild) + SIZE(root->rchild) + 1;
}
Node *insert(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,可以在这里插入新节点,且插入后该节点为叶子节点
if (root == NULL) {
return getNewNode(key);
}
if (root->key == key) {//这里不重复插入相同key值得节点
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//若插入key比当前节点的key小,则递归到当前节点的左子树中去插入
root->lchild = insert(root->lchild, key);
} else {//若插入key比当前节点的key大,则递归到当前节点的右子树中去插入
root->rchild = insert(root->rchild, key);
}
update_size(root);
return root;
}
Node *prodecessor(Node *root) {
Node *p = root->lchild;
while (p->rchild != NULL) {
p = p->rchild;
}
return p;
}
Node *erase(Node *root, int key) {
//root是空,则表明从根节点遍历到这个空节点都没有找到与参数key值一样的节点,直接返回
if (root == NULL) {
return root;
}
if (key < root->key) {//key值小于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, key);
} else if (key > root->key){//key值大于当前节点的key,则要删除的点在root的左子树上
root->rchild = erase(root->rchild, key);
} else {//key值与当前节点的key一样,则以度的数量开始区分删除情况。
if (root->lchild == NULL || root->rchild == NULL) {//删除度为0或者1都可以这个分支。
Node *p = root->lchild == NULL ? root->rchild : root->lchild;
free(root);
return p;
} else {////度为2:直接转化为删除该节点的前驱节点
Node *p = prodecessor(root);
root->key = p->key;
root->lchild = erase(root->lchild, p->key);
}
}
update_size(root);
return root;
}
void print_node(Node *root) {
printf("(%d[%d]: %d, %d)
", KEY(root), SIZE(root), KEY(root->lchild), KEY(root->rchild));
}
void _in_order(Node *root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return ;
}
_in_order(root->lchild);
print_node(root);
_in_order(root->rchild);
return ;
}
void in_order(Node *root) {
printf("binary tree:
");
_in_order(root);
printf("
");
}
int find_k(Node *root, int k) {
if (root == NULL || k == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (k == SIZE(root->lchild) + 1) {//若root节点的左子树节点数量 + 1等于 k,则root节点就是第K个节点
return root->key;
}
if (k <= SIZE(root->lchild)) {//若root节点的左子树节点数量大于等于k,则递归到左子树中去找第K个节点
return find_k(root->lchild, k);
}
//若root左子树节点数量 + 1小于K,则递归到右子树中去找右子树中第K - size(L(root)) - 1个节点。
if (k > SIZE(root->lchild) + 1) {
return find_k(root->rchild, k - SIZE(root->lchild) - 1);
}
}
void menu(void) {
printf("Please enter the operation:
");
printf("Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
");
printf("Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
");
printf("Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
");
printf("Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
");
printf("Press TRL + D to quit!
");
}
int main() {
Node *root = NULL;
int op, val;
menu();
while (~scanf("%d", &op)) {
if (op < 1 || op > 4) {
printf("please enter the right operation!
");
continue;
}
switch (op) {
case 1:
printf("Enter the key you want to insert: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
root = insert(root, val);
break;
case 2:
printf("Enter the key you want to delete: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
root = erase(root, val);
break;
case 3:
printf("Enter the index you are looking for:");
scanf("%d", &val);
printf("Find NO.%d of the binary tree, result: %d
", val, find_k(root, val));
break;
case 4:
printf("Enter a k for output top-k sequence: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
output_k(root, val);
printf("
");
break;
}
if (op != 3 && op != 4) {
in_order(root);
}
menu();
}
clear(root);
return 0;
}
测试结果
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 12
binary tree:
(12[1]: -1, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 8
binary tree:
(8[1]: -1, -1)
(12[2]: 8, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 10
binary tree:
(8[2]: -1, 10)
(10[1]: -1, -1)
(12[3]: 8, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 9
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[4]: 8, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 34
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[5]: 8, 34)
(34[1]: -1, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 23
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[6]: 8, 34)
(23[1]: -1, -1)
(34[2]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 20
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[7]: 8, 34)
(20[1]: -1, -1)
(23[2]: 20, -1)
(34[3]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 18
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[8]: 8, 34)
(18[1]: -1, -1)
(20[2]: 18, -1)
(23[3]: 20, -1)
(34[4]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 17
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[9]: 8, 34)
(17[1]: -1, -1)
(18[2]: 17, -1)
(20[3]: 18, -1)
(23[4]: 20, -1)
(34[5]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 19
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[10]: 8, 34)
(17[1]: -1, -1)
(18[3]: 17, 19)
(19[1]: -1, -1)
(20[4]: 18, -1)
(23[5]: 20, -1)
(34[6]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 21
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[11]: 8, 34)
(17[1]: -1, -1)
(18[3]: 17, 19)
(19[1]: -1, -1)
(20[5]: 18, 21)
(21[1]: -1, -1)
(23[6]: 20, -1)
(34[7]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 25
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[12]: 8, 34)
(17[1]: -1, -1)
(18[3]: 17, 19)
(19[1]: -1, -1)
(20[5]: 18, 21)
(21[1]: -1, -1)
(23[7]: 20, 25)
(25[1]: -1, -1)
(34[8]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
1
Enter the key you want to insert: 28
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[13]: 8, 34)
(17[1]: -1, -1)
(18[3]: 17, 19)
(19[1]: -1, -1)
(20[5]: 18, 21)
(21[1]: -1, -1)
(23[8]: 20, 25)
(25[2]: -1, 28)
(28[1]: -1, -1)
(34[9]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
2
Enter the key you want to delete: 17
binary tree:
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[12]: 8, 34)
(18[2]: -1, 19)
(19[1]: -1, -1)
(20[4]: 18, 21)
(21[1]: -1, -1)
(23[7]: 20, 25)
(25[2]: -1, 28)
(28[1]: -1, -1)
(34[8]: 23, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
3
Enter the index you are looking for:4
Find NO.4 of the binary tree, result: 12
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
3
Enter the index you are looking for:10
Find NO.10 of the binary tree, result: 25
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
4
Enter a k for output top-k sequence: 7
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[12]: 8, 34)
(18[2]: -1, 19)
(19[1]: -1, -1)
(20[4]: 18, 21)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
4
Enter a k for output top-k sequence: 3
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
4
Enter a k for output top-k sequence: 4
(8[3]: -1, 10)
(9[1]: -1, -1)
(10[2]: 9, -1)
(12[12]: 8, 34)
Please enter the operation:
Press 1 to insert a node to binary search tree
Press 2 to delete a node from binary search tree
Press 3 to find a node from binary search tree
Press 4 to output top-k sequence from binary search tree
Press TRL + D to quit!
原创博文,转发请加上原链接