std::vector
template < class T, class Alloc = allocator<T> > class vector; // generic template
vector是表示可以改变大小的数组的序列容器。
就像数组一样,向量对其元素使用连续的存储位置,这意味着也可以使用指向其元素的常规指针上的偏移量来访问它们的元素,并且与在数组中一样有效。但与数组不同的是,它们的大小可以动态变化,它们的存储由容器自动处理。
在内部,向量使用动态分配的数组来存储它们的元素。当插入新元素时,可能需要重新分配该数组以增加大小,这意味着分配一个新数组并将所有元素移至该数组。就处理时间而言,这是一项相对昂贵的任务,因此,向量不会在每次将元素添加到容器时重新分配。
相反,向量容器可能会分配一些额外的存储空间来适应可能的增长,因此容器的实际容量可能大于包含其元素所严格需要的存储空间(即它的大小)。库可以实施不同的增长策略来平衡内存使用和重新分配,但无论如何,重新分配应该只发生在对数增长的大小间隔上,以便可以为向量末尾的单个元素插入提供摊销常数时间复杂性(参见push_back)。
因此,与数组相比,向量消耗更多内存以换取管理存储和以有效方式动态增长的能力。
与其他动态序列容器(deques、list和forward_lists)相比,vector 访问其元素(就像数组一样)非常有效,并且从其末尾添加或删除元素也相对有效。对于涉及在结尾以外的位置插入或删除元素的操作,它们的性能比其他操作更差,并且迭代器和引用的一致性不如列表和forward_lists。
容器属性
序列
序列容器中的元素按严格的线性顺序排序。单个元素通过它们在此序列中的位置进行访问
动态数组
允许直接访问序列中的任何元素,甚至通过指针算术,并在序列末尾提供相对快速的元素添加/删除。
分配器感知
容器使用分配器对象来动态处理其存储需求。
模板参数
T
只有保证T 在移动时不会抛出,实现才能优化移动元素而不是在重新分配期间复制它们。
别名为成员类型vector::value_type。
Alloc
用于定义存储分配模型的分配器对象的类型。默认使用分配器类模板,它定义了最简单的内存分配模型,并且与值无关。
别名为成员类型vector::allocator_type。
构造函数
1 // construct/copy/destroy:
2 explicit vector(const Allocator& = Allocator()); //默认构造函数 构造一个没有元素的空容器
3
4 explicit vector(size_type n);
5 vector(size_type n, const bool& value,const Allocator& = Allocator());
6 //构造一个包含n 个元素的容器。每个元素都是val的副本(如果提供)
7
8 template <class InputIt>
9 vector(InputIt first, InputIt last,const Allocator& = Allocator());
10 //范围构造函数
11 //构造一个包含与范围[first,last)一样多的元素的容器,每个元素都从该范围内的对应元素以相同的顺序emplace 构造。
12
13 vector(const vector<bool,Allocator>& x);
14 vector(const vector&, const Allocator&);//拷贝构造函数
15
16 vector(vector&& x);
17 vector(vector&& x, const Allocator&);
18 //构造一个获取x元素的容器 可看作二维数组
19 //如果指定了alloc并且与x的分配器不同,则移动元素。否则,不构造任何元素(它们的所有权直接转移)。
20 //x处于未指定但有效的状态。
21
22 vector(initializer_list<bool>, const Allocator& = Allocator());
23 //初始化列表构造函数
迭代器
1 // iterators:
2 //负责返回指向第一个元素(或第一个字符的迭代器)。
3 iterator begin() noexcept;
4 const_iterator begin() const noexcept;
5
6 //负责返回容器(或者string)“尾元素的下一个位置”的迭代器
7 iterator end() noexcept;
8 const_iterator end() const noexcept;
9
10 //将vector反转后的开始指针返回(其实就是原来的end-1)
11 reverse_iterator rbegin() noexcept;
12 const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const noexcept;
13
14 //将vector反转构的结束指针返回(其实就是原来的begin-1)
15 reverse_iterator rend() noexcept;
16 const_reverse_iterator rend() const noexcept;
17
18 //为了便于得到const_iterator类型的返回值,C++11引入了cbegin和cend
19 //用法与begin和end相同,但返回的只能是const_iterator类型。
20 const_iterator cbegin() const noexcept;
21 const_iterator cend() const noexcept;
22 const_reverse_iterator crbegin() const noexcept;
23 const_reverse_iterator crend() const noexcept;
容量
1 // capacity:
2
3 size_type size() const noexcept; //返回容器大小
4 size_type max_size() const noexcept;//返回容器最大大小
5
6 void resize(size_type sz);
7 void resize(size_type sz, const bool& c); //为容器扩容
8
9 size_type capacity() const noexcept; //返回当前为vector分配的存储空间的大小,以元素表示
10
11 [[nodiscard]] bool empty() const noexcept; //判断容器是否为空
12
13 void reserve(size_type n); //请求更改容量 要求向量容量至少足以包含n个元素
14
15 void shrink_to_fit(); //请求容器减小其容量以适应其大小
16 //这可能会导致重新分配,但对向量大小没有影响并且不能改变其元素
元素访问
1 reference operator[](size_type n);
2 const_reference operator[](size_type n) const; //重载[] 下标访问
3
4 reference at(size_type n);
5 const_reference at(size_type n) const; //会进行边界检查,若越界会抛出out_of_range异常
6
7 reference front();
8 const_reference front() const; //访问第一个元素
9
10 reference back();
11 const_reference back() const; //访问最后一个元素
修改
1 // modifiers:
2
3 //在容器末尾插入一个新元素 将容器大小增加1
4 template <class... Args> void emplace_back(Args&&... args);
5 void push_back(const bool& x);
6 void push_back(bool&& x);
7
8 //删除容器末尾的元素 并且将容器大小减小1
9 void pop_back();
10
11 //往容器中插入元素
12 template <class... Args> iterator emplace(const_iterator position, Args&&... args);
13 iterator insert(const_iterator position, const bool& x);
14 iterator insert(const_iterator position, bool&& x);
15 iterator insert(const_iterator position, size_type n, const bool& x);
16 template <class InputIt>
17 iterator insert (const_iterator position, InputIt first,
18 InputIt last);
19 iterator insert(const_iterator position, initializer_list<bool>);
20
21 //删除元素
22 iterator erase(const_iterator position);
23 iterator erase(const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
24
25 //交换两个容器的元素
26 void swap(vector<bool,Allocator>&);
27 static void swap(reference x, reference y) noexcept;
28
29 void flip() noexcept;// flips all bits 翻转0 1
30 void clear() noexcept;// 清空容器
例子1 - 构造
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector> //std::vector
3
4 int main() {
5 // constructors used in the same order as described above:
6 std::vector<int> first; // empty vector of ints
7 std::vector<int> second(4, 100); // four ints with value 100
8 std::vector<int> third(second.begin(), second.end()); // iterating through second
9 std::vector<int> fourth(third); // a copy of third
10
11 // the iterator constructor can also be used to construct from arrays:
12 int myints[] = { 16,2,77,29 };
13 std::vector<int> fifth(myints, myints + sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int));
14
15 std::cout << "The contents of fifth are:";
16 for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = fifth.begin(); it != fifth.end(); ++it) {
17 std::cout << ' ' << *it;
18 }
19 //output : The contents of fifth are: 16 2 77 29
20 std::cout << '\n';
21 std::vector<std::vector<int> > sixth(4, fifth); //four vector<int> with value fifth
22 std::cout << "The contents of sixth are:\n";
23 for (std::vector<std::vector<int> >::iterator it1 = sixth.begin(); it1 != sixth.end(); ++it1) {
24 std::vector<int> tmp = *it1;
25 for (std::vector<int>::iterator it2 = tmp.begin(); it2 != tmp.end(); ++it2) {
26 std::cout << *it2 << ' ';
27 }
28 std::cout << '\n';
29 }
30 /*output:
31 The contents of sixth are:
32 16 2 77 29
33 16 2 77 29
34 16 2 77 29
35 16 2 77 29
36 */
37 return 0;
38 }

例子2 - 容量
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector> //std::vector
3
4 int main() {
5 std::vector<int> v(10);
6 std::cout << "v.empty() = " << (v.empty() ? "true\n" : "false\n");
7 std::cout << "v.size() = " << v.size() << '\n';
8 std::cout << "v.max_size() = " << v.max_size() << '\n';
9 std::cout << "v.front() = " << v.front() << '\n';
10 std::cout << "v.back() = " << v.back() << '\n';
11 v.reserve(15); //预留容量15
12 std::cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << '\n'; // 15
13 v.shrink_to_fit(); //缩小容器大小适应当前
14 std::cout << "v.capacity() = " << v.capacity() << '\n'; //10
15 return 0;
16 }

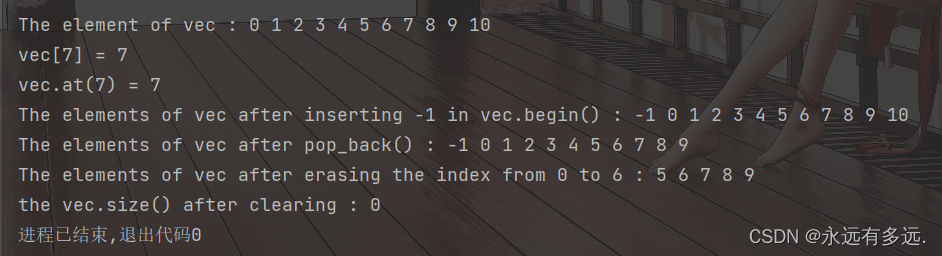
例子3-访问与修改
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector> //std::vector
3
4 int main() {
5 //example3 - element access and modifiy
6 std::vector<int> vec;
7 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
8 vec.push_back(i); //尾部添加元素
9 }
10 vec.emplace_back(10); //尾部添加元素
11 std::cout << "The element of vec : ";
12 for (auto &x: vec) {
13 std::cout << x << ' ';
14 }
15 std::cout << '\n';
16 std::cout << "vec[7] = " << vec[7] << '\n';
17 std::cout << "vec.at(7) = " << vec.at(7) << '\n';
18 //std::cout << "vec.at(13) = " << vec.at(13) << '\n';
19 //std::cout << "hello world" << '\n';
20
21 vec.insert(vec.begin(), -1); //在指定位置插入元素
22 std::cout << "The elements of vec after inserting -1 in vec.begin() : ";
23 for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it) {
24 std::cout << *it << ' ';
25 }
26 std::cout << '\n';
27 vec.pop_back();
28 std::cout << "The elements of vec after pop_back() : ";
29 for (auto &x: vec) {
30 std::cout << x << ' ';
31 }
32 std::cout << '\n';
33 std::cout << "The elements of vec after erasing the index from 0 to 6 : ";
34 vec.erase(vec.begin(), vec.begin() + 6);
35 for (auto &x: vec) {
36 std::cout << x << ' ';
37 }
38 std::cout << '\n';
39 vec.clear();//清空容器
40 std::cout << "the vec.size() after clearing : " << vec.size();
41 return 0;
42 }