1.前言
The visualization pipeline in VTK can be used to read or create data, analyze and create derivative version of this data, and write the data to disk or pass it along to the rendering engine for display. For example, you may read a 3D volume of data from disk, process it to create a set of triangles representing an isovalued surface through the volume, then write this geometric object back out to disk. Or, you may create a set of spheres and cylinders to represent atoms and bonds, then pass these off to the rendering engine for display.VTK的pipeline主要用于读取和创造数据,以及对现有数据进行分析和更改、把数据写到磁盘或者通过这个“管道”把数据送到渲染引擎中进行显示。例如,你可以从磁盘中读取一个三维数据、处理数据、进行绘制、写回磁盘。Pipeline一般都是在为Render Engine做准备工作。The Visualization Toolkit uses a data flow approach to transform information into graphical data. There are two basic types of objects involved in this approach.VTK才用数据流的方法将数据信息转换为图形数据,主要有两个类型的对象参与了这个过程: vtkDataObjectvtkAlgorithm。
2.vtkDataObject & vtkAlgorithm 数据对象和算法
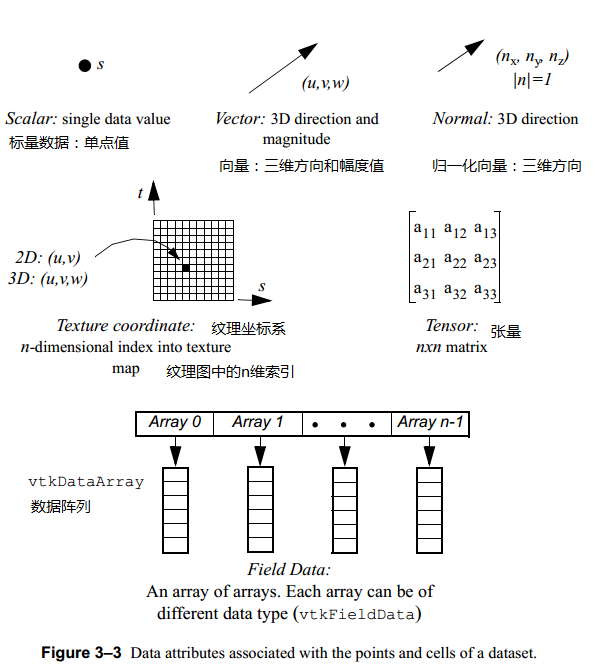
The attribute data can be associated with the points or cells of the dataset. Cells are topological organizations of points; cells form the atoms of the dataset and are used to interpolate information between points。下图显示了VTK支持的属性数据:
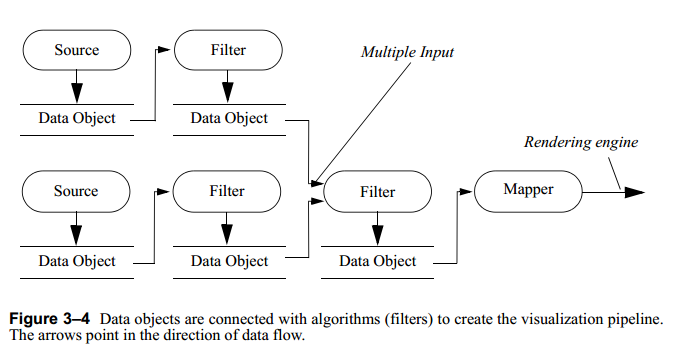
Algorithms, also referred to generally as filters, operate on data objects to produce new dataobjects. Algorithms and data objects are connected together to form visualization pipelines。算法,其实就是滤波器啦~把它作用在原始数据上可以生成新的数据对象。算法和数据对象联系在一起就形成了本节我们要学的“可视化管道技术”。下图是对可视化管道技术的一个描述:
this figure together with Next Figure illustrate some important visualization concepts. Source algorithms produce data by reading (reader objects) or constructing one or more data objects (procedural source objects). Filters ingest one or more data objects and generate one or more data objects on output. Mappers take the data and convert it into a visual representation that is displayed by the rendering engine. A writer can be thought of as a type of mapper that writes data to a file or stream.
这张图像和下图搭配在一起解释了一些重要的概念。源算法通过通过读取过构建数据产生数据;滤波器通过摄取一个或多个数据对象,生成一个或多个数据对象,输出。映射器得到这些数据,利用渲染引擎进行可视化显示。
3.several important issues regarding the construction of the visualization pipeline
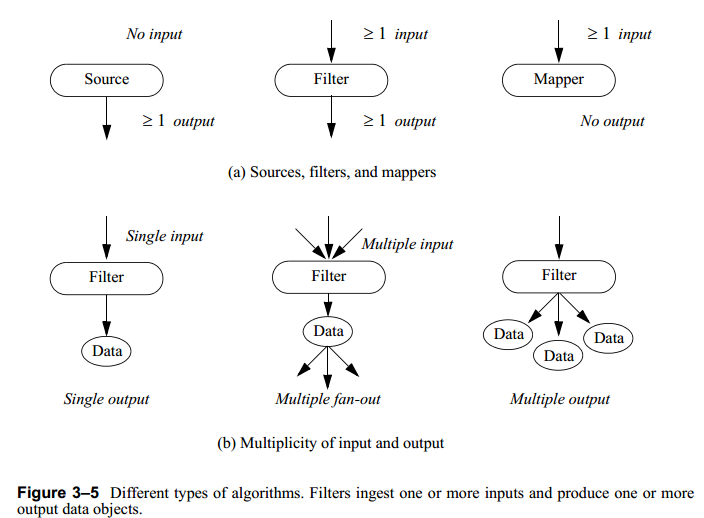
First, pipeline topology is constructed using variations of the methods which sets the input to the filter aFilter to the output of the filter anotherFilter. (Filters with multiple inputs and outputs have similar methods.)We only want to execute those portions of the pipeline necessary to bring the output up to date. The Visualization Toolkit uses a lazy evaluation scheme (executes only when the data is requested) based on an internal modification time of each object.aFilter->SetInputConnection( anotherFilter->GetOutputPort() );Third, the assembly of the pipeline requires that only those objects compatible with one another can fit together with the SetInputConnection() and GetOutputPort() methods. VTK produces errors at run-time if the data object types are incompatible.Finally, we must decide whether to cache, or retain, the data objects once the pipeline has executed. Since visualization datasets are typically quite large, this is important to the successful application of visualization tools. VTK offers methods to turn data caching on and off, use of reference counting to avoid copying data, and methods to stream data in pieces if an entire dataset cannot be held in memory.
4. Image Processing 图像处理
VTK supports an extensive set of image processing and volume rendering functionality. In VTK, both 2D (image) and 3D (volume) data are referred to as vtkImageData. An image dataset in VTK is one in which the data is arranged in a regular, axis-aligned array. Images, pixmaps, and bitmaps are examples of 2D image datasets; volumes (a stack of 2D images) is a 3D image dataset.Algorithms in the imaging pipeline always input and output image data objects. Because of the regular and simple nature of the data, the imaging pipeline has other important features. Volume rendering (体绘制)is used to visualize 3D vtkImageData , and special image viewers are used to view 2D vtkImageData. Almost all algorithms in the imaging pipeline are multithreaded(图像管道中的所有的算法都是多线程的) and are capable of streaming data in pieces to satisfy a user-specified memory limit.Filters automatically sense the number of cores and processors available on the system and create that number of threads during execution as well as automatically separating data into pieces that are streamed through the pipeline.