
public boolean hasNext() { return cursor < size || (forgetMeNot != null && !forgetMeNot.isEmpty()); } //内部的迭代器,就是数组的迭代,迭代指针cursor, public E next() { if (expectedModCount != modCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); if (cursor < size) return (E) queue[lastRet = cursor++]; if (forgetMeNot != null) { lastRet = -1; lastRetElt = forgetMeNot.poll(); if (lastRetElt != null) return lastRetElt; } throw new NoSuchElementException(); }

扩容: private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = queue.length; // 小于64扩大为原来2倍,大于等于64扩大为原来1.5倍, int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ? (oldCapacity + 2) : (oldCapacity >> 1)); // overflow-conscious code if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);//丢弃原来的数组,指向新的数组, }
public class zusheQueue { private static PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(3); public static void main(String[] args) { queue.offer(80); queue.offer(60); queue.offer(70); queue.offer(40); queue.offer(20); queue.offer(10); queue.offer(90); queue.offer(22); queue.offer(15); queue.offer(4); queue.offer(1); System.out.println(queue);//[1, 4, 20, 22, 10, 70, 90, 80, 40, 60, 15] 数组实现最小堆 System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll()); System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll()); System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll()); System.out.println("出来 "+queue.poll()); /*出来 1 出来 4 出来 10 出来 15 出来最小的*/ System.out.println(queue); Iterator i = queue.iterator(); while(i.hasNext()) { System.out.print(i.next() + " ");//1 4 20 22 10 70 90 80 40 60 15 } List<Integer> l = Arrays.asList(7,85,4,9,5,85,74,5,8); PriorityQueue<Integer> p = new PriorityQueue<>(l); System.out.println(p); } }
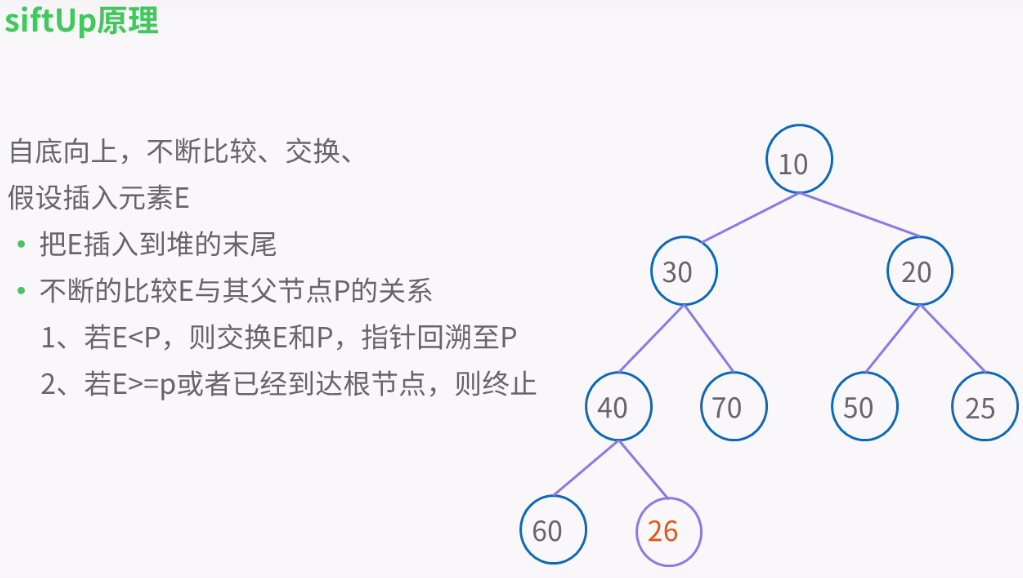
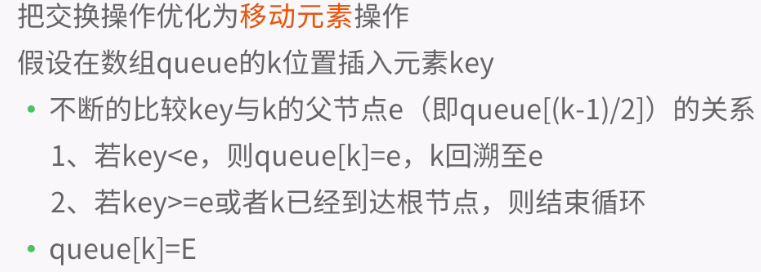
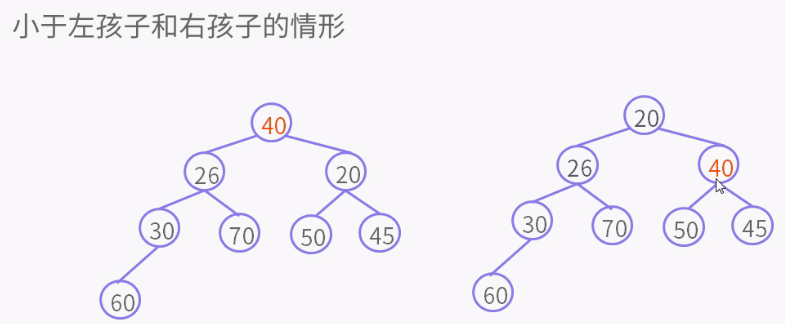
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x; while (k > 0) { int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; //无符号右移 Object e = queue[parent]; if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0) break; queue[k] = e; k = parent; } queue[k] = key; }

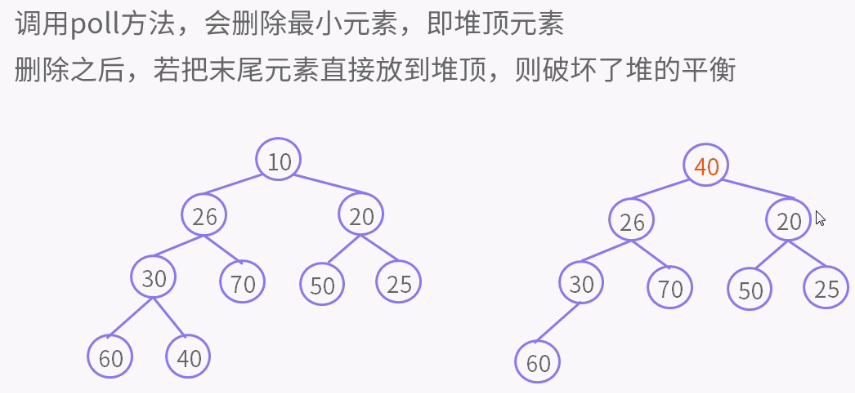


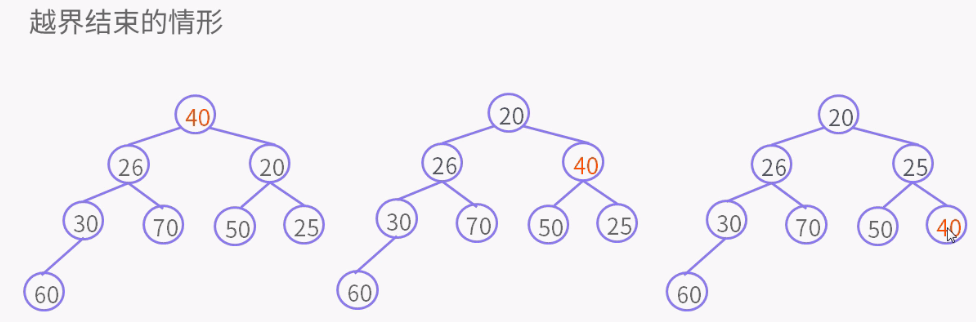

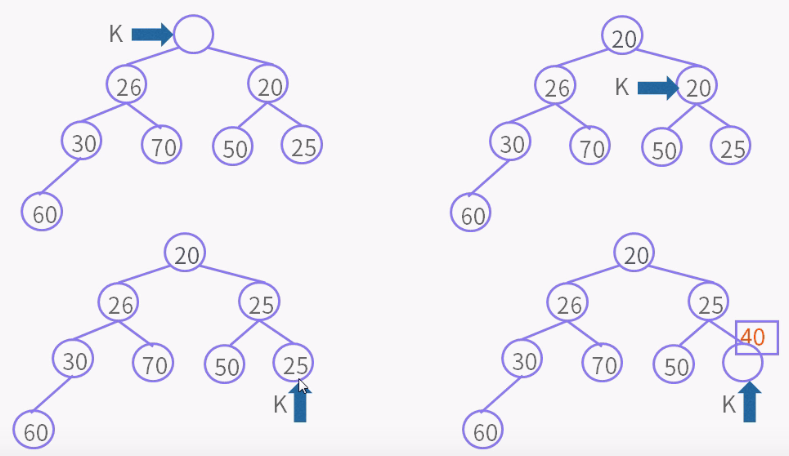
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) { // k = 0 Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x; int half = size >>> 1; // 非叶子节点 while (k < half) { int child = (k << 1) + 1; // child = 左孩子 Object c = queue[child]; // c = 左孩子 int right = child + 1;//right = 右孩子 if (right < size && ((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) //有右孩子,并且左孩子大于右孩子 c = queue[child = right];// c = 右孩子,child = 右孩子 if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0) //key小于右孩子,就是小于所有孩子 break; //结束循环 queue[k] = c; // 否则key大于右孩子,k位置是右孩子,就是较小的孩子 k = child; //指针k值为right右孩子的位置, 比较都是根据指针位置比较,放的时候才放对象。 } queue[k] = key; }


构造函数:

public PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) { if (c instanceof SortedSet<?>) { SortedSet<? extends E> ss = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c; this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) ss.comparator(); initElementsFromCollection(ss); } else if (c instanceof PriorityQueue<?>) { PriorityQueue<? extends E> pq = (PriorityQueue<? extends E>) c; this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) pq.comparator(); initFromPriorityQueue(pq); } else { this.comparator = null; initFromCollection(c); } }
private void initFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) { initElementsFromCollection(c); heapify(); }
private void initElementsFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); // If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it. if (a.getClass() != Object[].class) a = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class); int len = a.length; if (len == 1 || this.comparator != null) for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) if (a[i] == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.queue = a; this.size = a.length; }
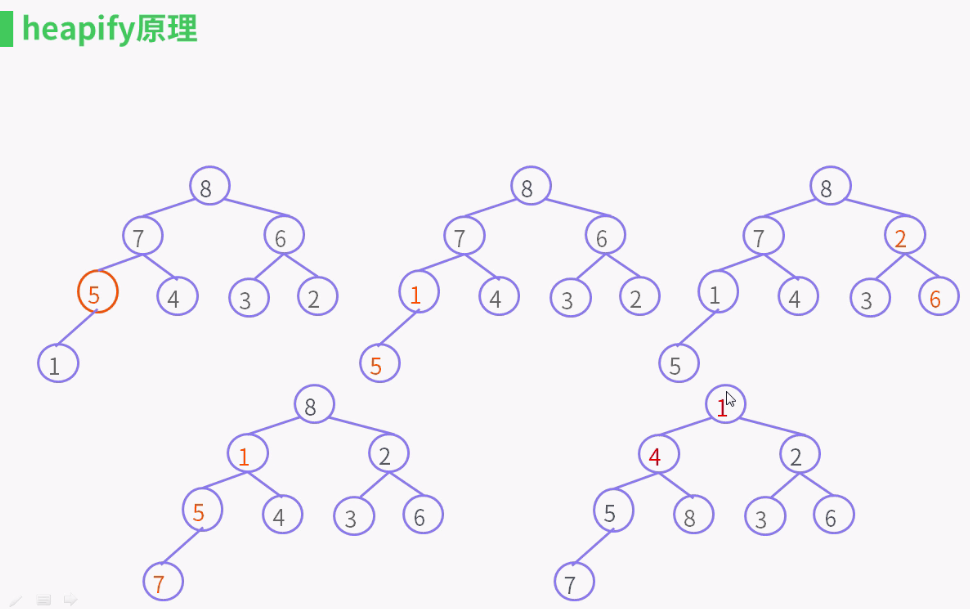
private void heapify() { for (int i = (size >>> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--) //(size >>> 1) - 1就是找到第一个非叶子节点,然后从下到上从右到左, siftDown(i, (E) queue[i]); }

public E poll() { if (size == 0) return null; int s = --size; modCount++; E result = (E) queue[0]; //取出第0个元素 E x = (E) queue[s]; //取出最后一个元素 queue[s] = null; // 最后一个元素置为空 if (s != 0) siftDown(0, x); // 最后一个元素不要先不要放在第0个元素位置,比较之后确定位置了再放。放置的都是左右孩子,改变的是k的值,key不到最后不放。 return result; //返回第0个元素 }
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) { Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x; int half = size >>> 1; while (k < half) { // sI, sV是左右子节点的较小位置和值,k,key是要比较的元素和准备放的位置(落之前要比较在放) int sI = (k << 1) + 1; // 较小位置=左孩子索引 Object sV = queue[sI];//较小值=左孩子 int right = sI+ 1; if (right < size && ((Comparable<? super E>) sV ).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0) //有右孩子,并且左孩子大于右孩子, sV = queue[sI= right]; // 较小位置=右孩子索引,较小值=右孩子, if (key.compareTo((E) sV ) <= 0) //key比左右都小,放上去, break; queue[k] = sV ;//否则key比子节点要大,交换位置,并且自己准备放在sl的位置。放置的都是左右孩子,改变的是k的值,key不到最后不放。 k = sI; //自己放在sl的位置之前,也要跟子节点比较一下,在放。 } queue[k] = key;//key放在k的位置 }