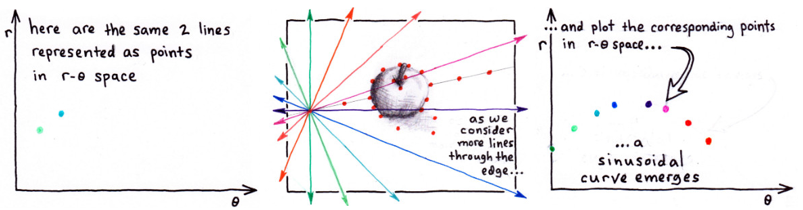
一、霍夫变换(Hough)
A-基本原理
一条直线可由两个点A=(X1,Y1)和B=(X2,Y2)确定(笛卡尔坐标)

另一方面,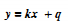 也可以写成关于(k,q)的函数表达式(霍夫空间):
也可以写成关于(k,q)的函数表达式(霍夫空间):
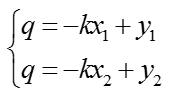
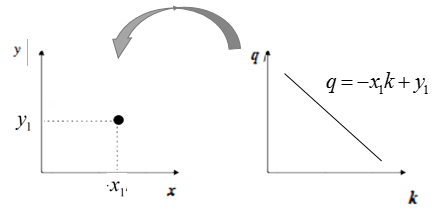
对应的变换可以通过图形直观表示:
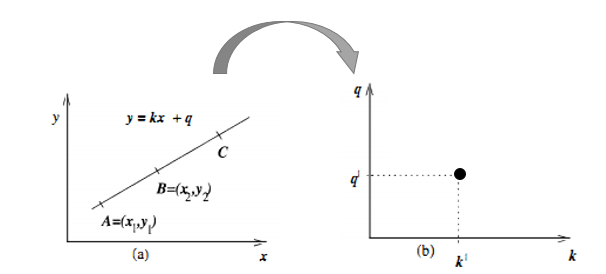
变换后的空间成为霍夫空间。即:笛卡尔坐标系中一条直线,对应霍夫空间的一个点。
反过来同样成立(霍夫空间的一条直线,对应笛卡尔坐标系的一个点):
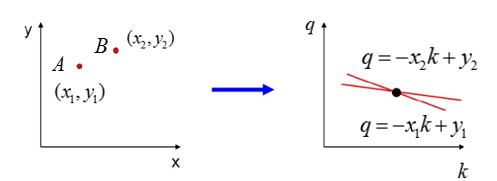
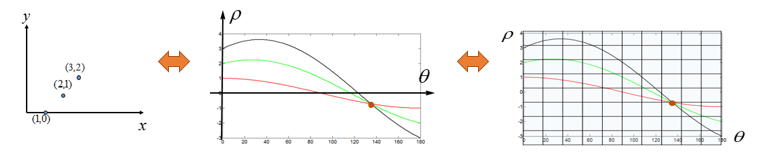
再来看看A、B两个点,对应霍夫空间的情形:
一步步来,再看一下三个点共线的情况:
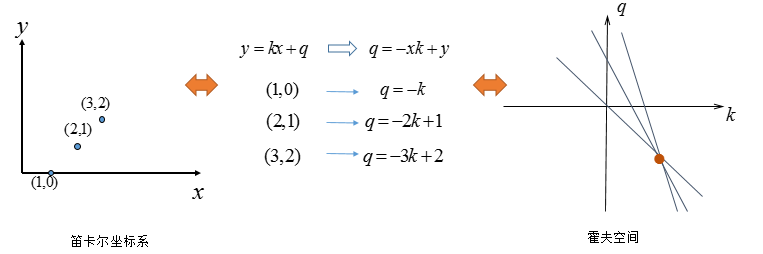
可以看出如果笛卡尔坐标系的点共线,这些点在霍夫空间对应的直线交于一点:这也是必然,共线只有一种取值可能。
如果不止一条直线呢?再看看多个点的情况(有两条直线):
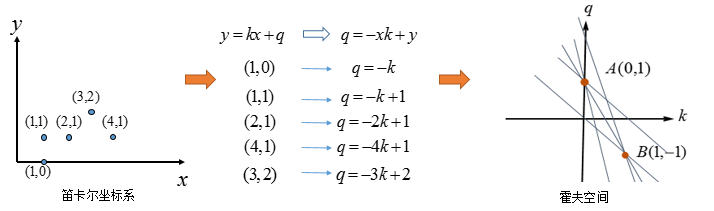
其实(3,2)与(4,1)也可以组成直线,只不过它有两个点确定,而图中A、B两点是由三条直线汇成,这也是霍夫变换的后处理的基本方式:选择由尽可能多直线汇成的点。
看看,霍夫空间:选择由三条交汇直线确定的点(中间图),对应的笛卡尔坐标系的直线(右图)。
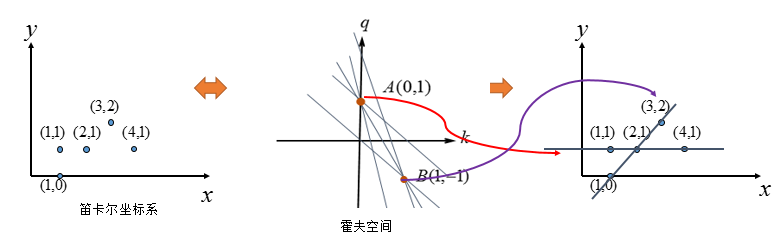
到这里问题似乎解决了,已经完成了霍夫变换的求解,但是如果像下图这种情况呢?
k=∞是不方便表示的,而且q怎么取值呢,这样不是办法。因此考虑将笛卡尔坐标系换为:极坐标表示。
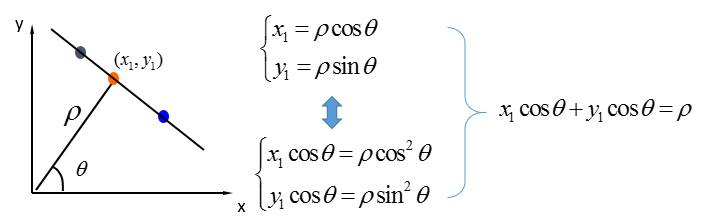
在极坐标系下,其实是一样的:极坐标的点→霍夫空间的直线,只不过霍夫空间不再是[k,q]的参数,而是![]() 的参数,给出对比图:
的参数,给出对比图:
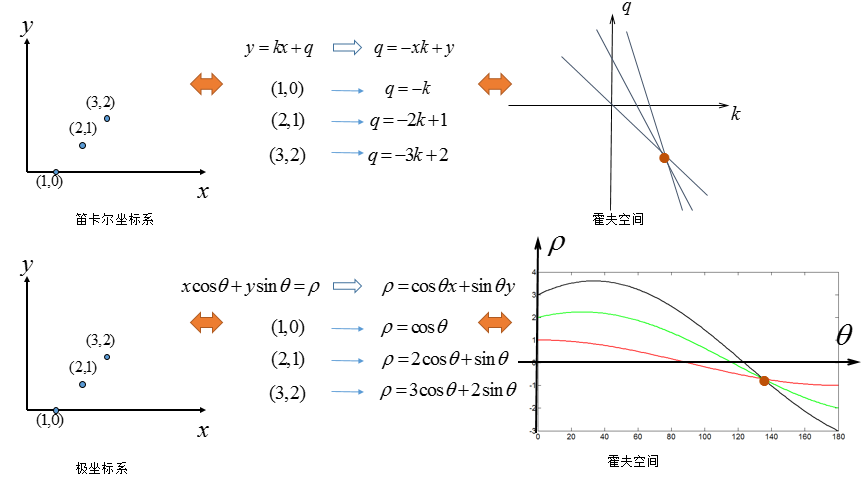
是不是就一目了然了?
给出霍夫变换的算法步骤:
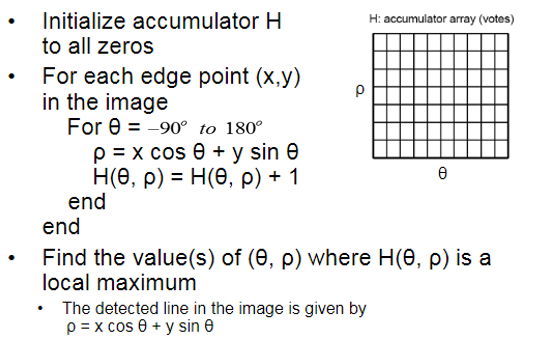
对应code:
1 function [ Hough, theta_range, rho_range ] = naiveHough(I)
2 %NAIVEHOUGH Peforms the Hough transform in a straightforward way.
3 %
4 [rows, cols] = size(I);
5
6 theta_maximum = 90;
7 rho_maximum = floor(sqrt(rows^2 + cols^2)) - 1;
8 theta_range = -theta_maximum:theta_maximum - 1;
9 rho_range = -rho_maximum:rho_maximum;
10
11 Hough = zeros(length(rho_range), length(theta_range));
12 for row = 1:rows
13 for col = 1:cols
14 if I(row, col) > 0 %only find: pixel > 0
15 x = col - 1;
16 y = row - 1;
17 for theta = theta_range
18 rho = round((x * cosd(theta)) + (y * sind(theta))); %approximate
19 rho_index = rho + rho_maximum + 1;
20 theta_index = theta + theta_maximum + 1;
21 Hough(rho_index, theta_index) = Hough(rho_index, theta_index) + 1;
22 end
23 end
24 end
25 end
其实本质上就是:
交点怎么求解呢?细化成坐标形式,取整后将交点对应的坐标进行累加,最后找到数值最大的点就是求解的![]() ,也就求解出了直线。
,也就求解出了直线。
B-理论应用
这里给出MATLAB自带的一个应用,主要是对一幅图像进行直线检验,原图像为:
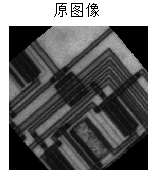
首先是对其进行边缘检测:
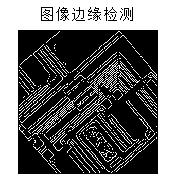
边缘检测后并二值化,就可以通过找非零点的坐标确定数据点。从而对数据点进行霍夫变换。对应映射到霍夫空间的结果为:
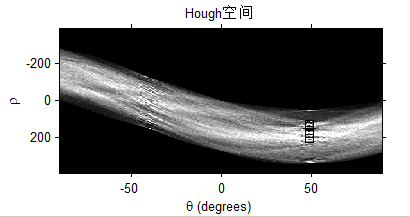
找出其中数值较大的一些点,通常可以给定一个阈值,Threshold一下。
这就完成了霍夫变换的整个过程。这个时候求解出来了其实就是多条直线的斜率k以及截距q,通常会根据直线的特性进一步判断,从而将直线变为线段:
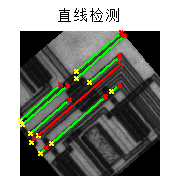
不过这一步更类似后处理,其实已经不是霍夫变换本身的特性了。
给出对应的代码:
1 clc;clear all;close all;
2 I = imread('circuit.tif');
3 rotI = imrotate(I,40,'crop');
4 subplot 221
5 fig1 = imshow(rotI);
6 BW = edge(rotI,'canny');
7 title('原图像');
8 subplot 222
9 imshow(BW);
10 [H,theta,rho] = hough(BW);
11 title('图像边缘检测');
12 subplot 223
13 imshow(imadjust(mat2gray(H)),[],'XData',theta,'YData',rho,...
14 'InitialMagnification','fit');
15 xlabel(' heta (degrees)'), ylabel('
ho');
16 axis on, axis normal, hold on;
17 colormap(hot)
18 P = houghpeaks(H,5,'threshold',ceil(0.7*max(H(:))));
19 x = theta(P(:,2));
20 y = rho(P(:,1));
21 plot(x,y,'s','color','black');
22 lines = houghlines(BW,theta,rho,P,'FillGap',5,'MinLength',7);
23 title('Hough空间');
24 subplot 224, imshow(rotI), hold on
25 max_len = 0;
26 for k = 1:length(lines)
27 xy = [lines(k).point1; lines(k).point2];
28 plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),'LineWidth',2,'Color','green');
29
30 % Plot beginnings and ends of lines
31 plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'x','LineWidth',2,'Color','yellow');
32 plot(xy(2,1),xy(2,2),'x','LineWidth',2,'Color','red');
33
34 % Determine the endpoints of the longest line segment
35 len = norm(lines(k).point1 - lines(k).point2);
36 if ( len > max_len)
37 max_len = len;
38 xy_long = xy;
39 end
40 end
41
42 % highlight the longest line segment
43 plot(xy_long(:,1),xy_long(:,2),'LineWidth',2,'Color','red');
44 title('直线检测');
对比自带的Hough与编写的Hough:
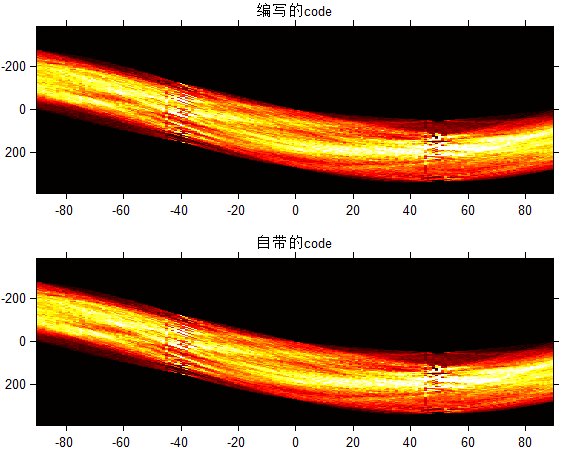
效果还是比较接近的。
看到Stackoverflow上的一个答案,觉得很好,收藏一下: