PriorityBlockingQueue是一个支持优先级的无界阻塞队列,直到系统资源耗尽。默认情况下元素采用自然顺序升序排列。也可以自定义类实现compareTo()方法来指定元素排序规则,或者初始化PriorityBlockingQueue时,指定构造参数Comparator来对元素进行排序。但需要注意的是不能保证同优先级元素的顺序。PriorityBlockingQueue也是基于最小二叉堆实现,使用基于CAS实现的自旋锁来控制队列的动态扩容,保证了扩容操作不会阻塞take操作的执行。
PriorityBlockingQueue有四个构造方法:
// 默认的构造方法,该方法会调用this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null),即默认的容量是11
public PriorityBlockingQueue()
// 根据initialCapacity来设置队列的初始容量
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity)
// 根据initialCapacity来设置队列的初始容量,并根据comparator对象来对数据进行排序
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator)
// 根据集合来创建队列
public PriorityBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c)
public class PriorityBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 5595510919245408276L; private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11; private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; private transient Object[] queue; private transient int size; private transient Comparator<? super E> comparator; private final ReentrantLock lock; private final Condition notEmpty; private transient volatile int allocationSpinLock;//扩容时候用到,自旋锁 private PriorityQueue<E> q;//数组实现的最小堆,writeObject和readObject用到。 为了兼容之前的版本,只有在序列化和反序列化才非空 public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator) { if (initialCapacity < 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); this.lock = new ReentrantLock(); this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); this.comparator = comparator; this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity]; //构造函数没有初始化allocationSpinLock,q } public PriorityBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) { this.lock = new ReentrantLock(); this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); boolean heapify = true; // true if not known to be in heap order boolean screen = true; // true if must screen for nulls if (c instanceof SortedSet<?>) {// 如果传入集合是有序集,则无须进行堆有序化 SortedSet<? extends E> ss = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c; this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) ss.comparator(); heapify = false;//不需要重建堆 }// 如果传入集合是PriorityBlockingQueue类型,则不进行堆有序化 else if (c instanceof PriorityBlockingQueue<?>) { PriorityBlockingQueue<? extends E> pq = (PriorityBlockingQueue<? extends E>) c; this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) pq.comparator(); screen = false; if (pq.getClass() == PriorityBlockingQueue.class) // exact match heapify = false;//不需要重建堆 } Object[] a = c.toArray(); int n = a.length; // If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it. if (a.getClass() != Object[].class) a = Arrays.copyOf(a, n, Object[].class); if (screen && (n == 1 || this.comparator != null)) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (a[i] == null) throw new NullPointerException(); } this.queue = a; this.size = n; if (heapify) heapify();//重建堆 } private void removeAt(int i) { Object[] array = queue; int n = size - 1; if (n == i) // removed last element array[i] = null; else { E moved = (E) array[n]; array[n] = null; Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator; if (cmp == null) siftDownComparable(i, moved, array, n); else siftDownUsingComparator(i, moved, array, n, cmp); if (array[i] == moved) { if (cmp == null) siftUpComparable(i, moved, array); else siftUpUsingComparator(i, moved, array, cmp); } } size = n; } private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array, int n) {//元素x放到k的位置 if (n > 0) { Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>)x; int half = n >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least Object c = array[child]; int right = child + 1; if (right < n && ((Comparable<? super T>) c).compareTo((T) array[right]) > 0) c = array[child = right]; if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0)//比子节点小就不动,小堆 break; array[k] = c; k = child; } array[k] = key; } } private static <T> void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array) {//元素x放到k的位置 Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>) x; while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; Object e = array[parent]; if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)//比父亲大就不动,小堆 break; array[k] = e; k = parent; } array[k] = key; } public boolean offer(E e) { if (e == null)// 若插入的元素为null,则直接抛出NullPointerException异常 throw new NullPointerException(); final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); int n, cap; Object[] array; while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length)) tryGrow(array, cap); try { Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator; if (cmp == null) siftUpComparable(n, e, array);//准备放在最后size位置处 else siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp); size = n + 1; notEmpty.signal();// 唤醒等待在空上的线程 } finally { lock.unlock(); } return true; } public E take() throws InterruptedException { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lockInterruptibly(); E result; try { while ( (result = dequeue()) == null) notEmpty.await(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } return result; } public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lockInterruptibly(); E result; try { while ( (result = dequeue()) == null && nanos > 0) nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos); } finally { lock.unlock(); } return result; } public E peek() { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { return (size == 0) ? null : (E) queue[0]; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public int size() { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { return size; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } private int indexOf(Object o) { if (o != null) { Object[] array = queue; int n = size; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) if (o.equals(array[i])) return i; } return -1; } public boolean remove(Object o) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { int i = indexOf(o); if (i == -1) return false; removeAt(i); return true; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public boolean contains(Object o) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { return indexOf(o) != -1; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } private E dequeue() { int n = size - 1; if (n < 0) return null; else { Object[] array = queue; E result = (E) array[0]; E x = (E) array[n]; array[n] = null; Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator; if (cmp == null) siftDownComparable(0, x, array, n); else siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, array, n, cmp); size = n; return result; } } private void heapify() { Object[] array = queue; int n = size; int half = (n >>> 1) - 1; Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator; if (cmp == null) { for (int i = half; i >= 0; i--) siftDownComparable(i, (E) array[i], array, n);//数组重建为堆 } else { for (int i = half; i >= 0; i--) siftDownUsingComparator(i, (E) array[i], array, n, cmp); } } public void clear() { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { Object[] array = queue; int n = size; size = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) array[i] = null; } finally { lock.unlock(); } public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {//批量获取元素 if (c == null) throw new NullPointerException(); if (c == this) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (maxElements <= 0) return 0; final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { int n = Math.min(size, maxElements); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 循环遍历,不断弹出队首元素; c.add((E) queue[0]); // In this order, in case add() throws. dequeue(); } return n; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
放,取,移除 的时候都加锁,同时只能一个线程操作。
private PriorityQueue<E> q;//数组实现的最小堆,writeObject和readObject用到。
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException { lock.lock(); try { // avoid zero capacity argument q = new PriorityQueue<E>(Math.max(size, 1), comparator); q.addAll(this); s.defaultWriteObject(); } finally { q = null; lock.unlock(); } } private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { try { s.defaultReadObject(); int sz = q.size(); SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, sz); this.queue = new Object[sz]; comparator = q.comparator(); addAll(q); } finally { q = null; } }
private transient volatile int allocationSpinLock;//扩容时候用到
不扩容就是正常的获取锁之后加入元素。
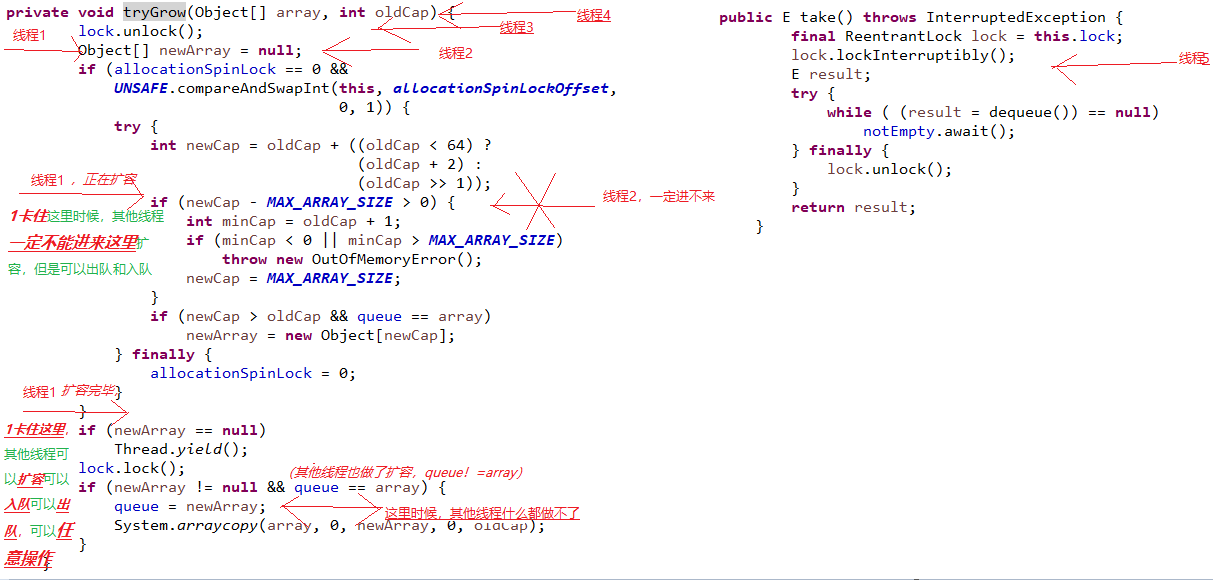
扩容时候释放了锁,如果取的线程获取了锁可以取,如果offer的线程获取了锁可以放(方法中释放了锁,别的线程就可以进去这个方法,也可以进去其他需要锁的方法)
释放了lock锁加了一把allocationSpinLock 锁(这个锁:获取到的走进去,没有获取到的跳过。)
private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {//旧数组和容量 lock.unlock(); // 释放锁,防止阻塞出队操作 Object[] newArray = null; //释放了锁,多个线程可以进来这里,但是只有一个线程可以执行if里面的代码,也就是只有一个线程可以扩容, if (allocationSpinLock == 0 && // 使用CAS操作来修改allocationSpinLock UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset, 0, 1)) { try {// 容量越小增长得越快,若容量小于64,则新容量是oldCap * 2 + 2,否则是oldCap * 1.5 int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ? (oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small (oldCap >> 1)); if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { // 扩容后超过最大容量处理 int minCap = oldCap + 1; if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)//整数溢出 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }//queue是公共变量, if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array) newArray = new Object[newCap]; } finally {// 解锁,因为只有一个线程到此,因而不需要CAS操作; allocationSpinLock = 0; } }//失败扩容的线程newArray == null,调用Thread.yield()让出cpu, 让扩容线程扩容后优先调用lock.lock重新获取锁, //但是这得不到一定的保证,有可能调用Thread.yield()的线程先获取了锁。 if (newArray == null) Thread.yield(); lock.lock();//有可能扩容的线程先走到这里,也有可能没有扩容的线程先走到这里。 //准备赋值给共有变量queue,要加锁, //扩容的线程newArray != null ,没有扩容的线程newArray = null if (newArray != null && queue == array) {//再次进入while循环去扩容。 queue = newArray; System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap); } } private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; private static final long allocationSpinLockOffset; static { try { UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class<?> k = PriorityBlockingQueue.class; allocationSpinLockOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("allocationSpinLock")); //allocationSpinLock这个字段 } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } }
PriorityBlockingQueue扩容时,因为增加堆数组的长度并不影响队列中元素的出队操作,因而使用自旋CAS操作实现的锁来控制扩容操作,仅在数组引用替换和拷贝元素时才加锁,从而减少了扩容对出队操作的影响。
数组变成Iterator取遍历:
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new Itr(toArray()); } public Object[] toArray() { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { return Arrays.copyOf(queue, size); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } final class Itr implements Iterator<E> { final Object[] array; // Array of all elements int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet; // index of last element, or -1 if no such Itr(Object[] array) { lastRet = -1; this.array = array; } public boolean hasNext() { return cursor < array.length; } public E next() { if (cursor >= array.length) throw new NoSuchElementException(); lastRet = cursor; return (E)array[cursor++]; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); removeEQ(array[lastRet]); lastRet = -1; } }
PriorityBlockingQueue中查找元素的效率indexOf()是偏低的,由于二叉堆并没有限制左右子节点的大小规则,因而需要变量整个数组进行查找,因而效率为O(n)。一些优先队列的实现会对此进行优化,给每个元素添加一个索引字段用于标记元素在堆数组中的位置,比如:ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.DelayedWorkQueue通过ScheduledFutureTask中的heapIndex来标记任务在堆数组中的位置。
PBQSpliterator没看