一. 基本概念
1.共享锁:(holdlock)
(1). select的时候会自动加上共享锁,该条语句执行完,共享锁立即释放,与事务是否提交没有关系。
(2). 显式通过添加(holdlock)来显式添加共享锁(比如给select语句显式添加共享锁),当在事务里的时候,需要事务结束,该共享锁才能释放。
(3). 同一资源,共享锁和排它锁不能共存,意味着update之前必须等资源上的共享锁释放后才能进行。
(4). 共享锁和共享锁可以共存在一个资源上,意味着同一个资源允许多个线程同时进行select。
2. 排它锁:(xlock)
(1). update(或 insert 或 delete)的时候加自动加上排它锁,该条语句执行完,排它锁立即释放,如果有事务的话,需要事务提交,该排它锁才能释放。
(2). 显式的通过添加(xlock)来显式的添加排它锁(比如给select语句显式添加排它锁),如果有事务的话,需要事务提交,该排它锁才能释放。
(2). 同一资源,共享锁和排它锁不能共存,意味着update之前必须等资源上的共享锁释放后才能进行。
3. 更新锁:(updlock)
(1). 更新锁只能显式的通过(updlock)来添加,当在事务里的时候,需要事务结束,该更新锁才能释放。
(2). 共享锁和更新锁可以同时在同一个资源上,即加了更新锁,其他线程仍然可以进行select。
(3). 更新锁和更新锁不能共存(同一时间同一资源上不能存在两个更新锁)。
(4). 更新锁和排它锁不兼容。
(5). 利用更新锁来解决死锁问题,要比xlock性能高一些,因为加了updlock后,其他线程是可以进行select的。
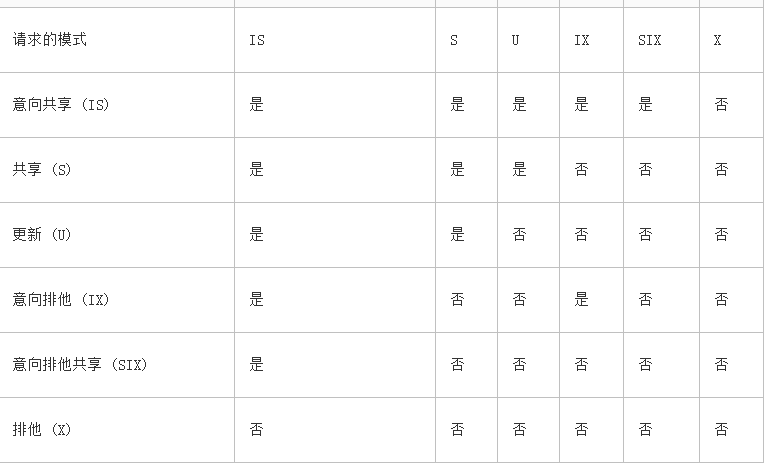
4. 意向锁
意向锁分为三种:意向共享 (IS)、意向排他 (IX) 和意向排他共享 (SIX)。 意向锁可以提高性能,因为数据库引擎仅在表级检查意向锁来确定事务是否可以安全地获取该表上的锁,而不需要检查表中的每行或每页上的锁以确定事务是否可以锁定整个表.
T1:select * from table (xlock) where id=10
T2:select * from table (tablock)
分析:T1线程执行该语句时,会对该表id=10的这一行加排他锁,同时会对整个表加上意向排它锁(IX),当T2执行的时候,不需要逐条去检查资源,只需要看到该表已经存在【意向排它锁】,就直接等待。
PS: update table set xx=xx where id=1, 不光会对id=1的这条记录加排它锁,还会对整张表加意向排它锁。
5. 计划锁(Schema Locks)
用jdbc向数据库发送了一条新的sql语句,数据库要先对之进行编译,在编译期间,也会加锁,称之为:计划锁。
编译这条语句过程中,其它线程可以对表做任何操作(update、delete、加排他锁等等),但不能做DDL(比如alter table)操作。
6. 锁的颗粒:行锁、页锁、表锁
(1). rowlock:行锁---对每一行加锁,然后释放。(对某行加共享锁)
(2). paglock:页锁---1执行时,会先对第一页加锁,读完第一页后,释放锁,再对第二页加锁,依此类推。(对某页加共享锁)
假设前10行记录恰好是一页(当然,一般不可能一页只有10行记录),那么T1执行到第一页查询时,并不会阻塞T2的更新。
(3). tablock:表锁---对整个表加锁,然后释放。 (对整张表加共享锁)
注:
1. 以上三种锁执行完该语句后即可释放,无须等待事务的提交,与事务是否提交没有关系。
2. 以上三种锁划分的角度不同,都是共享锁,所以他们相互之间是可以共存的。
7. rowlock、paglock、tablock 和 holdlock的区别
二者无非是划分的角度不同,其实都是共享锁,但在释放上有所不同
tablock(rowlock、paglock):对表、行、页加共享锁,只要语句执行完,就释放,与事务是否提交没关系。
holdlock:对表加共享锁,必须等着事务执行完,才能释放。
8. tablockx对表加排它锁,在有事务和没事务的时候的区别
(1). 无事务的时候:其他线程无法对该表进行读和更新,除非加tablockx的语句执行完,才能进行。
(2). 有事务的时候:必须整个事务执行了commit或rollback后才会释放该排他锁。
xlock还可这么用:select * from table(xlock tablock) 效果等同于select * from table(tablockx)
9.各种锁的兼容关系
二. 实战测试
1. 测试共享锁和共享锁可以共存

1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("测试共享锁和共享锁可以共存"); 3 Console.WriteLine("共享锁select默认添加:1, 共享锁(holdlock)显式添加:2"); 4 string num = Console.ReadLine(); 5 if (num == "1") 6 { 7 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 8 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 11 //select的时候会加共享锁 12 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 13 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 14 15 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 16 Console.ReadKey(); 17 try 18 { 19 tx.Commit(); 20 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 21 } 22 catch (Exception ex) 23 { 24 tx.Rollback(); 25 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 26 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 else if (num == "2") 31 { 32 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 33 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 34 { 35 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 36 //显式的通过holdlock添加 37 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor(holdlock) where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 38 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 39 40 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 41 Console.ReadKey(); 42 try 43 { 44 tx.Commit(); 45 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 46 } 47 catch (Exception ex) 48 { 49 tx.Rollback(); 50 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 51 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 }
结论:
默认加 或者 显式(holdlock)的方式加,都能共存。
2. 测试排它锁和排它锁不能共存

1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("测试排它锁和排它锁不能共存"); 3 Console.WriteLine("排它锁update默认添加:1, 排它锁(xlock)显式添加:2"); 4 string num = Console.ReadLine(); 5 if (num == "1") 6 { 7 Console.WriteLine("排它锁业务"); 8 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 9 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("开始更新"); 12 //update的时候会自动加排它锁 13 var result = db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("update OrderInfor set userName='lmr2' where id=2"); 14 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 15 Console.ReadKey(); 16 try 17 { 18 tx.Commit(); 19 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 20 } 21 catch (Exception ex) 22 { 23 tx.Rollback(); 24 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 25 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 26 } 27 } 28 29 } 30 else if (num == "2") 31 { 32 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 33 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 34 { 35 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 36 //select的时候会对id=1的那行加上排它锁,同时对整张表加上意向排它锁,当别的线程查询该表时,不用逐条去检查资源 37 //只需要看到该表存在【意向排它锁】,就会等待,无论查询id等于几,都会等待 38 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor (xlock) where id=1").FirstOrDefault(); 39 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 40 41 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 42 Console.ReadKey(); 43 try 44 { 45 tx.Commit(); 46 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 47 } 48 catch (Exception ex) 49 { 50 tx.Rollback(); 51 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 52 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 57 }
结论:
1. 关于排它锁,无论是显式(xlock)模式添加还是update默认加的模式,如果在事务里都需要事务提交才能释放。
2. 默认与默认、显式与显式、默认与显式 这三种组合关系都不能共存,所以证明排它锁和排它锁之间不能共存。
3. 注意:这里加排他锁,会在表层次上加上意向排它锁,与操作那条数据无关。
3. 测试共享锁和排它锁不能共存(显式和隐式) (两个结论未完成)

1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("测试排它锁和排它锁不能共存"); 3 Console.WriteLine("默认select共享锁:1, 显式共享锁(holdlock):2,默认update排它锁:3,显式排它锁(xlock):4"); 4 string num = Console.ReadLine(); 5 6 if (num == "1") 7 { 8 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 9 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 12 //select的时候会加共享锁 13 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 14 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 15 16 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 17 Console.ReadKey(); 18 try 19 { 20 tx.Commit(); 21 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 22 } 23 catch (Exception ex) 24 { 25 tx.Rollback(); 26 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 27 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 else if (num == "2") 32 { 33 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 34 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 35 { 36 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 37 //显式的通过holdlock添加 38 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor(holdlock) where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 39 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 40 41 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 42 Console.ReadKey(); 43 try 44 { 45 tx.Commit(); 46 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 47 } 48 catch (Exception ex) 49 { 50 tx.Rollback(); 51 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 52 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 else if (num == "3") 57 { 58 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 59 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 60 { 61 Console.WriteLine("开始更新"); 62 //update的时候会自动加排它锁 63 var result = db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("update OrderInfor set userName='lmr2' where id=2"); 64 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 65 Console.ReadKey(); 66 try 67 { 68 tx.Commit(); 69 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 70 } 71 catch (Exception ex) 72 { 73 tx.Rollback(); 74 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 75 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 else if (num == "4") 80 { 81 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 82 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 83 { 84 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 85 //select的时候会对id=1的那行加上排它锁,同时对整张表加上意向排它锁,当别的线程查询该表时,不用逐条去检查资源 86 //只需要看到该表存在【意向排它锁】,就会等待,无论查询id等于几,都会等待 87 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor (xlock) where id=1").FirstOrDefault(); 88 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 89 90 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 91 Console.ReadKey(); 92 try 93 { 94 tx.Commit(); 95 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 96 } 97 catch (Exception ex) 98 { 99 tx.Rollback(); 100 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 101 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 102 } 103 } 104 } 105 106 107 }
结论:
1.默认select共享锁先执行,未提交事务的情况下,默认update排它锁 和 显式排它锁(xlock)都能正常执行。,
证明:默认共享锁语句执行完立即释放,与事务是否提交没有关系
2.显式共享锁(holdlock),未提交事务的情况下,默认update排它锁 和 显式排它锁(xlock)都 不能 正常执行,
证明:显式共享锁(holdlock)需要事务提交才能释放,同时也证明共享锁和排它锁不能共存。
3.默认update排它锁先执行,未提交事务的情况下,默认select共享锁能执行,显式共享锁(holdlock)不能执行。
证明:
4.显式排它锁(xlock)先执行,未提交事务的情况下,默认select共享锁能执行,显式共享锁(holdlock)不能执行。
证明:
4. 测试共享锁、更新锁、排它锁间的关系

1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("测试更新锁、排它锁、共享锁间的关系"); 3 Console.WriteLine("更新锁业务输入:1, 排它锁业务输入:2,共享锁输入:3"); 4 string num = Console.ReadLine(); 5 if (num == "1") 6 { 7 Console.WriteLine("更新锁业务"); 8 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 9 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 12 //显式的添加更新锁 13 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor(updlock) where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 14 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 15 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 16 Console.ReadKey(); 17 try 18 { 19 tx.Commit(); 20 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 21 } 22 catch (Exception ex) 23 { 24 tx.Rollback(); 25 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 26 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 else if (num == "2") 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine("排它锁业务"); 33 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 34 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 35 { 36 Console.WriteLine("开始更新"); 37 //update的时候会自动加排它锁 38 var result = db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("update OrderInfor set userName='lmr2' where id=2"); 39 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 40 Console.ReadKey(); 41 try 42 { 43 tx.Commit(); 44 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 45 } 46 catch (Exception ex) 47 { 48 tx.Rollback(); 49 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 50 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 else if (num == "3") 55 { 56 Console.WriteLine("共享锁业务"); 57 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 58 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 59 { 60 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 61 //select的时候会自动加共享锁 62 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 63 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 64 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 65 Console.ReadKey(); 66 try 67 { 68 tx.Commit(); 69 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 70 } 71 catch (Exception ex) 72 { 73 tx.Rollback(); 74 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 75 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 }
结论:
1. 更新锁需要事务提交才能释放。
2. 更新锁和更新锁不能共存。
3. 更新锁和排它锁不能共存。
4. 更新锁和共享锁可以共存。
5. 测试表锁和排它锁不能共存

1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("测试表锁和排它锁的问题"); 3 Console.WriteLine("表锁业务输入:1, 排它锁业务输入:2"); 4 string num = Console.ReadLine(); 5 if (num == "1") 6 { 7 Console.WriteLine("表锁业务"); 8 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 9 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 12 13 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor(tablock) where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 14 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 15 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 16 Console.ReadKey(); 17 try 18 { 19 tx.Commit(); 20 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 21 } 22 catch (Exception ex) 23 { 24 tx.Rollback(); 25 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 26 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 else if (num == "2") 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine("排它锁业务"); 33 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 34 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 35 { 36 Console.WriteLine("开始更新"); 37 //update的时候会自动加排它锁 38 var result = db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("update OrderInfor set userName='lmr2' where id=2"); 39 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 40 Console.ReadKey(); 41 try 42 { 43 tx.Commit(); 44 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 45 } 46 catch (Exception ex) 47 { 48 tx.Rollback(); 49 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 50 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 }
结论:
1. 先执行表锁,事务未提交的情况下,排它锁能正常进行。
证明:表锁只要执行完该语句立即释放,与事务是否提交没有关系。
2. 先执行默认排它锁,事务未提交的情况想,表锁不能运行。
证明:默认的排它锁必须等待事务提交完才能释放,同时证明排它锁和表锁不能共存 (表锁在这里的特点和共享锁一样,实质表锁也就是个共享锁,只是划分的角度不同)
6. 测试行锁和排它锁不能共存

1 { 2 Console.WriteLine("测试行锁和排它锁的问题"); 3 Console.WriteLine("行锁业务输入:1, 排它锁业务输入:2"); 4 string num = Console.ReadLine(); 5 if (num == "1") 6 { 7 Console.WriteLine("行锁业务"); 8 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 9 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine("开始查询"); 12 13 var orderInfor = db.Database.SqlQuery<OrderInfor>("select * from OrderInfor(rowlock) where id=2").FirstOrDefault(); 14 Console.WriteLine($"id为:{orderInfor.id},userName为:{orderInfor.userName},destination为:{orderInfor.destination}"); 15 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 16 Console.ReadKey(); 17 try 18 { 19 tx.Commit(); 20 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 21 } 22 catch (Exception ex) 23 { 24 tx.Rollback(); 25 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 26 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 else if (num == "2") 31 { 32 Console.WriteLine("排它锁业务"); 33 using (LockDemoDBEntities1 db = new LockDemoDBEntities1()) 34 using (var tx = db.Database.BeginTransaction()) 35 { 36 Console.WriteLine("开始更新"); 37 //update的时候会自动加排它锁 38 var result = db.Database.ExecuteSqlCommand("update OrderInfor set userName='lmr2' where id=1"); 39 Console.WriteLine("按任意键进行事务提交"); 40 Console.ReadKey(); 41 try 42 { 43 tx.Commit(); 44 Console.WriteLine("事务提交成功"); 45 } 46 catch (Exception ex) 47 { 48 tx.Rollback(); 49 Console.WriteLine("事务提交失败"); 50 Console.WriteLine(ex.Message); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 }
结论:
1. 先执行行锁,事务未提交的情况下,排它锁能正常进行。
证明:行锁只要执行完该语句立即释放,与事务是否提交没有关系。
2. 先执行默认排它锁,事务未提交的情况想,行锁不能运行。
证明:默认的排它锁必须等待事务提交完才能释放,同时证明排它锁和行锁不能共存 (行锁在这里的特点和共享锁一样,实质表锁也就是个共享锁,只是划分的角度不同)。
7. 测试页锁和排它锁不能共存(与表锁、行锁类似,不单独测试)
三. 事务隔离级别
1. 四种错误
(1). 脏读:第一个事务读取第二个事务正在更新的数据,如果第二个事务还没有更新完成,那么第一个事务读取的数据将是一半为更新过的,一半还没更新过的数据,这样的数据毫无意义。
(2). 幻读:第一个事务读取一个结果集后,第二个事务,对这个结果集进行“增删”操作,然而第一个事务中再次对这个结果集进行查询时,数据发现丢失或新增。
(3). 更新丢失:多个用户同时对一个数据资源进行更新,必定会产生被覆盖的数据,造成数据读写异常。
(4). 不可重复读:如果一个用户在一个事务中多次读取一条数据,而另外一个用户则同时更新啦这条数据,造成第一个用户多次读取数据不一致。
2. 死锁
(1). 定义:相互等待对方释放资源,造成资源读写拥挤堵塞的情况,就被称为死锁现象,也叫做阻塞。如下面的例子:
1 begin tran 2 select * from OrderInfor(holdlock) where id='333' 3 waitfor delay '0:0:8' --等待8秒执行下面的语句 4 update OrderInfor set userName='ypf1' where id='333' 5 commit tran
分析:线程T1 和 线程T2 同时执行该事务,假设线程T1先执行完select,线程T2随后执行完select,线程T1要执行update语句的时候,根据数据库策略需要将【共享锁】提升为【排它锁】才能执行,所以必须等线程T2上的【共享锁】释放,而线程T2需要事务提交完才能释放锁,同时T1的【共享锁】不释放导致T2要一直等待,这样造成了T1和T2相互等待的局面,就是死锁现象。
(2). 数据库的默认处理思路的逻辑:
数据库并不会出现无限等待的情况,是因为数据库搜索引擎会定期检测这种状况,一旦发现有情况,立马【随机】选择一个事务作为牺牲品。牺牲的事务,将会回滚数据。有点像两个人在过独木桥,两个无脑的人都走在啦独木桥中间,如果不落水,必定要有一个人给退回来。这种相互等待的过程,是一种耗时耗资源的现象,所以能避则避。
(3). 手动控制锁级别:
语法:set deadlock_priority <级别>
死锁处理的优先级别为 low<normal<high,不指定的情况下默认为normal,牺牲品为随机。如果指定,牺牲品为级别低的。
还可以使用数字来处理标识级别:-10到-5为low,-5为normal,-5到10为high,数越小,级别越低,越先牺牲,越先回滚。
(4). 案例测试
事先准备: 使用【LockDemoDB】中的OrderInfor表进行测试, 事先插入一条测试数据,之后都使用该数据进行测试。
1 insert into OrderInfor values('333','ypf','去青岛','lmr','1')
在两个窗口里(即两个线程)执行下面一段代码:
1 -- 线程1执行下面语句 2 begin tran 3 begin try 4 set deadlock_priority -9 5 select * from OrderInfor(holdlock) where id='333' 6 waitfor delay '0:0:8' --等待8秒执行下面的语句 7 update OrderInfor set userName='ypf1' where id='333' 8 commit tran 9 end try 10 begin catch 11 rollback tran 12 end catch
1 -- 线程2测试(下面语句单独开一个窗口进行测试) 2 begin tran 3 begin try 4 set deadlock_priority -8 5 select * from OrderInfor(holdlock) where id='333' 6 waitfor delay '0:0:8' --等待8秒执行下面的语句 7 update OrderInfor set userName='ypf2' where id='333' 8 commit tran 9 end try 10 begin catch 11 rollback tran 12 end catch
分析:线程1和线程2分别执行下面语句,产生死锁,由于线程1设置的级别 -9 < -8,所以线程1牺牲且回滚,最后是线程2执行的结果,userName为ypf2 .
(5). 扩展补充
A. 查看锁活动情况
1 select * from sys.dm_tran_locks
B. 查看事务活动情况
1 dbcc opentran
C. 设置锁的超时时间
1 set lock_timeout 4000
PS:
发生死锁的时候,数据库引擎会自动检测死锁,解决问题,然而这样子是很被动,只能在发生死锁后,等待处理。然而我们也可以主动出击,设置锁超时时间,一旦资源被锁定阻塞,超过设置的锁定时间,阻塞语句自动取消,释放资源,报1222错误。
好东西一般都具有两面性,调优的同时,也有他的不足之处,那就是一旦超过时间,语句取消,释放资源,但是当前报错事务,不会回滚,会造成数据错误,你需要在程序中捕获1222错误,用程序处理当前事务的逻辑,使数据正确。为0时,即为一旦发现资源锁定,立即报错,不在等待,当前事务不回滚,设置时间需谨慎处理后事啊,你hold不住的。
拓展杀死锁和进程

1 --检测死锁 2 --如果发生死锁了,我们怎么去检测具体发生死锁的是哪条SQL语句或存储过程? 3 --这时我们可以使用以下存储过程来检测,就可以查出引起死锁的进程和SQL语句。SQL Server自带的系统存储过程sp_who和sp_lock也可以用来查找阻塞和死锁, 但没有这里介绍的方法好用。 4 5 use master 6 go 7 create procedure sp_who_lock 8 as 9 begin 10 declare @spid int,@bl int, 11 @intTransactionCountOnEntry int, 12 @intRowcount int, 13 @intCountProperties int, 14 @intCounter int 15 16 create table #tmp_lock_who ( 17 id int identity(1,1), 18 spid smallint, 19 bl smallint) 20 21 IF @@ERROR<>0 RETURN @@ERROR 22 23 insert into #tmp_lock_who(spid,bl) select 0 ,blocked 24 from (select * from sysprocesses where blocked>0 ) a 25 where not exists(select * from (select * from sysprocesses where blocked>0 ) b 26 where a.blocked=spid) 27 union select spid,blocked from sysprocesses where blocked>0 28 29 IF @@ERROR<>0 RETURN @@ERROR 30 31 -- 找到临时表的记录数 32 select @intCountProperties = Count(*),@intCounter = 1 33 from #tmp_lock_who 34 35 IF @@ERROR<>0 RETURN @@ERROR 36 37 if @intCountProperties=0 38 select '现在没有阻塞和死锁信息' as message 39 40 -- 循环开始 41 while @intCounter <= @intCountProperties 42 begin 43 -- 取第一条记录 44 select @spid = spid,@bl = bl 45 from #tmp_lock_who where Id = @intCounter 46 begin 47 if @spid =0 48 select '引起数据库死锁的是: '+ CAST(@bl AS VARCHAR(10)) + '进程号,其执行的SQL语法如下' 49 else 50 select '进程号SPID:'+ CAST(@spid AS VARCHAR(10))+ '被' + '进程号SPID:'+ CAST(@bl AS VARCHAR(10)) +'阻塞,其当前进程执行的SQL语法如下' 51 DBCC INPUTBUFFER (@bl ) 52 end 53 54 -- 循环指针下移 55 set @intCounter = @intCounter + 1 56 end 57 58 drop table #tmp_lock_who 59 60 return 0 61 end 62 63 64 --杀死锁和进程 65 --如何去手动的杀死进程和锁?最简单的办法,重新启动服务。但是这里要介绍一个存储过程,通过显式的调用,可以杀死进程和锁。 66 67 use master 68 go 69 70 if exists (select * from dbo.sysobjects where id = object_id(N'[dbo].[p_killspid]') and OBJECTPROPERTY(id, N'IsProcedure') = 1) 71 drop procedure [dbo].[p_killspid] 72 GO 73 74 create proc p_killspid 75 @dbname varchar(200) --要关闭进程的数据库名 76 as 77 declare @sql nvarchar(500) 78 declare @spid nvarchar(20) 79 80 declare #tb cursor for 81 select spid=cast(spid as varchar(20)) from master..sysprocesses where dbid=db_id(@dbname) 82 open #tb 83 fetch next from #tb into @spid 84 while @@fetch_status=0 85 begin 86 exec('kill '+@spid) 87 fetch next from #tb into @spid 88 end 89 close #tb 90 deallocate #tb 91 go 92 93 --用法 94 exec p_killspid 'newdbpy' 95 96 --查看锁信息 97 --如何查看系统中所有锁的详细信息?在企业管理管理器中,我们可以看到一些进程和锁的信息,这里介绍另外一种方法。 98 --查看锁信息 99 create table #t(req_spid int,obj_name sysname) 100 101 declare @s nvarchar(4000) 102 ,@rid int,@dbname sysname,@id int,@objname sysname 103 104 declare tb cursor for 105 select distinct req_spid,dbname=db_name(rsc_dbid),rsc_objid 106 from master..syslockinfo where rsc_type in(4,5) 107 open tb 108 fetch next from tb into @rid,@dbname,@id 109 while @@fetch_status=0 110 begin 111 set @s='select @objname=name from ['+@dbname+']..sysobjects where id=@id' 112 exec sp_executesql @s,N'@objname sysname out,@id int',@objname out,@id 113 insert into #t values(@rid,@objname) 114 fetch next from tb into @rid,@dbname,@id 115 end 116 close tb 117 deallocate tb 118 119 select 进程id=a.req_spid 120 ,数据库=db_name(rsc_dbid) 121 ,类型=case rsc_type when 1 then 'NULL 资源(未使用)' 122 when 2 then '数据库' 123 when 3 then '文件' 124 when 4 then '索引' 125 when 5 then '表' 126 when 6 then '页' 127 when 7 then '键' 128 when 8 then '扩展盘区' 129 when 9 then 'RID(行 ID)' 130 when 10 then '应用程序' 131 end 132 ,对象id=rsc_objid 133 ,对象名=b.obj_name 134 ,rsc_indid 135 from master..syslockinfo a left join #t b on a.req_spid=b.req_spid 136 137 go 138 drop table #t
3. 事务隔离级别
read uncommitted:这个隔离级别最低啦,可以读取到一个事务正在处理的数据,但事务还未提交,这种级别的读取叫做脏读。
read committed:这个级别是默认选项,不能脏读,不能读取事务正在处理没有提交的数据,但能修改。
repeatable read:不能读取事务正在处理的数据,也不能修改事务处理数据前的数据。
snapshot:指定事务在开始的时候,就获得了已经提交数据的快照,因此当前事务只能看到事务开始之前对数据所做的修改。
serializable:最高事务隔离级别,只能看到事务处理之前的数据。
事先准备: 使用【LockDemoDB】中的OrderInfor表进行测试, 事先插入一条测试数据,之后都使用该数据进行测试。
线程1执行下面代码:
1 begin tran 2 update OrderInfor set userName='ypf1' where id='333' 3 waitfor delay '0:0:8' --等待8秒执行下面的语句 4 rollback tran
线程1执行后,开启一个新线程(在一个新窗口)马上执行下面代码:
情况1
1 --1. 设置允许脏读,能马上读出来数据 2 set tran isolation level read uncommitted 3 select * from OrderInfor where id='333' --读取的数据为正在修改的数据 ,即为脏读 4 5 --8秒之后数据已经回滚,查出来的数据是回滚后的数据 ypf 6 waitfor delay '0:0:8' 7 select * from OrderInfor where id='333'
情况2
1 --2. 设置不允许脏读,不能马上读出来数据(数据库默认就是这种模式) 2 set tran isolation level read committed 3 select * from OrderInfor where id='333' 4 5 6 --可以修改(但也得等线程1执行完事务后),8s后显示的是 ypf2,而不是原回滚后的数据ypf 7 update OrderInfor set userName='ypf2' where id='333' 8 waitfor delay '0:0:8' 9 select * from OrderInfor where id='333'
其它三种暂不测试了,与此同样道理进行测试。
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 本人才疏学浅,用郭德纲的话说“我是一个小学生”,如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
