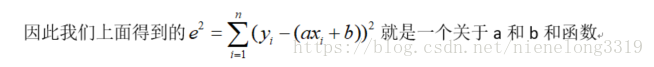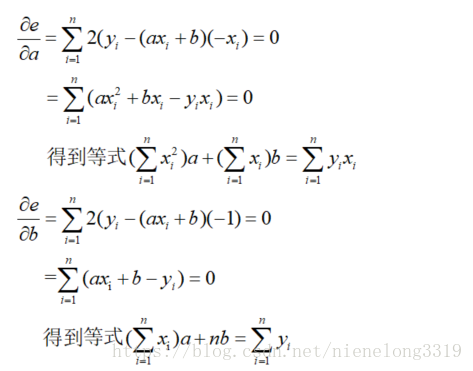最小二乘法拟合直线
概念:最小二乘法多项式直线拟合,根据给定的点,求出它的函数y=f(x),当然求得准确的函数是不太可能的,但是我们能求出它的近似曲线y=φ(x)
原理
假设有点 , I = 1,2,3,……n,求近似曲线y=φ(x),并且使得y=φ(x)与y=f(x)的平方偏差和最小,偏差
其中我们要找到一组最好的a b ,“最好的”就是要使选出的a b能使得所有的误差达到最小化。
在此要注意以下,y=ax+b 这里面的未知量是什么,很自然的说法是x y,实际上并不是,我们不用去解这个x和y ,因为x和y已经是给定的值了,当我们在找这条直线的时候,我们实际上并不关心x的值有多好,我们要的就是a 和b这两个变量,它们可以描述x和y之间的关系,我们就是在试图找出那条最适合的直线所对应的a和b。
可以看到最小二乘法对各个变量求偏导,使得偏导值为0,即可得到最小值,因为e是关于a b的函数,导数为0的点必定是最小值,进入正题
分别对 a b求偏导可以得到:
Halcon最小二乘法拟合直线
1 首先随机生成一组数据
2
3 Mx:=[100:10:500]
4
5 tuple_length(Mx,len)
6
7 tuple_gen_const(len,5,r)
8
9 Ma:=2
10
11 Mb:=40
12
13 tuple_rand(len , noise)
14
15 My:= Ma *Mx + Mb*noise
16
17 gen_circle(ContCircle, My, Mx, r)
1 接下来用矩阵进行最小二乘求解
2
3 * y = ax + b
4
5 * y1 = ax1 + b
6
7 * y2 = ax2 + b
8
9 * ... .......
10
11 * yn = ax + b
1 create_matrix(len,1,My,y)
2
3 create_matrix(len,2,1,x)
4
5 set_value_matrix(x, [0:len-1], gen_tuple_const(len, 0),Mx)
6
7
8 * XT 代表X的转置 inv(*)代表*的逆
9
10 * x beta = y
11
12 * xT x beta = xT y
13
14 * beta = inv( xT x) xT y
15
16 mult_matrix(x,x,'ATB',xtx)
17
18 mult_matrix(x,y,'ATB',xty)
19
20 invert_matrix(xtx,'general', 0, invxtx)
21
22 mult_matrix(invxtx,xty,'AB', beta)
23
24 get_full_matrix(beta, Values)
25
26 Newy:=Values[0] * [10,800] + Values[1]
27
28 gen_contour_polygon_xld(Contour, Newy, [10,800])
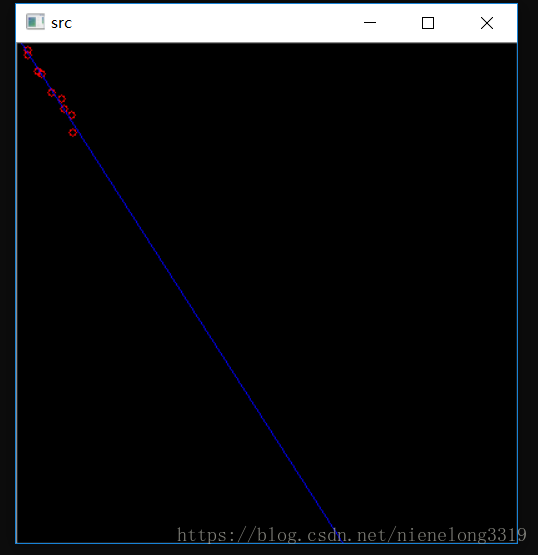
OpenCV最小二乘法拟合直线
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<opencv2opencv.hpp>
3 using namespace std;
4 using namespace cv;
5
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 vector<Point>points;
10 //(27 39) (8 5) (8 9) (16 22) (44 71) (35 44) (43 57) (19 24) (27 39) (37 52)
11
12 points.push_back(Point(27, 39));
13 points.push_back(Point(8, 5));
14 points.push_back(Point(8, 9));
15 points.push_back(Point(16, 22));
16 points.push_back(Point(44, 71));
17 points.push_back(Point(35, 44));
18 points.push_back(Point(43, 57));
19 points.push_back(Point(19, 24));
20 points.push_back(Point(27, 39));
21 points.push_back(Point(37, 52));
22 Mat src = Mat::zeros(400, 400, CV_8UC3);
23
24 for (int i = 0;i < points.size();i++)
25 {
26 //在原图上画出点
27 circle(src, points[i], 3, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8);
28 }
29 //构建A矩阵
30 int N = 2;
31 Mat A = Mat::zeros(N, N, CV_64FC1);
32
33 for (int row = 0;row < A.rows;row++)
34 {
35 for (int col = 0; col < A.cols;col++)
36 {
37 for (int k = 0;k < points.size();k++)
38 {
39 A.at<double>(row, col) = A.at<double>(row, col) + pow(points[k].x, row + col);
40 }
41 }
42 }
43 //构建B矩阵
44 Mat B = Mat::zeros(N, 1, CV_64FC1);
45 for (int row = 0;row < B.rows;row++)
46 {
47
48 for (int k = 0;k < points.size();k++)
49 {
50 B.at<double>(row, 0) = B.at<double>(row, 0) + pow(points[k].x, row)*points[k].y;
51 }
52 }
53 //A*X=B
54 Mat X;
55 //cout << A << endl << B << endl;
56 solve(A, B, X,DECOMP_LU);
57 cout << X << endl;
58 vector<Point>lines;
59 for (int x = 0;x < src.size().width;x++)
60 { // y = b + ax;
61 double y = X.at<double>(0, 0) + X.at<double>(1, 0)*x;
62 printf("(%d,%lf)
", x, y);
63 lines.push_back(Point(x, y));
64 }
65 polylines(src, lines, false, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, 8);
66 imshow("src", src);
67
68 //imshow("src", A);
69 waitKey(0);
70 return 0;
71 }
C++最小二乘法拟合直线
1 #include
2 #include
3 #include
4
5 using namespace std;
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 int num = 0;
10
11 cout << " Input how many numbers you want to calculate:";
12 cin >> num;
13
14 valarray data_x(num);
15 valarray data_y(num);
16
17 while( num )
18 {
19 cout << "Input the "<< num <<" of x:";
20 cin >> data_x[num-1];
21 cout << "Input the "<< num <<" of y:";
22 cin >> data_y[num-1];
23 num--;
24 }
25
26 double A =0.0;
27 double B =0.0;
28 double C =0.0;
29 double D =0.0;
30
31 A = (data_x*data_x).sum();
32 B = data_x.sum();
33 C = (data_x*data_y).sum();
34 D = data_y.sum();
35
36 double k,b,tmp =0;
37 if(tmp=(A*data_x.size()-B*B))
38 {
39 k = (C*data_x.size()-B*D)/tmp;
40 b = (A*D-C*B)/tmp;
41 }
42
43 else
44 {
45 k=1;
46 b=0;
47 }
48
49 cout <<"k="< cout <<"b="<</p>
50
51 return 0;
52 }