面试折在了dijsktra algorithm上,我一个暴风哭泣……
本来是想复习一下Dijsktra算法,又看到了Prim's algorithm 等系列,今天就着这个机会都好好复习一下。
---------------------------正文分割线------------------------------------------
Dijsktra Algorithm
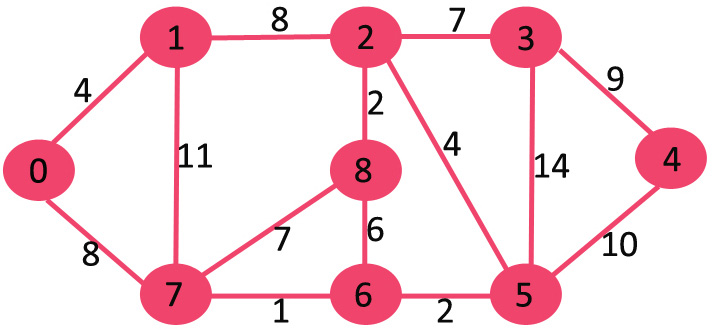
给出一个图以及一个起点,找到从起点到其他所有点的最短路径。
Dijsktra 与 Prim 最小生成树算法类似, 也生成SPT(shortest path tree)并将给定起点作为根节点。
我们维护两个集合,一个集合维护在SPT中的节点S1,另一个集合维护还没有被包含在SPT中的节点S2,在本算法的每一步,我们从S2中找到距根节点最近的点。
以下为使用Dijsktra算法来在给定图中找到起点节点到其他所有节点最短路径的具体步骤:
1.建立SptSet来存储SPT中的树中的节点,并且记录从根节点到这些节点的最短距离。初始化事,该集合为空
2. 给图中的除起点外的每一个节点一个无穷大的初始距离值,起点初始距离为0,这样我们可以最先选择它并从它开始(实现起点)。
3.(while)当SptSet没有图中存储所有的点时:
a. 选择不在SptSet中并且离起点有最短距离的点u
b. 将u加入到SptSet中
c. 更新u所有邻接点的距离。为了更新距离,遍历所有的邻接点。对每一个邻接点v,如果从起点到u的值的总和加上u-v的权重 小于 v点现在的距离值,此时我们更新v的距离值。
举例说明
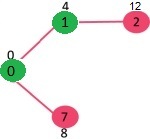
现在我们初始化距离值:{0, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF},此时SptSet为空:{}
当前我们选择0点并且将其加入SptSet:{0}, 并且更新与0点邻接的点的距离 {4, 8, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF}
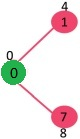
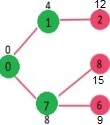
选择此时距离原点最近的点,并且将其加入SptSet,然后更新距离
此时SptSet:{0, 1} 距离:{8, 12, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF}
选择此时7距原点最近,加入SptSet并且更新距离值:
SptSet:{0, 1, 7} 距离:{9, 12, 15, INF, INF, INF}
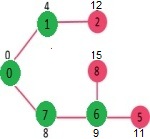
此时6距0最近,加入SptSet并且更新距离值
SptSet: {0, 1, 7, 6} 距离: {11, 12, 15, INF, INF}
此时5距0最近,加入SptSet并且更新距离
SptSet: {0, 1, 7, 6, 5}
直至最后形成最小生成树:
实现(邻接矩阵):
// A C++ program for Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm. // The program is for adjacency matrix representation of the graph #include <stdio.h> #include <limits.h> // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 9 // A utility function to find the vertex with minimum distance value, from // the set of vertices not yet included in shortest path tree int minDistance(int dist[], bool sptSet[]) { // Initialize min value int min = INT_MAX, min_index; for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) if (sptSet[v] == false && dist[v] <= min) min = dist[v], min_index = v; return min_index; } // A utility function to print the constructed distance array int printSolution(int dist[], int n) { printf("Vertex Distance from Source "); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) printf("%d tt %d ", i, dist[i]); } // Function that implements Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm // for a graph represented using adjacency matrix representation void dijkstra(int graph[V][V], int src) { int dist[V]; // The output array. dist[i] will hold the shortest // distance from src to i bool sptSet[V]; // sptSet[i] will true if vertex i is included in shortest // path tree or shortest distance from src to i is finalized // Initialize all distances as INFINITE and stpSet[] as false for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) dist[i] = INT_MAX, sptSet[i] = false; // Distance of source vertex from itself is always 0 dist[src] = 0; // Find shortest path for all vertices for (int count = 0; count < V-1; count++) { // Pick the minimum distance vertex from the set of vertices not // yet processed. u is always equal to src in the first iteration. int u = minDistance(dist, sptSet); // Mark the picked vertex as processed sptSet[u] = true; // Update dist value of the adjacent vertices of the picked vertex. for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) // Update dist[v] only if is not in sptSet, there is an edge from // u to v, and total weight of path from src to v through u is // smaller than current value of dist[v] if (!sptSet[v] && graph[u][v] && dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u]+graph[u][v] < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + graph[u][v]; } // print the constructed distance array printSolution(dist, V); } // driver program to test above function int main() { /* Let us create the example graph discussed above */ int graph[V][V] = {{0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0}, {4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0}, {0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2}, {0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6}, {8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7}, {0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0} }; dijkstra(graph, 0); return 0; }
邻接链表
// C / C++ program for Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm for adjacency // list representation of graph #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <limits.h> // A structure to represent a node in adjacency list struct AdjListNode { int dest; int weight; struct AdjListNode* next; }; // A structure to represent an adjacency liat struct AdjList { struct AdjListNode *head; // pointer to head node of list }; // A structure to represent a graph. A graph is an array of adjacency lists. // Size of array will be V (number of vertices in graph) struct Graph { int V; struct AdjList* array; }; // A utility function to create a new adjacency list node struct AdjListNode* newAdjListNode(int dest, int weight) { struct AdjListNode* newNode = (struct AdjListNode*) malloc(sizeof(struct AdjListNode)); newNode->dest = dest; newNode->weight = weight; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; } // A utility function that creates a graph of V vertices struct Graph* createGraph(int V) { struct Graph* graph = (struct Graph*) malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)); graph->V = V; // Create an array of adjacency lists. Size of array will be V graph->array = (struct AdjList*) malloc(V * sizeof(struct AdjList)); // Initialize each adjacency list as empty by making head as NULL for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i) graph->array[i].head = NULL; return graph; } // Adds an edge to an undirected graph void addEdge(struct Graph* graph, int src, int dest, int weight) { // Add an edge from src to dest. A new node is added to the adjacency // list of src. The node is added at the begining struct AdjListNode* newNode = newAdjListNode(dest, weight); newNode->next = graph->array[src].head; graph->array[src].head = newNode; // Since graph is undirected, add an edge from dest to src also newNode = newAdjListNode(src, weight); newNode->next = graph->array[dest].head; graph->array[dest].head = newNode; } // Structure to represent a min heap node struct MinHeapNode { int v; int dist; }; // Structure to represent a min heap struct MinHeap { int size; // Number of heap nodes present currently int capacity; // Capacity of min heap int *pos; // This is needed for decreaseKey() struct MinHeapNode **array; }; // A utility function to create a new Min Heap Node struct MinHeapNode* newMinHeapNode(int v, int dist) { struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode = (struct MinHeapNode*) malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeapNode)); minHeapNode->v = v; minHeapNode->dist = dist; return minHeapNode; } // A utility function to create a Min Heap struct MinHeap* createMinHeap(int capacity) { struct MinHeap* minHeap = (struct MinHeap*) malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeap)); minHeap->pos = (int *)malloc(capacity * sizeof(int)); minHeap->size = 0; minHeap->capacity = capacity; minHeap->array = (struct MinHeapNode**) malloc(capacity * sizeof(struct MinHeapNode*)); return minHeap; } // A utility function to swap two nodes of min heap. Needed for min heapify void swapMinHeapNode(struct MinHeapNode** a, struct MinHeapNode** b) { struct MinHeapNode* t = *a; *a = *b; *b = t; } // A standard function to heapify at given idx // This function also updates position of nodes when they are swapped. // Position is needed for decreaseKey() void minHeapify(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int idx) { int smallest, left, right; smallest = idx; left = 2 * idx + 1; right = 2 * idx + 2; if (left < minHeap->size && minHeap->array[left]->dist < minHeap->array[smallest]->dist ) smallest = left; if (right < minHeap->size && minHeap->array[right]->dist < minHeap->array[smallest]->dist ) smallest = right; if (smallest != idx) { // The nodes to be swapped in min heap MinHeapNode *smallestNode = minHeap->array[smallest]; MinHeapNode *idxNode = minHeap->array[idx]; // Swap positions minHeap->pos[smallestNode->v] = idx; minHeap->pos[idxNode->v] = smallest; // Swap nodes swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[smallest], &minHeap->array[idx]); minHeapify(minHeap, smallest); } } // A utility function to check if the given minHeap is ampty or not int isEmpty(struct MinHeap* minHeap) { return minHeap->size == 0; } // Standard function to extract minimum node from heap struct MinHeapNode* extractMin(struct MinHeap* minHeap) { if (isEmpty(minHeap)) return NULL; // Store the root node struct MinHeapNode* root = minHeap->array[0]; // Replace root node with last node struct MinHeapNode* lastNode = minHeap->array[minHeap->size - 1]; minHeap->array[0] = lastNode; // Update position of last node minHeap->pos[root->v] = minHeap->size-1; minHeap->pos[lastNode->v] = 0; // Reduce heap size and heapify root --minHeap->size; minHeapify(minHeap, 0); return root; } // Function to decreasy dist value of a given vertex v. This function // uses pos[] of min heap to get the current index of node in min heap void decreaseKey(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int v, int dist) { // Get the index of v in heap array int i = minHeap->pos[v]; // Get the node and update its dist value minHeap->array[i]->dist = dist; // Travel up while the complete tree is not hepified. // This is a O(Logn) loop while (i && minHeap->array[i]->dist < minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2]->dist) { // Swap this node with its parent minHeap->pos[minHeap->array[i]->v] = (i-1)/2; minHeap->pos[minHeap->array[(i-1)/2]->v] = i; swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[i], &minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2]); // move to parent index i = (i - 1) / 2; } } // A utility function to check if a given vertex // 'v' is in min heap or not bool isInMinHeap(struct MinHeap *minHeap, int v) { if (minHeap->pos[v] < minHeap->size) return true; return false; } // A utility function used to print the solution void printArr(int dist[], int n) { printf("Vertex Distance from Source "); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%d %d ", i, dist[i]); } // The main function that calulates distances of shortest paths from src to all // vertices. It is a O(ELogV) function void dijkstra(struct Graph* graph, int src) { int V = graph->V;// Get the number of vertices in graph int dist[V]; // dist values used to pick minimum weight edge in cut // minHeap represents set E struct MinHeap* minHeap = createMinHeap(V); // Initialize min heap with all vertices. dist value of all vertices for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) { dist[v] = INT_MAX; minHeap->array[v] = newMinHeapNode(v, dist[v]); minHeap->pos[v] = v; } // Make dist value of src vertex as 0 so that it is extracted first minHeap->array[src] = newMinHeapNode(src, dist[src]); minHeap->pos[src] = src; dist[src] = 0; decreaseKey(minHeap, src, dist[src]); // Initially size of min heap is equal to V minHeap->size = V; // In the followin loop, min heap contains all nodes // whose shortest distance is not yet finalized. while (!isEmpty(minHeap)) { // Extract the vertex with minimum distance value struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode = extractMin(minHeap); int u = minHeapNode->v; // Store the extracted vertex number // Traverse through all adjacent vertices of u (the extracted // vertex) and update their distance values struct AdjListNode* pCrawl = graph->array[u].head; while (pCrawl != NULL) { int v = pCrawl->dest; // If shortest distance to v is not finalized yet, and distance to v // through u is less than its previously calculated distance if (isInMinHeap(minHeap, v) && dist[u] != INT_MAX && pCrawl->weight + dist[u] < dist[v]) { dist[v] = dist[u] + pCrawl->weight; // update distance value in min heap also decreaseKey(minHeap, v, dist[v]); } pCrawl = pCrawl->next; } } // print the calculated shortest distances printArr(dist, V); } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { // create the graph given in above fugure int V = 9; struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V); addEdge(graph, 0, 1, 4); addEdge(graph, 0, 7, 8); addEdge(graph, 1, 2, 8); addEdge(graph, 1, 7, 11); addEdge(graph, 2, 3, 7); addEdge(graph, 2, 8, 2); addEdge(graph, 2, 5, 4); addEdge(graph, 3, 4, 9); addEdge(graph, 3, 5, 14); addEdge(graph, 4, 5, 10); addEdge(graph, 5, 6, 2); addEdge(graph, 6, 7, 1); addEdge(graph, 6, 8, 6); addEdge(graph, 7, 8, 7); dijkstra(graph, 0); return 0; }
以上均来自于:
1. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-algorithms-set-6-dijkstras-shortest-path-algorithm/