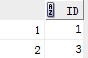
在mysql中,如果把表的主键设为auto_increment类型,数据库就会自动为主键赋值。例如:
CREATE TABLE google(id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,NAME VARCHAR(15),age INT,email VARCHAR(50),gender VARCHAR(10)) insert into google(name,age,email,gender) values('yaomajor',13,'yaomajor@qq.com','男'); select id from google;
由此可见,一旦把id设为auto_increment类型,mysql数据库会自动按递增的方式为主键赋值。
Sql Server
在MS SQLServer中,如果把表的主键设为identity类型,数据库就会自动为主键赋值。例如:
create table emp(id int identity(1,1) primary key not null, name varchar(15)); insert into emp(name) values('name1'),('name2'); select id from emp;
 查询结果和mysql的一样。
查询结果和mysql的一样。
由此可见,一旦把id设为identity类型,MS SQLServer数据库会自动按递增的方式为主键赋值。identity包含两个参数,第一个参数表示起始值,第二个参数表示增量。
以前经常会碰到这样的问题,当我们删除了一条自增长列为1的记录以后,再次插入的记录自增长列是2了。我们想在插入一条自增长列为1的记录是做不到的。通过设置SET IDENTITY_INSERT <table_name> ON;来取消自增长,等我们插入完数据以后在关闭这个功能。实验如下:
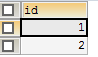
--step1:创建表 create table customers( id int identity primary key not null, name varchar(15) ); --step2:执行插入操作 insert into customers(id,name) values(1,'name1'); --报错:An explicit value for the identity column in table 'customers' can only be specified when a column list is used and IDENTITY_INSERT is ON. --step3:放开主键列的自增长 SET IDENTITY_INSERT customers ON; --step4:插入两条记录,主键分别为1和3。插入成功 insert into customers(id,name) values(1,'name1'); insert into customers(id,name) values(3,'name1'); --step5:再次插入一个主键为2的记录。插入成功 insert into customers(id,name) values(2,'name1'); --step6:插入重复主键, --报错:Violation of PRIMARY KEY constraint 'PK__customer__3213E83F00551192'. Cannot insert duplicate key in object 'dbo.customers'. insert into customers(id,name) values(3,'name1'); --step7:关闭IDENTITY_INSERT SET IDENTITY_INSERT customers OFF;
2、从序列中获取自动增长的标识符
Oracle
在Oracle中,可以为每张表的主键创建一个单独的序列,然后从这个序列中获取自动增加的标识符,把它赋值给主键。例如一下语句创建了一个名为customer_id_seq的序列,这个序列的起始值为1,增量为2。
create sequence customer_id_seq increment by 2 start with 1
一旦定义了customer_id_seq序列,就可以访问序列的curval和nextval属性。
- curval:返回序列的当前值
- nextval:先增加序列的值,然后返回序列值
以下sql语句先创建了customers表,然后插入两条记录,在插入时设定了id和name字段的值,其中id字段的值来自于customer_id_seq序列。最后查询customers表中的id字段。
create table customers(id int primary key not null, name varchar(15)); insert into customers values(customer_id_seq.nextval, 'name1'); insert into customers values(customer_id_seq.nextval, 'name2'); select id from customers;
如果在oracle中执行以上语句,查询结果为: